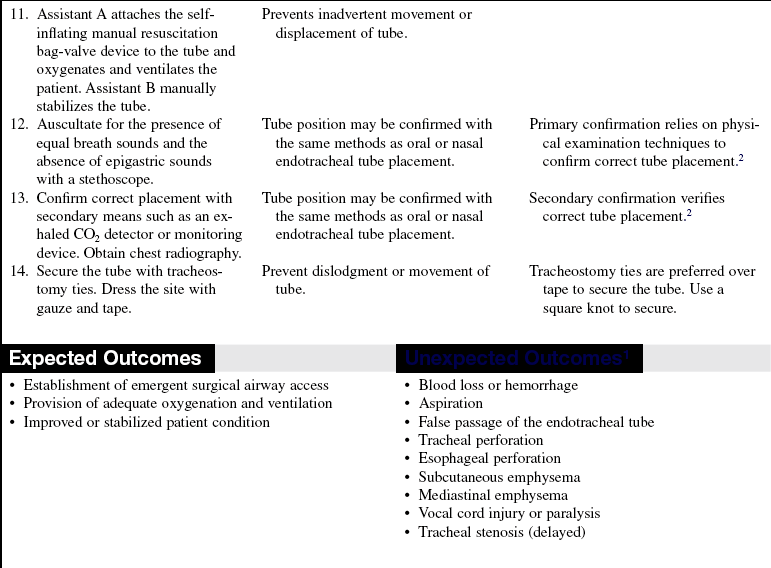
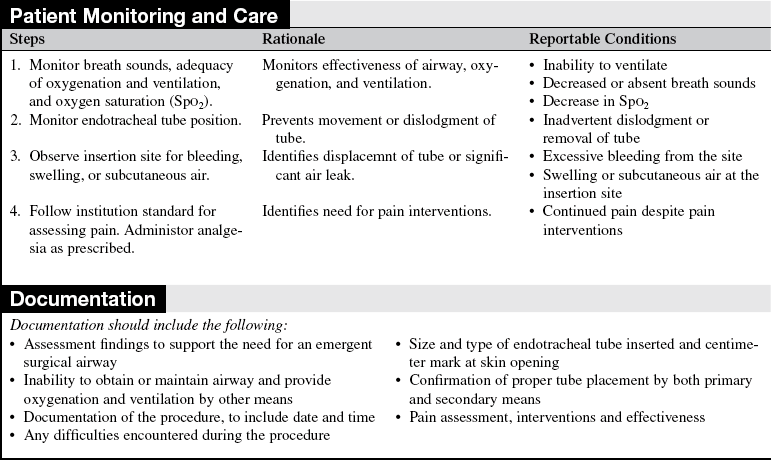
Surgical Cricothyrotomy (Assist)
PREREQUISITE NURSING KNOWLEDGE
• Surgical cricothyrotomy is used only when the airway cannot be obtained or maintained by standard means such as self-inflating manual resuscitation bag-valve-mask device, the use of airway adjuncts (oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airways), endotracheal intubation, or rescue airway (Combitube, laryngeal mask airway [LMA], or King Airway).3,4
• Surgical cricothyrotomy may be needed in patients with facial or neck trauma. Maintenance of the airway may be difficult in these patients because the injuries often disrupt the lower facial structures and make an adequate seal with a self-inflating manual resuscitation bag-valve-mask device difficult to obtain. The airway may also be obstructed or disrupted making endotracheal intubation difficult or ineffective.
• Difficulty in obtaining or maintaining an airway may result from upper airway obstruction as a result of trauma, allergic reactions with swelling and angioedema, foreign bodies, anatomic variations, and bleeding.2
• The need for emergent surgical cricothyrotomy must be determined quickly. This intervention is potentially life-saving, and implementation cannot be delayed.
• Surgical cricothyrotomy requires specialized training and should be performed only by highly skilled medical providers.2
• Commercially prepared cricothyrotomy kits are available and often use a modified Seldinger technique with a guidewire or dilator system.
Contraindications
Relative
In young children, the airway is funnel-shaped with the narrowest portion at the cricoid ring rather than the vocal cords as in adults. This narrowing increases the risk of development of subglottic stenosis after cricothyrotomy. Percutaneous transtracheal ventilation via needle cricothyrotomy is the method of choice for surgical airway management in young children.6
EQUIPMENT
• Personal protective equipment (face mask, eye protection, gown, sterile gloves)
• Suction device and suction catheter
• Tracheal (Trousseau) dilator or nasal speculum
• 5.0 to 6.0 cuffed endotracheal tube or no. 4 tracheostomy tube
• Self-inflating manual resuscitation bag-valve-mask device with oxygen source
Additional equipment, to have available as needed, includes the following:
• Commercially prepared kit such as the Melker Emergency Cricothyrotomy Catheter (Cook Medical, Inc, Bloomington, Ind; www.cookmedical.com), which uses a specially designed airway and a modified Seldinger technique for insertion
PATIENT AND FAMILY EDUCATION
• A patient who needs emergency surgical cricothyrotomy is likely unresponsive from the inability to maintain the airway and adequate oxygenation and ventilation; therefore, patient education is not possible. If the patient is responsive, the airway and ventilatory efforts are adequate and surgical cricothyrotomy is not indicated.
• Family members should be provided with a quick and concise explanation of the emergent need to create an artificial airway. This information is often best explained by another member of the healthcare team, rather than the provider performing the procedure, to prevent any delay in establishing the airway. If possible, obtain consent for the procedure from the family member.
PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND PREPARATION
Patient Assessment
 Open the airway with a jaw-thrust or chin-lift maneuver. If traumatic injury is suspected, maintain cervical stabilization. Assess for presence of foreign bodies, secretions, or other obstructions. Use suction to clear and maintain the airway.
Open the airway with a jaw-thrust or chin-lift maneuver. If traumatic injury is suspected, maintain cervical stabilization. Assess for presence of foreign bodies, secretions, or other obstructions. Use suction to clear and maintain the airway.  Rationale: Often airway patency can be achieved and maintained with simple maneuvers such as patient positioning, use of an airway maneuver, suction, or insertion of an oral or nasal pharyngeal airway.
Rationale: Often airway patency can be achieved and maintained with simple maneuvers such as patient positioning, use of an airway maneuver, suction, or insertion of an oral or nasal pharyngeal airway.
 If the patient has potential for airway compromise (i.e. bleeding, swelling, or traumatic injuries) and is alert and able to maintain the airway, allow the patient to maintain a position of comfort and suction to maintain a patent airway. Do not attempt to place the patient in a supine position because this may cause significant airway compromise.
If the patient has potential for airway compromise (i.e. bleeding, swelling, or traumatic injuries) and is alert and able to maintain the airway, allow the patient to maintain a position of comfort and suction to maintain a patent airway. Do not attempt to place the patient in a supine position because this may cause significant airway compromise.  Rationale: If the patient has the ability to maintain his or her own airway, allowing the patient to remain in an upright position, with suction if necessary, assists the patient in maintaining the airway. If the patient is placed in a supine position for packaging or transport, this move may cause significant airway compromise.
Rationale: If the patient has the ability to maintain his or her own airway, allowing the patient to remain in an upright position, with suction if necessary, assists the patient in maintaining the airway. If the patient is placed in a supine position for packaging or transport, this move may cause significant airway compromise.
 Assess rate, depth of respirations, accessory muscle use, chest wall motion, and breath sounds. If equipment is available, monitor oxygen saturation.
Assess rate, depth of respirations, accessory muscle use, chest wall motion, and breath sounds. If equipment is available, monitor oxygen saturation.
 If respiratory efforts are inadequate, attempt ventilation with a self-inflating manual resuscitation bag-valve-mask device and supplemental oxygen.
If respiratory efforts are inadequate, attempt ventilation with a self-inflating manual resuscitation bag-valve-mask device and supplemental oxygen.
 If an airway cannot be maintained or oxygenation and ventilation are adequate with a self-inflating manual resuscitation bag-valve-mask device, prepare for endotracheal intubation. If intubation is not possible, prepare for emergent surgical cricothyrotomy.
If an airway cannot be maintained or oxygenation and ventilation are adequate with a self-inflating manual resuscitation bag-valve-mask device, prepare for endotracheal intubation. If intubation is not possible, prepare for emergent surgical cricothyrotomy.
•  Rationale: This process is to identify inadequate respiratory efforts quickly and determine the optimal method for providing oxygenation and ventilation.
Rationale: This process is to identify inadequate respiratory efforts quickly and determine the optimal method for providing oxygenation and ventilation.
Patient Preparation
• Verify correct patient with two identifiers.  Rationale: Prior to performing a procedure, the nurse should ensure the correct identification of the patient for the intended intervention.
Rationale: Prior to performing a procedure, the nurse should ensure the correct identification of the patient for the intended intervention.
• Perform a pre-procedure verification and time out, if non-emergent.  Rationale: Ensures patient safety.
Rationale: Ensures patient safety.
• Position the patient supine and maintain cervical spine stabilization if indicated.  Rationale: Patients who need emergent surgical cricothyrotomy often have traumatic injuries that require cervical spine stabilization.
Rationale: Patients who need emergent surgical cricothyrotomy often have traumatic injuries that require cervical spine stabilization.
• Continue attempts to ventilate and oxygenate the patient with a self-inflating manual resuscitation bag-valve-mask device if patient is apneic or respiratory efforts are inadequate. 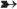 Rationale: This action can prevent further hypoxia and hypercarbia.
Rationale: This action can prevent further hypoxia and hypercarbia.
References
![]() 1. American College of Surgeons, Airway and ventilatory management. advanced trauma life support. ed 7. ACS, Chicago, 2004.
1. American College of Surgeons, Airway and ventilatory management. advanced trauma life support. ed 7. ACS, Chicago, 2004.
2. American Heart Association, Airway, airway adjuncts, -oxygenation and ventilation. advanced cardiac life -supportprinciples and practice. AHA, Dallas, 2006.
![]() 3. McGill, J, Clinton, JE, Ruiz, E. Cricothyrotomy in the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 1982; 11:361–364.
3. McGill, J, Clinton, JE, Ruiz, E. Cricothyrotomy in the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 1982; 11:361–364.
4. Northwest, MedStar. Critical Care Air Medical Transport Service. In: Surgical cricothyrotomy: protocol and procedure book. Spokane, WA: Northwest MedStar; 2008:133–134.
![]() 5. Sanders, MJ. Mosby’s paramedic textbook, ed 2. St Louis: Mosby; 2001.
5. Sanders, MJ. Mosby’s paramedic textbook, ed 2. St Louis: Mosby; 2001.
6. Tintinalli, JE, Kelen, GD, Stapczynski, JS, Emergency -medicine. a comprehensive study guide. ed 6. McGraw-Hill, New York, 2004.