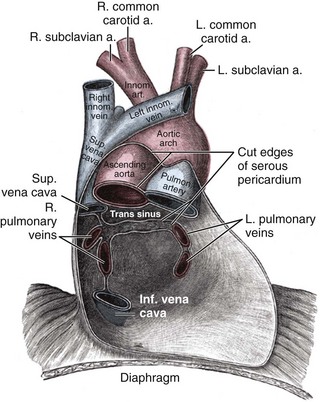
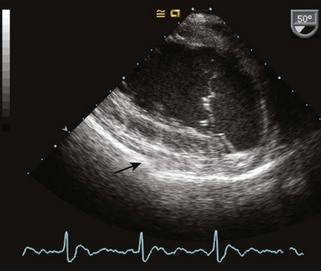
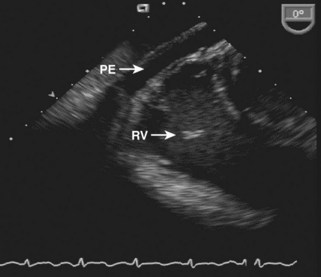
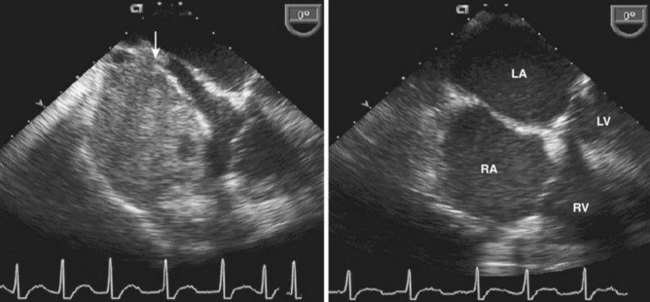
12 Pericardial Disease
Introduction
Background
Overview of Echocardiographic Approach
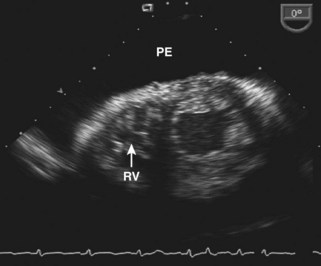
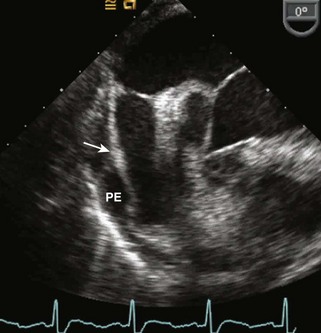
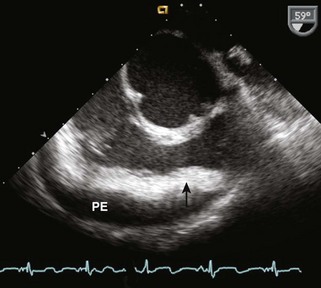
Pericardial Effusion
Background
TABLE 12-1 OVERVIEW OF PERICARDIAL DISEASE ETIOLOGIES AND ASSOCIATED SYNDROMES
| Etiology | Clinical Endpoints |
|---|---|
| Idiopathic | |
| Infectious | |
| Bacterial | Acute pericarditis |
| Tuberculous | Acute pericarditis, constrictive pericarditis |
| Viral | Acute pericarditis |
| Parasitic | Acute pericarditis |
| Connective tissue disease | |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | Pericarditis, pericardial effusion |
| Scleroderma | Pericarditis |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Pericarditis, pericardial effusion |
| Wegener’s granulomatosis | Pericarditis, pericardial effusion |
| Post-myocardial infarction | |
| Dressler’s syndrome | Acute pericarditis, pericardial effusion |
| Ventricular rupture | Pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade |
| Metabolic | |
| Uremia | Pericardial effusion |
| Myxedema | Pericardial effusion |
| Trauma | Pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade |
| Postradiation | Acute pericarditis, constrictive pericarditis |
| Postoperatively after cardiac surgery | Pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade, constrictive pericarditis |
| Neoplastic | |
| Primary pericardial and cardiac tumors | Pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade |
| Metastatic disease | Pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade |
| Congestive heart failure | Pericardial effusion |
| Aortic dissection, left ventricular rupture | Pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade |
| Postoperatively after cardiac catheter or electrophysiologic procedures | Pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade |
Overview of Echocardiographic Approach
Anatomic Imaging
Step 1: 2D Image Acquisition
TABLE 12-2 TRANSTHORACIC VERSUS TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY VIEWS FOR THE IMAGING OF PERICARDIAL EFFUSIONS
| TTE | TEE | |
|---|---|---|
| Useful echocardiographic views | Parasternal long axis | ME four-chamber |
| Parasternal short axis | ME RV inflow-outflow | |
| Apical four-chamber subcostal | Transgastric mid short axis | |
| Benefits and limits | Less invasive technique | Better detection of posterior effusion |
| Poor image quality after cardiac surgery | More invasive |
ME, midesophageal; RV, right ventricular; TEE, transesophageal echocardiography; TTE, transthoracic echocardiography.
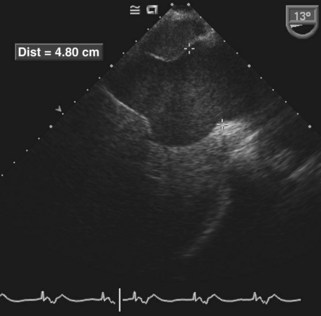
Step 2: Image Analysis
TABLE 12-3 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC GRADING OF PERICARDIAL EFFUSIONS
| Location of the Effusion | Distance between Pericardial Layers | |
|---|---|---|
| Small | Posterior only | <0.5 cm |
| Moderate | Anterior and posterior | 0.5-2 cm |
| Large | Anterior and posterior | >2 cm |
Pitfalls
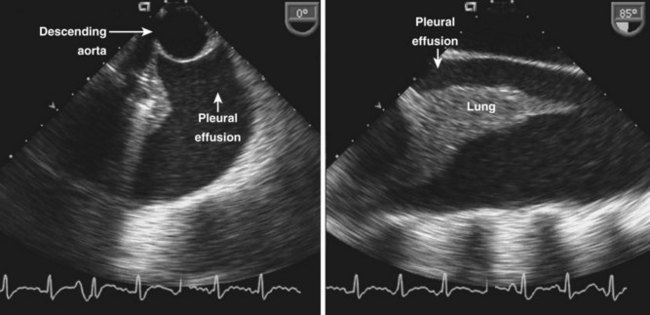
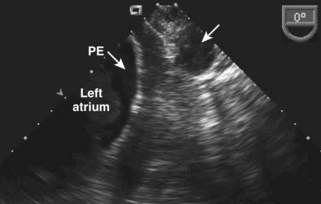
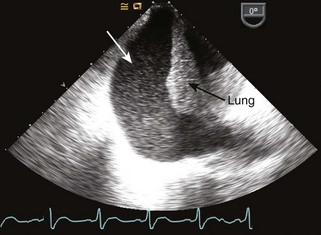
Pericardial versus Pleural Effusion
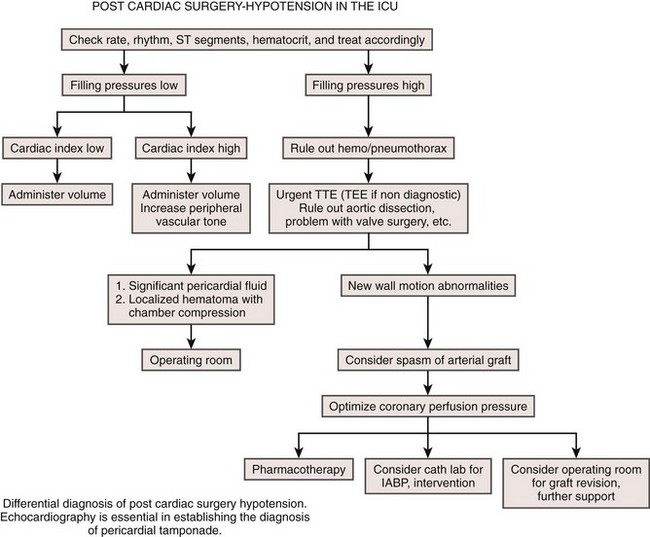
Cardiac Tamponade
Background
Overview of Echocardiographic Approach
Anatomic Imaging
Step 1: Image Acquisition
Step 2: Image Analysis
Pitfalls
Step 1: Acquisition of Physiologic Data
Step 2: Analysis of Physiologic Data
Pitfalls
Alternative Approaches
Key Points
Constrictive Pericarditis
Background
| 1 | High atrial pressures increase early filling of the ventricles |
| 2 | Ventricular filling is quickly offset by the constriction resulting in a rapid rise of the intraventricular pressure in diastole |
| 3 | RV systolic pressure is only mildly elevated, whereas RV diastolic pressures are markedly increased (usually more than one third of systolic pressure) |
| 4 | In classic constrictive pericarditis, there is equalization and elevation of diastolic pressures in all cardiac chambers |
| 5 | Ventricular volume is limited by pericardial constraint |
| 6 | Increased early diastolic RV filling goes along with decreased early diastolic LV filling, which is referred to as exaggerated ventricular interdependence |
LV, left ventricular; RV, right ventricular.
Overview of Echocardiographic Approach
Anatomic Imaging
Step 1: Image Acquisition
Pitfalls
Step 1: Acquisition of Physiologic Data
Step 2: Analysis of Physiologic Data
TABLE 12-5 COMPARISON OF CONSTRICTIVE PERICARDITIS AND RESTRICTIVE CARDIOMYOPATHY
| Constrictive Pericarditis | Restrictive Cardiomyopathy | |
|---|---|---|
| Hemodynamics | ||
| RA pressure | Elevated | Elevated |
| Pulmonary artery pressures | Mildly elevated | At least moderately elevated |
| 2D | ||
| Pericardial thickening and fusion of both layers, no effusion | LV hypertrophy, normal systolic function | |
| Septal bounce | Usually normal septal motion | |
| Spectral Doppler | ||
| Transmitral and transtricuspid inflow E > a Increased E-wave velocity Shortened deceleration time Respiratory variation of E-wave velocity and IVRT |
Transmitral and transtricuspid inflow E < A (early stage) E >> A (late stage) No respiratory variations |
|
| Pulmonary veins Blunted S-wave, large D-wave |
||
| Hepatic veins Large A-wave Prominent y descent |
||
| Tissue Doppler | ||
| E′ > 8 cm/s | E′ < 8 cm/s | |
| Color M-mode | ||
| Flow propagation > 45 cm/s | Flow propagation < 45 cm/s |
IVRT, isovolumic relaxation time; LV, left ventricular; RA, right atrial; 2D, two-dimensional.
Pitfalls
Differential Diagnosis of Constrictive Pericarditis
Alternative Approaches
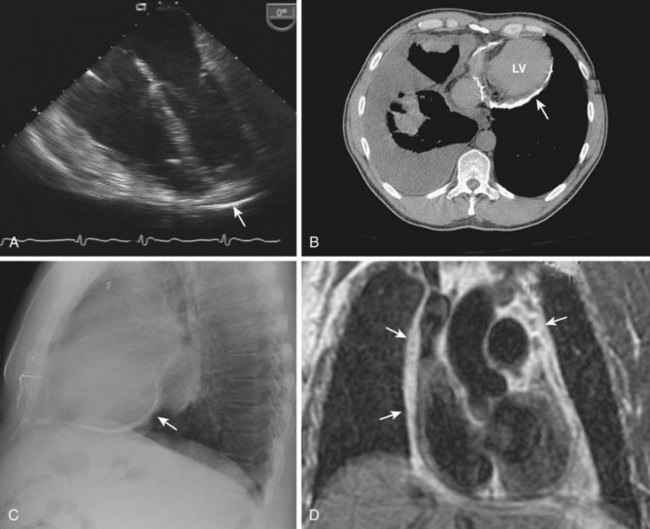
Figure 12-14 Thickened and calcified pericardium (arrows) seen with TEE (A), CT scan (B), chest x-ray (C), and MRI (D).
Key Points
Other Pericardial Diseases
Acute Pericarditis
Epicardial Fat
Congenital Absence of the Pericardium
Pericardial Cysts and Tumors
Surgical Considerations
Pericardiocentesis
Pericardial Window
Pericardiectomy
1 Goldstein JA. Cardiac tamponade, constrictive pericarditis, and restrictive cardiomyopathy. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2004;29:503-567.
2 Khandaker MH, Espinosa RE, Nishimura RA, et al. Pericardial disease: Diagnosis and management. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85:572-593.
3 Wann S, Passen E. Echocardiography in pericardial disease. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008;21:7-13.
4 D’Cruz IA, Kanuru N. Echocardiography of serous effusions adjacent to the heart. Echocardiography. 2001;18:445-456.
5 Reddy PS. Spectrum of hemodynamic changes in cardiac tamponade. Am J Cardiol. 1990;66:1487-1491.
6 Yared K, Baggish AL, Picard MH, et al. Multimodality imaging of pericardial disease. J Am Coll Cardiol Imaging. 2010;3:650-660.
7 Hatle LK, Appleton CP, Popp RL. Differentiation of constrictive pericarditis and restrictive cardiomyopathy by Doppler echocardiography. Circulation. 1989;79:357-370.
8 Schwefer M, Aschenbach R, Heidemann J, et al. Constrictive pericarditis, still a diagnostic challenge: Comprehensive review of clinical management. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009;36:502-510.