CASE 87
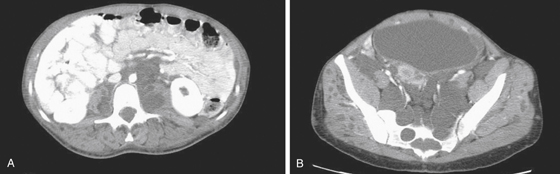
History: A 35-year-old woman with 6 months of vague abdominal discomfort.
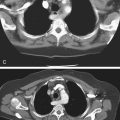
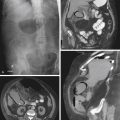
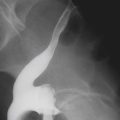
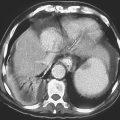
1. Which of the following should be included in the differential diagnosis of the imaging finding shown in Figure A? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN)
2. What is the hereditary description of neurofibromatosis?
3. What part of the body does neurofibromatosis most commonly affect?
4. Which of the following statements regarding neurofibromatosis is true?
A. Hypertension developing in a patient with neurofibromatosis is usually due to a pheochromocytoma.
B. Abdominal lesions in neurofibromatosis usually arise in the mesentery.
C. Most abdominal tumors in neurofibromatosis are leiomyomas.
D. Barium small bowel series can show malabsorption.
ANSWERS
CASE 87
Neurofibromatosis of the Abdomen
1. B, C, and D
2. A
3. A
4. D
References
Hartley N, Rajesh A, Verma R, et al: Abdominal manifestations of neurofibromatosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2008;32:4–8.
Cross-Reference
Gastrointestinal Imaging: THE REQUISITES, 3rd ed, p 131.
Comment
Neurofibromatosis is an autosomal dominant disease that can affect multiple organ systems. The best-known area affected is the skin. However, the process can be much more far ranging and dangerous. The disease has been divided into two types, neurofibromatosis type 1 (von Recklinghausen’s disease), which accounts for almost 90% of cases, and type 2, which involves the acoustic nerves. Neurofibromatosis type 1 is one of the more common autosomal hereditary disorders (1 in 4000). Involvement of the abdomen and GI tract can be extensive, as seen in this patient (see figures). Tumors may be found within the liver or mesentery as well as in the bowel itself. It can result in GI bleeding, obstruction, or intussusception, chronic abdominal pain, and distention. There is thought to be an increased incidence of adenocarcinoma of the small bowel when the gut is involved.