CHAPTER 1 Vascular Access
Step 1: Surgical Anatomy
Step 2: Preoperative Considerations
Step 3: Operative Steps
1 General Concepts
2 Temporary Central Lines
3 Tunneled Central Lines
4 Access by Anatomic Site
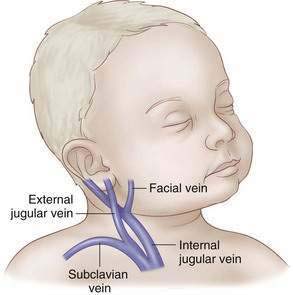
Neck
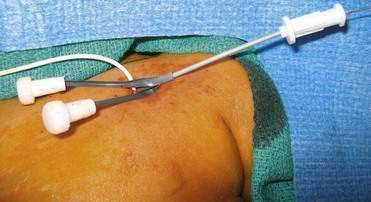
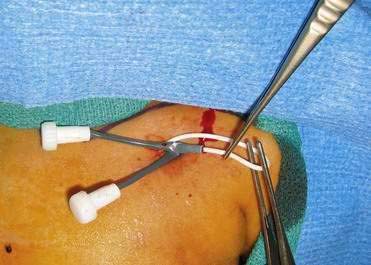
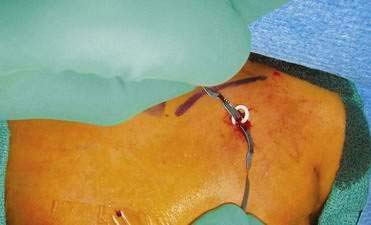
External Jugular Cutdown
Internal Jugular Cutdown
Internal Jugular, Percutaneous
Subclavian Vein, Percutaneous
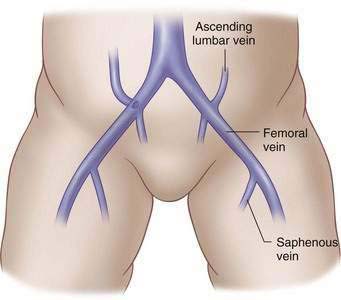
Femoral Vein
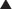 A small transverse incision is made medial to the pulse 1 cm below the inguinal ligament in infants and 2 to 3 cm below the inguinal ligament in children or adolescents.
A small transverse incision is made medial to the pulse 1 cm below the inguinal ligament in infants and 2 to 3 cm below the inguinal ligament in children or adolescents.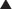 The vein is isolated and controlled proximally and distally with fine absorbable ties. Lidocaine is dripped onto the vessel to reduce spasm.
The vein is isolated and controlled proximally and distally with fine absorbable ties. Lidocaine is dripped onto the vessel to reduce spasm.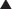 Puncture the skin 1 or 2 cm below the inguinal ligament and medial to the palpable pulse. The needle should be angled 30 degrees above the skin, and the trajectory should point toward the umbilicus. Advance slowly, aspirating continually until venous blood is obtained. The wire is advanced under fluoroscopic guidance into the inferior vena cava.
Puncture the skin 1 or 2 cm below the inguinal ligament and medial to the palpable pulse. The needle should be angled 30 degrees above the skin, and the trajectory should point toward the umbilicus. Advance slowly, aspirating continually until venous blood is obtained. The wire is advanced under fluoroscopic guidance into the inferior vena cava.Step 4: Postoperative Care
Arterial Access
Radial Artery
Posterior Tibial Artery
Step 5: Pearls and Pitfalls
Aitken DR, Minton JP. The “pinch-off sign”: A warning of impending problems with permanent subclavian catheters. Am J Surg. 1984;148:633-636.
Bagwell CE, Salzberg AM, Sonnino RE, et al. Potentially lethal complications of central venous catheter placement. J Pediatr Surg. 2000;35(5):709-713.
Lavandosky G, Gomez R, Montes J. Potentially lethal misplacement of femoral central venous catheters. Crit Care Med. 1996;24(5):893-896.
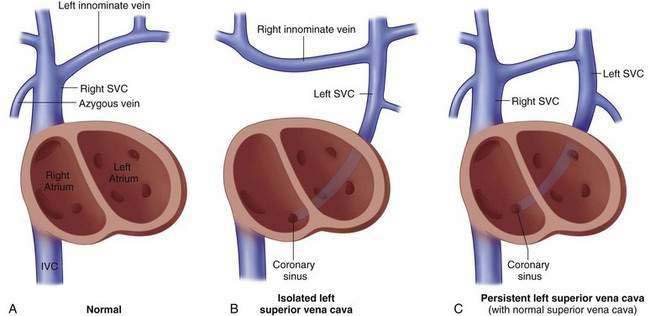
Mowery N, Billmire DF, Schamberger M, et al. Incidence of persistent left superior vena cava in esophageal atresia. J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41:484-486.
Singer RL, Wolfson PJ. Experience with umbilical artery cutdowns in neonates. Pediatr Surg Int. 1990;5:295-297.
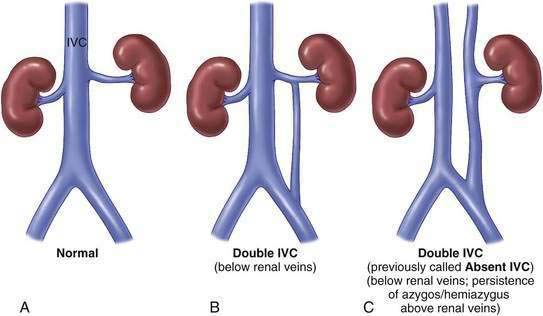
Skandalakis JE. The superior and inferior venae cavae. In: Skandalakis JE, Gray SW, editors. Embryology for surgeons. 2nd ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 1994:1032-1051.
Van Engelenburg KCA, Festen C. Cardiac tamponade: A rare but life-threatening complication of central venous catheters in children. J Pediatr Surg. 1998;33:1822-1824.
Warner BW, Ryckman FC. A simple technique to redirect malpositioned Silastic central venous catheters. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 1992;16(5):473-476. 1992