Choledocholithiasis: Stones within common bile duct (CBD)
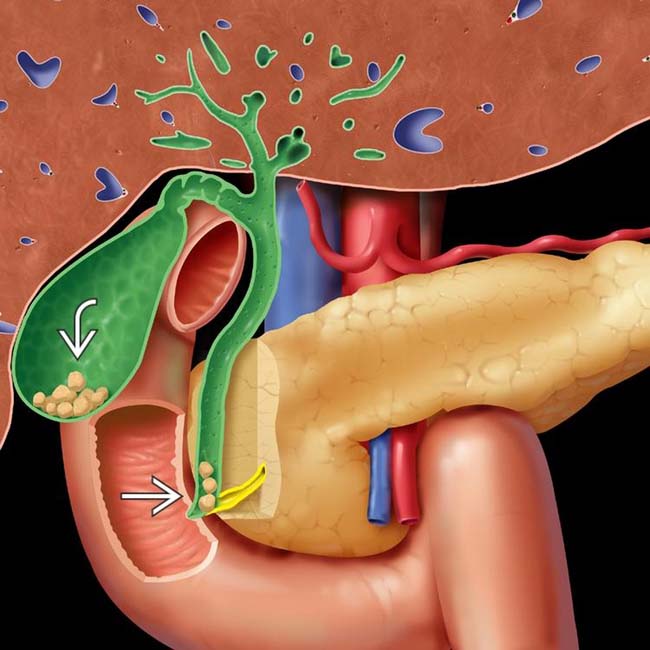
 and choledocholithiasis
and choledocholithiasis  . While most gallstones are asymptomatic, migration of stones to the cystic duct and common bile duct (CBD) may cause numerous complications, including biliary colic, cholecystitis, biliary obstruction, and pancreatitis.
. While most gallstones are asymptomatic, migration of stones to the cystic duct and common bile duct (CBD) may cause numerous complications, including biliary colic, cholecystitis, biliary obstruction, and pancreatitis.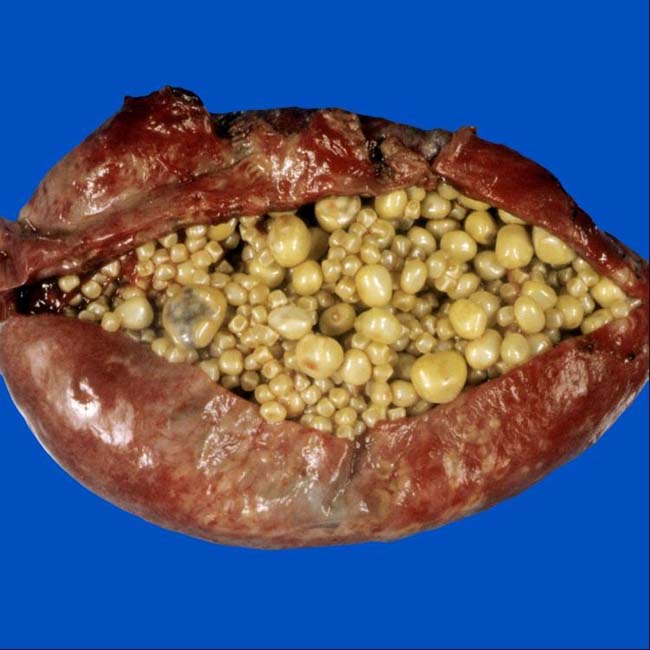
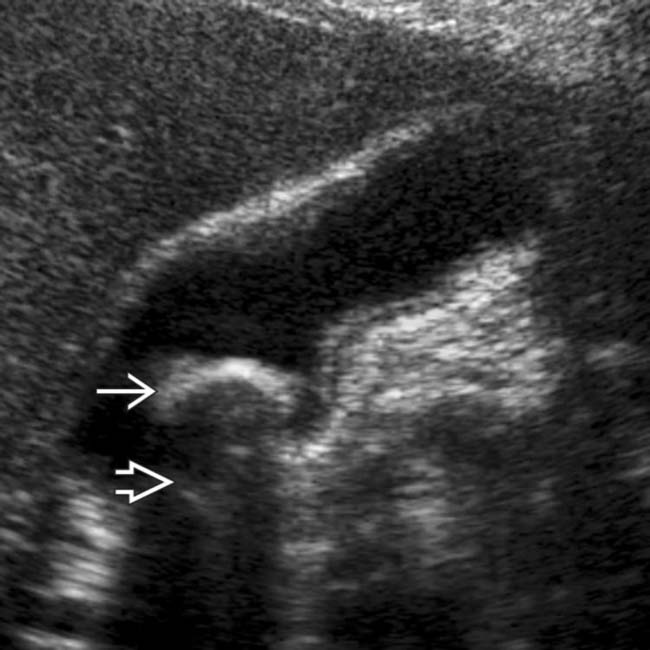
 within the GB lumen. Note the presence of posterior acoustic shadowing
within the GB lumen. Note the presence of posterior acoustic shadowing  . The GB wall thickness is normal and there is no pericholecystic fluid to suggest cholecystitis.
. The GB wall thickness is normal and there is no pericholecystic fluid to suggest cholecystitis.TERMINOLOGY
IMAGING
General Features
CT Findings
• Single or multiple filling defects in GB or ducts
 Density varies: Calcium density, soft tissue density, or lucent (pure cholesterol or gas-containing)
Density varies: Calcium density, soft tissue density, or lucent (pure cholesterol or gas-containing)
 Pattern of calcification: Uniformly calcified, laminated, rim calcification, or central nidus of calcification
Pattern of calcification: Uniformly calcified, laminated, rim calcification, or central nidus of calcification
 Density varies: Calcium density, soft tissue density, or lucent (pure cholesterol or gas-containing)
Density varies: Calcium density, soft tissue density, or lucent (pure cholesterol or gas-containing) Pattern of calcification: Uniformly calcified, laminated, rim calcification, or central nidus of calcification
Pattern of calcification: Uniformly calcified, laminated, rim calcification, or central nidus of calcificationUltrasonographic Findings
• Gallstones
PATHOLOGY
General Features
• Etiology
 Cholesterol stones
Cholesterol stones
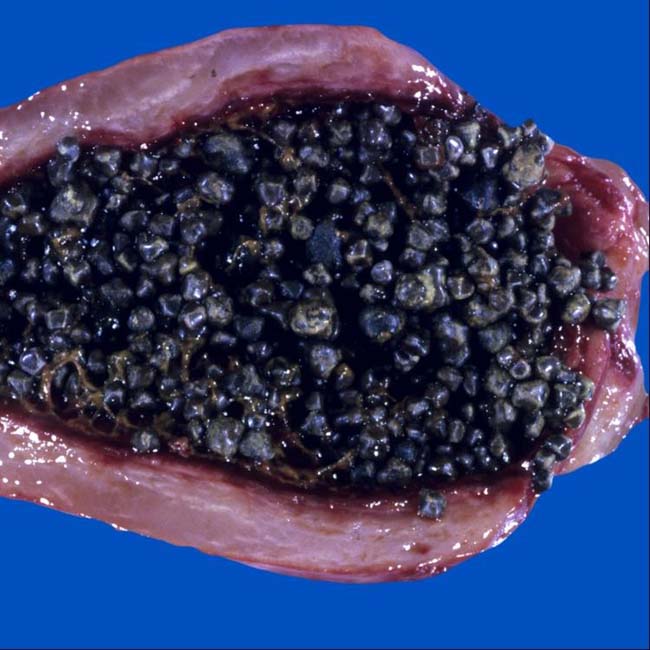
 Pigment stones
Pigment stones
 Cholesterol stones
Cholesterol stones
 Pigment stones
Pigment stones
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
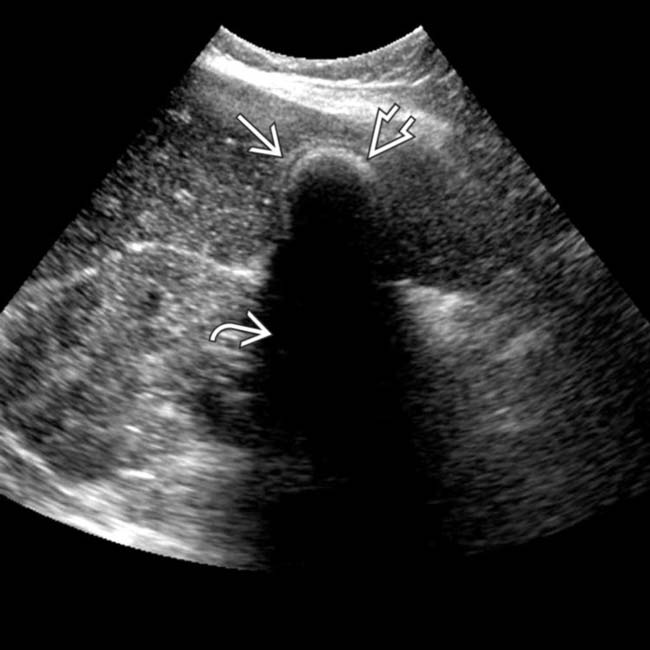
 delineating the GB wall, the “echo” is the hypoechoic stripe created by a thin layer of bile
delineating the GB wall, the “echo” is the hypoechoic stripe created by a thin layer of bile  , and the “shadow” is the posterior acoustic shadowing
, and the “shadow” is the posterior acoustic shadowing  behind a superficial layer of stones.
behind a superficial layer of stones.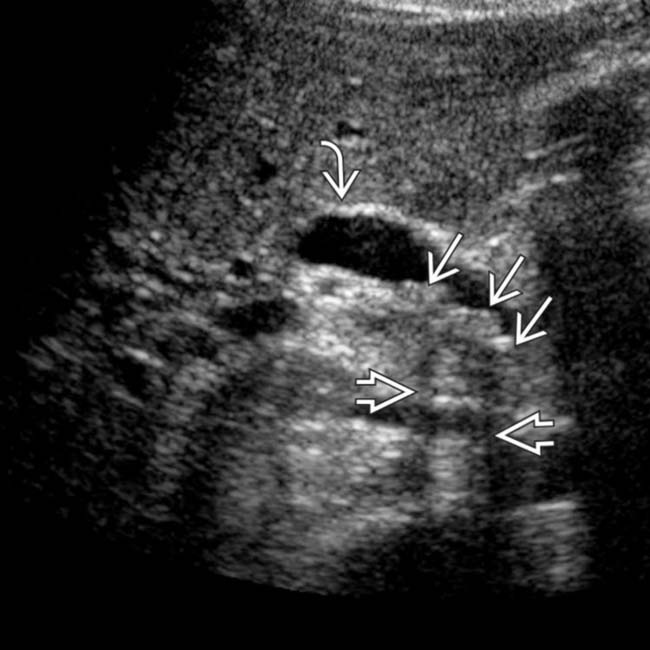
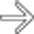
 in the CBD. The stones are associated with posterior acoustic shadowing
in the CBD. The stones are associated with posterior acoustic shadowing  and cause mild CBD dilatation
and cause mild CBD dilatation  .
.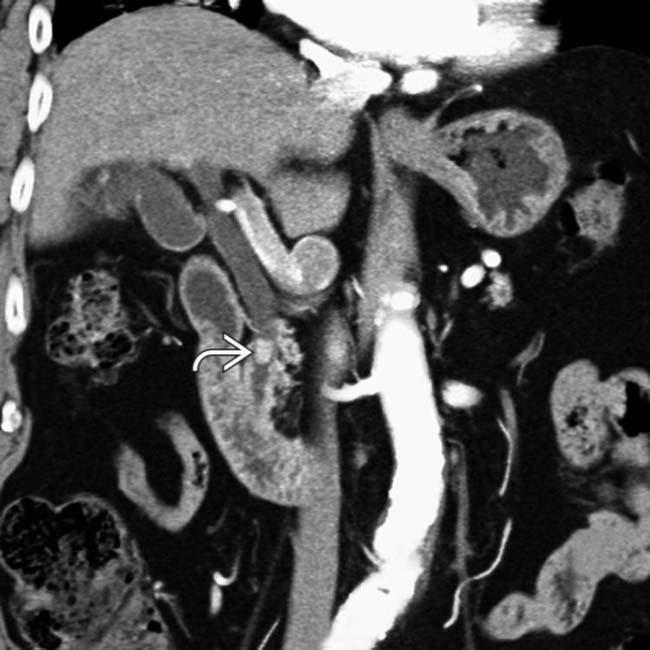
 in the distal CBD resulting in mild upstream CBD dilatation. CT is only 80% sensitive for gallstones, although identification of stones in the CBD is easier when causing biliary obstruction.
in the distal CBD resulting in mild upstream CBD dilatation. CT is only 80% sensitive for gallstones, although identification of stones in the CBD is easier when causing biliary obstruction.
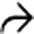 in the CBD.
in the CBD.
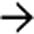 with a “Mercedes-Benz” shape within a large gallstone. The gas itself is of no diagnostic significance and is not a sign of infection. This patient has cholecystitis, evidenced by GB wall thickening
with a “Mercedes-Benz” shape within a large gallstone. The gas itself is of no diagnostic significance and is not a sign of infection. This patient has cholecystitis, evidenced by GB wall thickening  .
.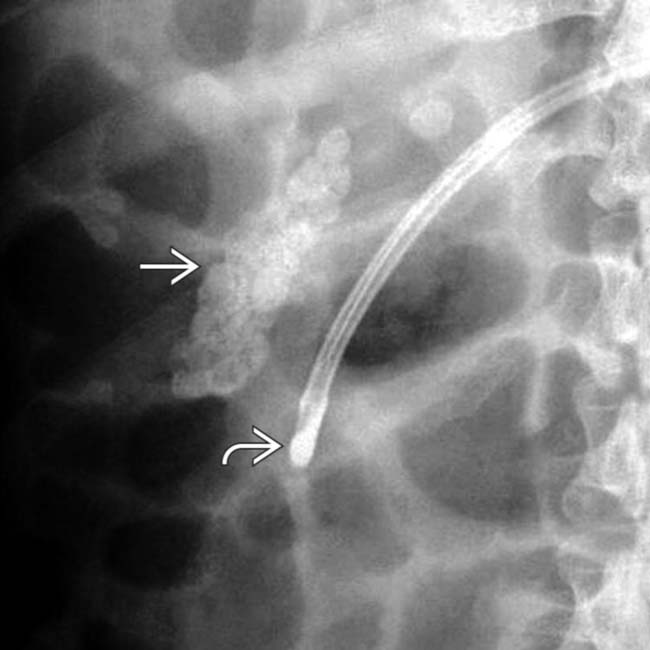
 . Calcium bilirubinate stones are typically multiple, small, and radiopaque. A feeding tube
. Calcium bilirubinate stones are typically multiple, small, and radiopaque. A feeding tube  marks the 2nd portion of the duodenum.
marks the 2nd portion of the duodenum.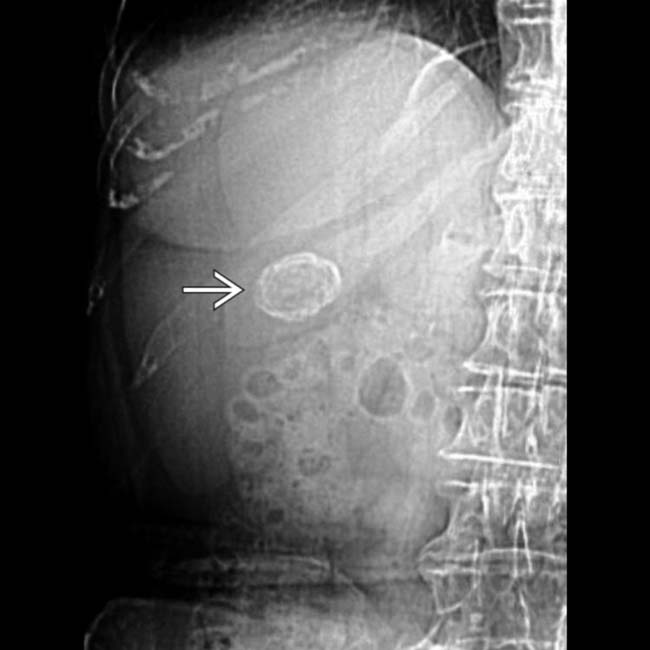
 in the right upper quadrant, a typical appearance for a large gallstone.
in the right upper quadrant, a typical appearance for a large gallstone.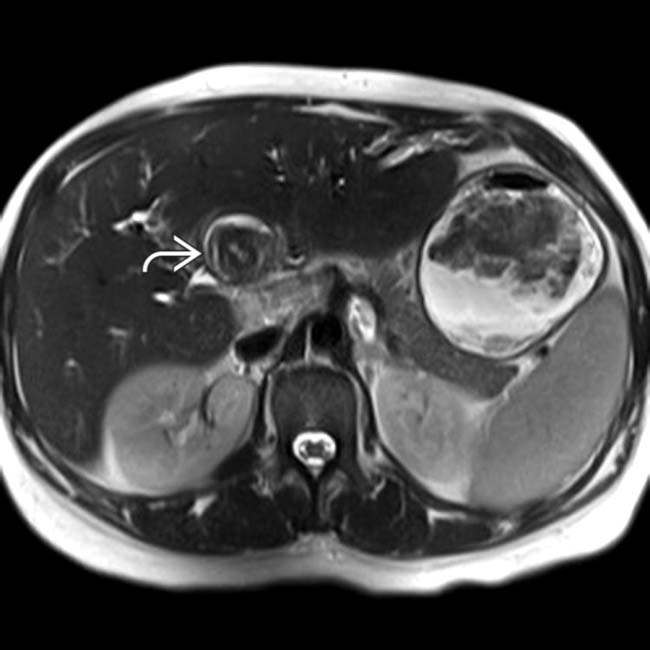
 (with some linear higher signal within the stone) in the proximal common duct near the confluence of the ducts. Stones are typically hypointense on T1WI & T2WI, but as in this case, can be have somewhat heterogeneous signal with areas of higher signal within the stone.
(with some linear higher signal within the stone) in the proximal common duct near the confluence of the ducts. Stones are typically hypointense on T1WI & T2WI, but as in this case, can be have somewhat heterogeneous signal with areas of higher signal within the stone.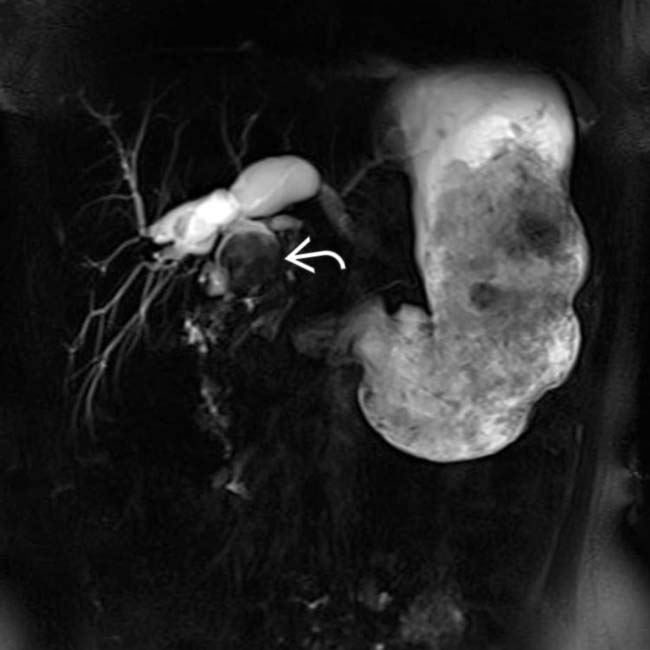
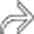 , visible as a large, hypointense filling defect in the proximal common duct, is causing significant biliary obstruction.
, visible as a large, hypointense filling defect in the proximal common duct, is causing significant biliary obstruction.
 within the GB, but normal bile ducts. This patient had a CT scan on which these stones were not visible, since cholesterol stones are often isodense to bile.
within the GB, but normal bile ducts. This patient had a CT scan on which these stones were not visible, since cholesterol stones are often isodense to bile.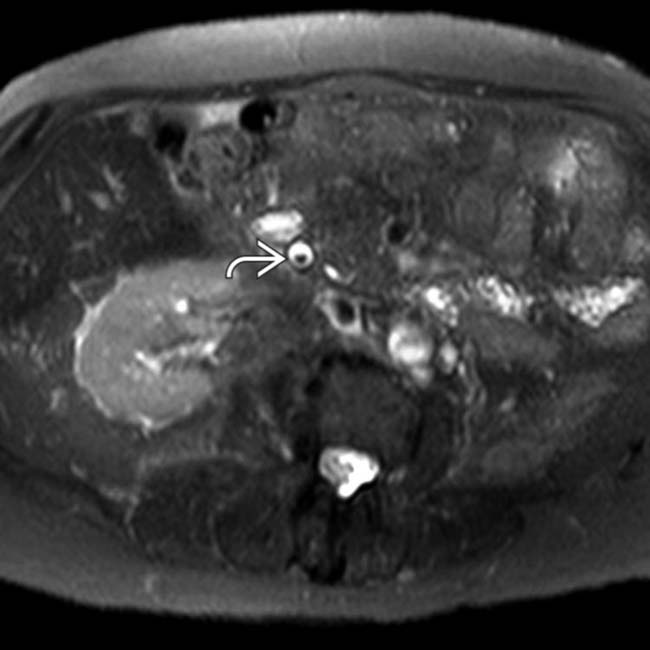
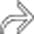 in the distal CBD, the characteristic appearance of a stone on MR.
in the distal CBD, the characteristic appearance of a stone on MR.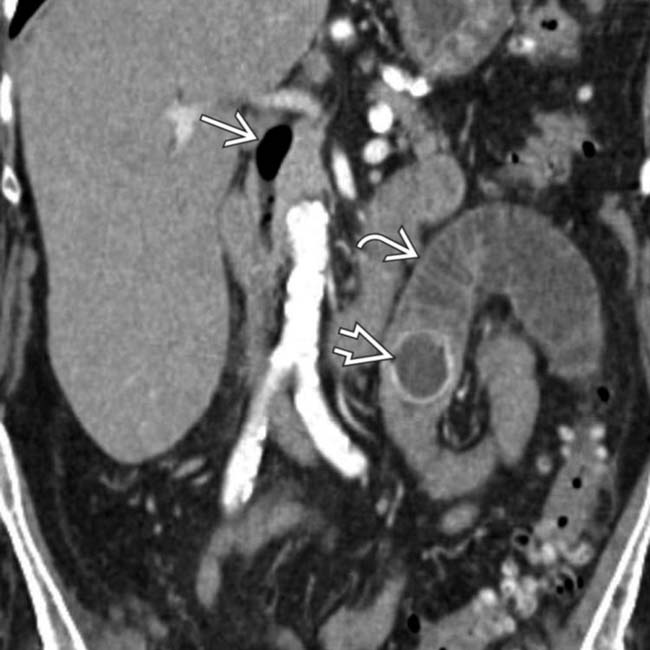
 , a calcified stone
, a calcified stone  at the site of transition, and pneumobilia
at the site of transition, and pneumobilia  , the classic Rigler triad of findings associated with gallstone ileus. Gallstones typically enter the bowel through a cholecystoduodenal fistula.
, the classic Rigler triad of findings associated with gallstone ileus. Gallstones typically enter the bowel through a cholecystoduodenal fistula.
 in the hepatorenal fossa. Dropped gallstones can be asymptomatic or serve as the nidus for future infection.
in the hepatorenal fossa. Dropped gallstones can be asymptomatic or serve as the nidus for future infection.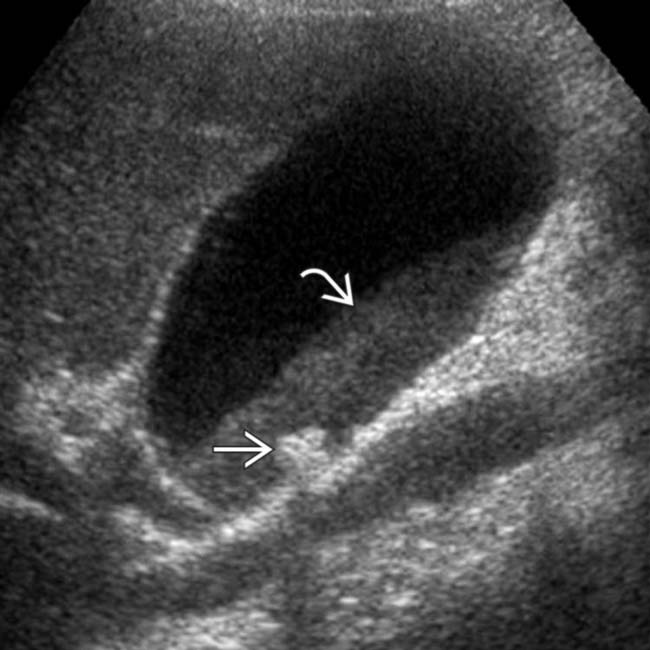
 , with hypoechoic material layering within the GB. Notice the lack of posterior acoustic shadowing, unlike the gallstone
, with hypoechoic material layering within the GB. Notice the lack of posterior acoustic shadowing, unlike the gallstone 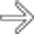 also seen in the GB.
also seen in the GB.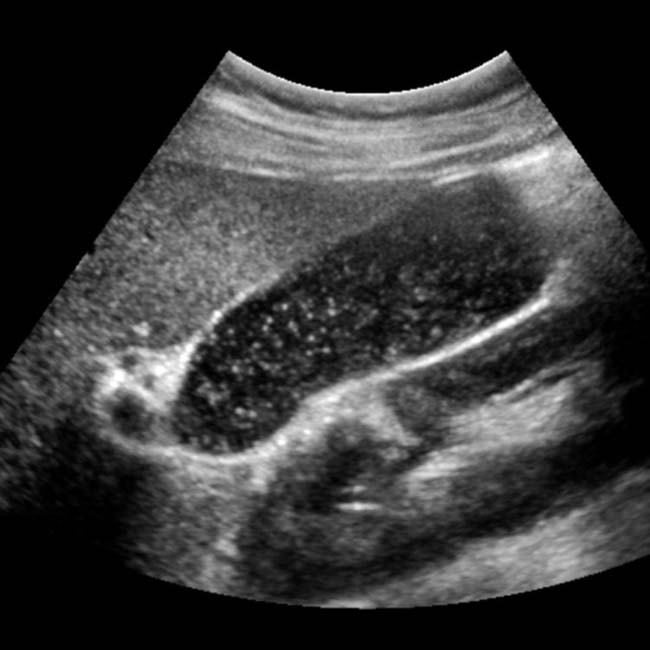
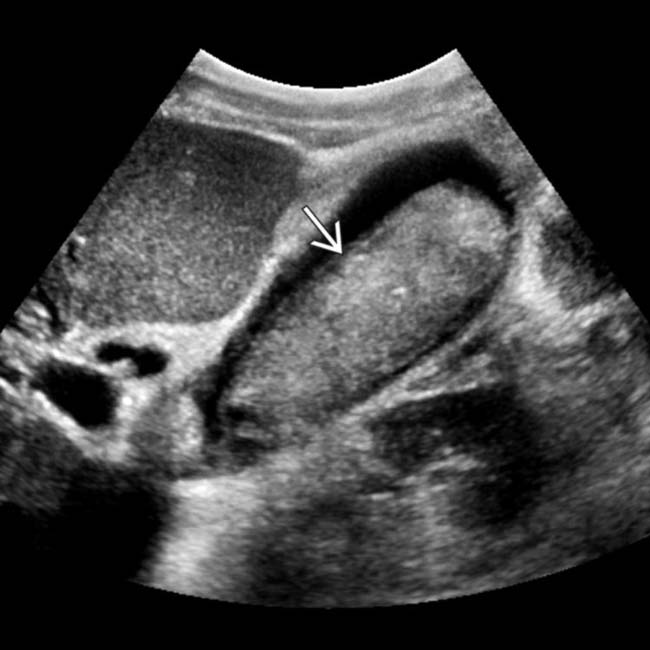
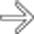 in the GB. Notice that bile outlines the entirety of the mass without a clear attachment to the wall, and there is no acoustic shadowing.
in the GB. Notice that bile outlines the entirety of the mass without a clear attachment to the wall, and there is no acoustic shadowing.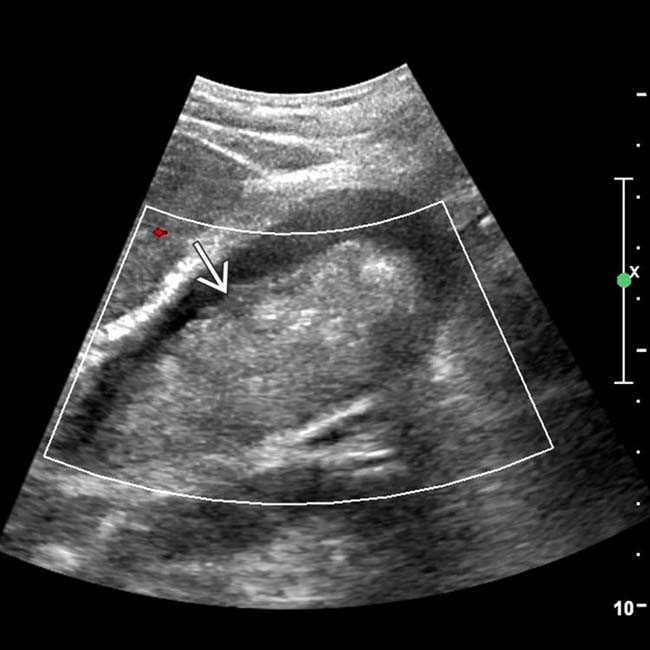
 . The mass was noted to be mobile when the patient was repositioned. These are characteristic features of tumefactive sludge, which should not be confused with malignancy.
. The mass was noted to be mobile when the patient was repositioned. These are characteristic features of tumefactive sludge, which should not be confused with malignancy.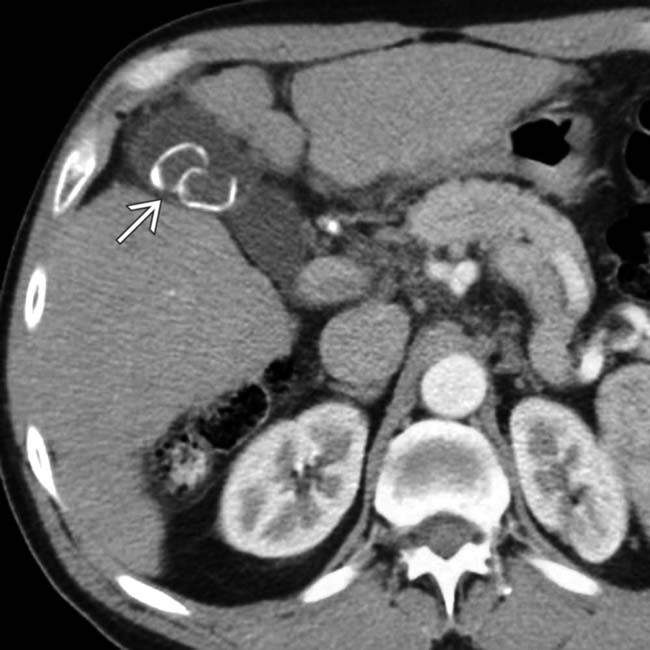
 that are isodense to bile except for surface “eggshell” calcification that makes them visible.
that are isodense to bile except for surface “eggshell” calcification that makes them visible.
 in the right upper quadrant. CT (not shown) confirmed that these are cholesterol gallstones.
in the right upper quadrant. CT (not shown) confirmed that these are cholesterol gallstones.
 and a poorly defined GB wall
and a poorly defined GB wall  . A gangrenous GB was also demonstrated on a subsequent CT scan and resected at surgery.
. A gangrenous GB was also demonstrated on a subsequent CT scan and resected at surgery.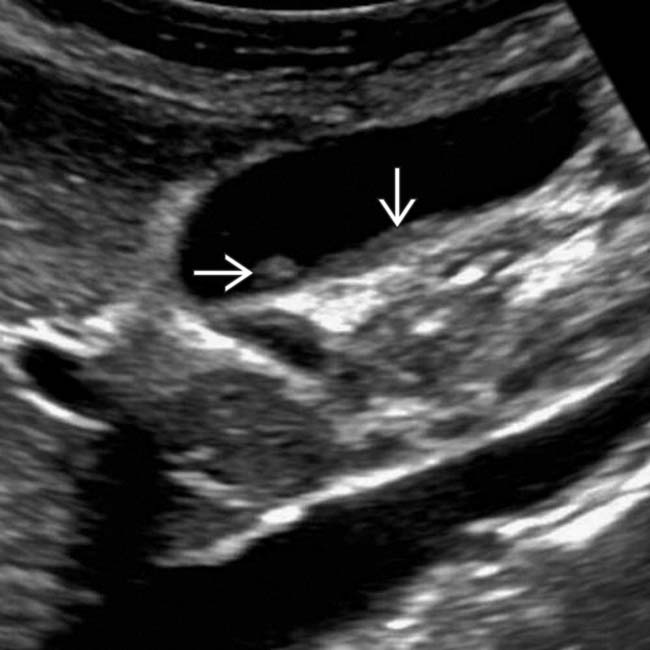
 within the GB that moves with changes in position, findings typical of sludge.
within the GB that moves with changes in position, findings typical of sludge.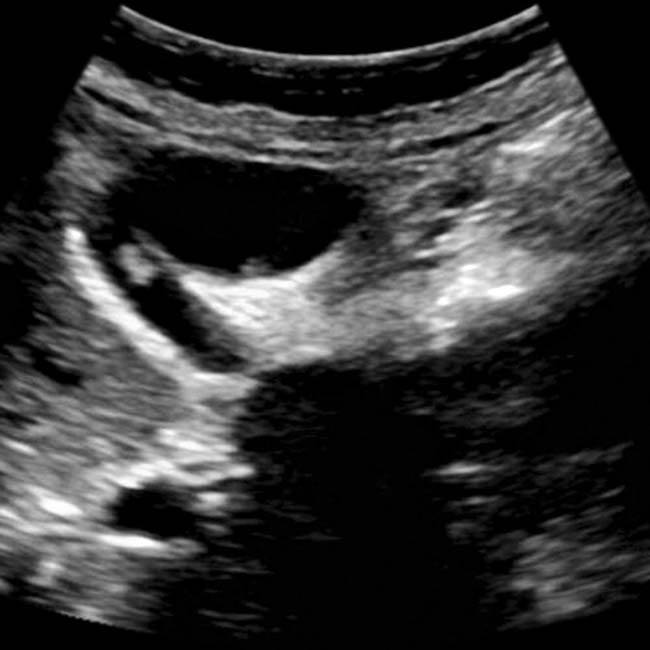
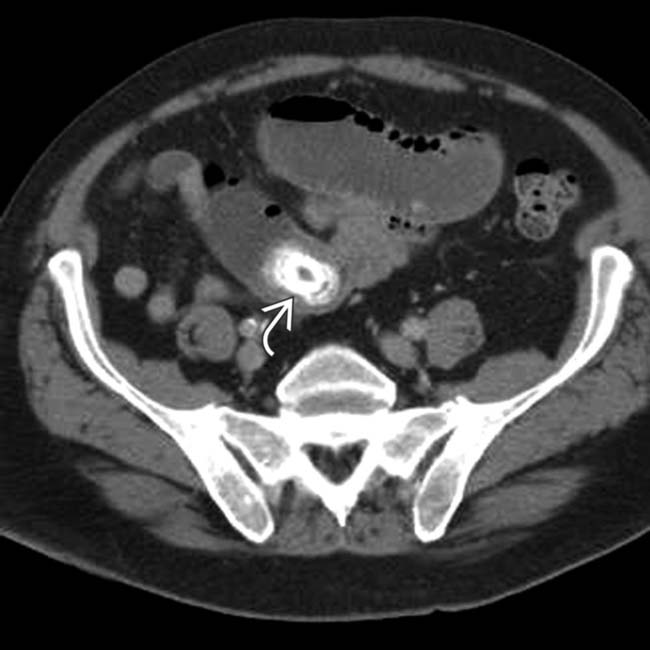
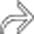 causing proximal bowel obstruction, a so-called gallstone ileus.
causing proximal bowel obstruction, a so-called gallstone ileus.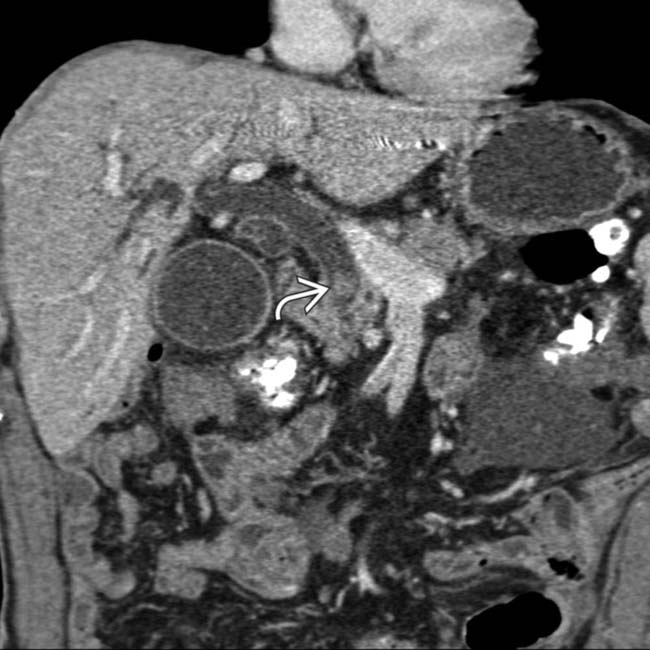
 in the CBD. Stones can be quite difficult to appreciate on CT when they are not calcified.
in the CBD. Stones can be quite difficult to appreciate on CT when they are not calcified.


















































































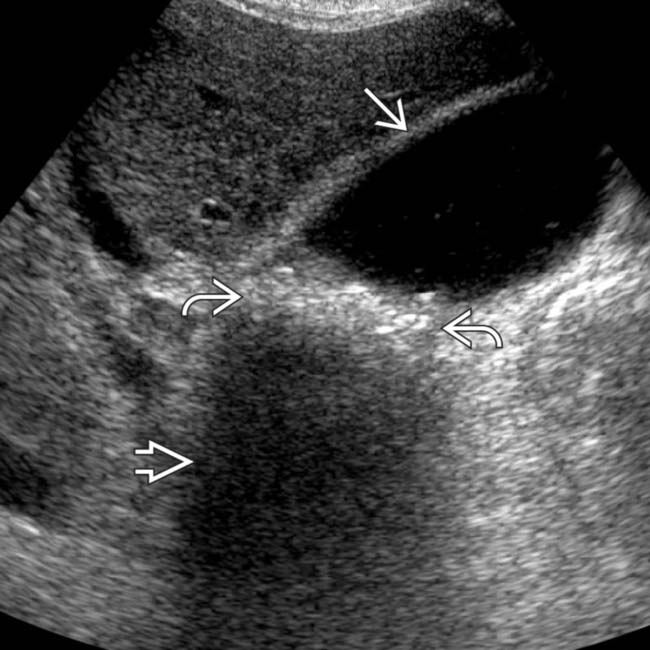
 with posterior acoustic shadowing
with posterior acoustic shadowing  . The gallbladder wall is normal
. The gallbladder wall is normal  .
. 
 with posterior acoustic shadowing
with posterior acoustic shadowing  . The GB wall is not thickened
. The GB wall is not thickened