CHAPTER 9 Pulmonary Function Testing
3 Besides abnormal pulmonary function tests, what are recognized risk factors for postoperative pulmonary complications?
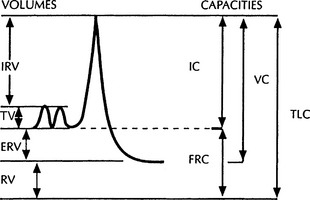
5 Describe standard lung volumes
The tidal volume (TV) is the volume of air inhaled and exhaled with each normal breath. Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) is the volume of air that can be maximally inhaled beyond a normal TV. Expiratory reserve volume (ERV) is the maximal volume of air that can be exhaled beyond a normal TV. Residual volume (RV) is the volume of air that remains in the lung after maximal expiration (Figure 9-1).
6 What are the lung capacities?
Lung capacities are composed of two or more lung volumes. Total lung capacity (TLC) is the sum of IRV, tidal volume (TV), ERV, and RV. Vital capacity (VC) is the sum of IRV, TV, and ERV. Inspiratory capacity (IC) is the sum of IRV and TV. Functional residual capacity (FRC) is the volume of air in the lung at the end of a normal expiration and is the sum of RV and ERV (see Figure 9-1).
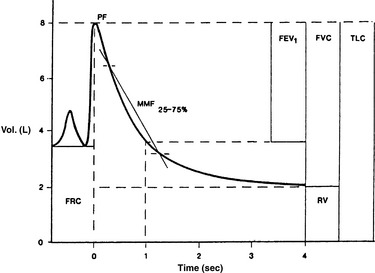
8 What information is obtained from spirometry?
Spirometry is the foundation of pulmonary function testing and provides timed measurements of expired lung volumes (Figure 9-2). With automated equipment it is possible to interpret more than 15 different measurements from spirometry alone. Forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), FEV1/FVC ratio, and flow between 25% and 75% of the FVC (mean maximal flow [MMF]25-75) are the most clinically helpful indices obtained from spirometry. Although spirometry demonstrates airflow limitations, it does not determine the cause (e.g., airway obstruction vs. decreased alveolar elastic recoil vs. decreased muscle strength). It is also effort dependent and requires a motivated patient.
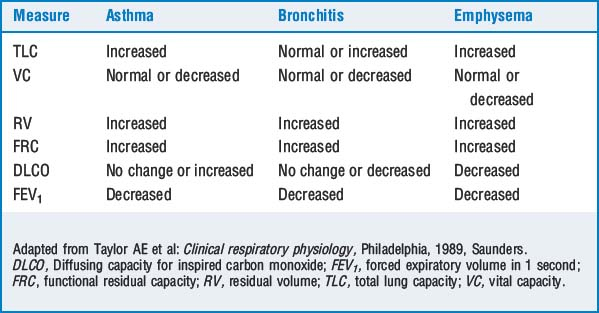
12 Review obstructive airway diseases and their pulmonary function test abnormalities
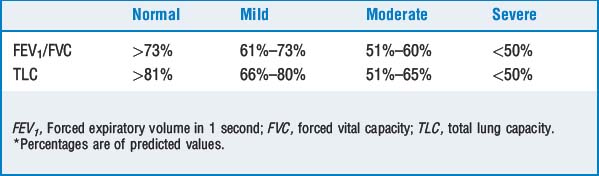
Obstructive airway diseases, including asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, cystic fibrosis, and bronchiolitis, exhibit diminished expiratory airflow and involve airways distal to the carina. The FEV1, FEV1/FVC ratio, and the forced expiratory flow at 25% to 75% of FVC (FEF25-75) are below predicted values. A decreased FEF25-75 reflects collapse of the small airways and is a sensitive indicator of early airway obstruction. The FVC may be normal or decreased as a result of respiratory muscle weakness or dynamic airway collapse with subsequent air trapping. Table 9-1 compares the alterations in measures of lung function in various obstructive lung diseases. Table 9-2 grades the severity of obstruction based on the FEV1/FVC ratio.
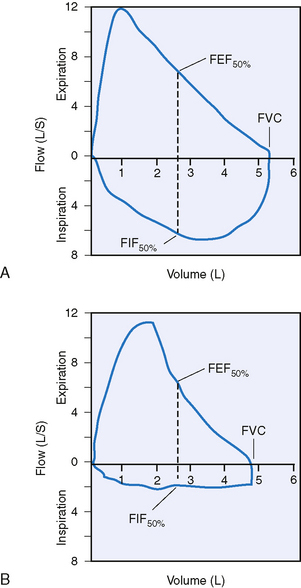
14 What is a flow-volume loop and what information does it provide?
Using routine spirometric values, flow-volume loops assist in identifying the anatomic location of airway obstruction. Forced expiratory and inspiratory flow at 50% of FVC (FEF50 and FIF50) are shown in Figure 9-3. Note that expiratory flow is represented above the x-axis, whereas inspiratory flow is represented below the axis. In a normal flow-volume loop the FEF50/FIF50 ratio is 1.
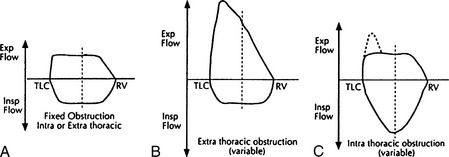
15 What are the characteristic patterns of the flow-volume loop in a fixed airway obstruction, variable extrathoracic obstruction, and intrathoracic obstruction?
Upper airway lesions (e.g., tracheal stenosis) are fixed when there is a plateau during both inspiration and expiration. The FEF50/FIF50 ratio remains unchanged. An extrathoracic obstruction occurs when the lesion (e.g., tumor) is located above the sternal notch and is characterized by a flattening of the flow-volume loop during inspiration. The flattening of the loop represents no further increase in airflow because the mass causes airway collapse. The FEF50/FIF50 ratio is >1. An intrathoracic obstruction is characterized by a flattening of the expiratory loop of a flow-volume loop, and the FEF50/FIF50 ratio is <1. The lesion causes airway collapse during expiration (Figure 9-4).
18 What pulmonary function test values predict increased perioperative pulmonary complications after abdominal or thoracic surgery?
TABLE 9-3 Pulmonary Function Criteria Suggesting Increased Risk for Abdominal and Thoracic Surgery
| Abdominal | Thoracic | |
|---|---|---|
| FVC | <70% predicted | <70% predicted or <1.7 L |
| FEV1 | <70% predicted | <2 L,* <1 L,† <0.6 L‡ |
| FEV1/FVC | <65% | <35% |
| MVV | <50% predicted | <50% predicted or <28 L/min |
| RV | <47% predicted | |
| DLCO | <50% | |
| VO2 | <15 ml/kg/min |
DLCO, Diffusing capacity for inspired carbon monoxide; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FVC, forced vital capacity; MVV, maximal voluntary ventilation; RV, residual volume; VO2, oxygen consumption.
Data from Gass GD, Olsen GN: Preoperative pulmonary function testing to predict postoperative morbidity and mortality, Chest 89:127–135, 1986.
19 Are there absolute values of specific pulmonary function tests below which the risk of surgery is prohibitive?
KEY POINTS: Pulmonary Function Testing