CASE 81
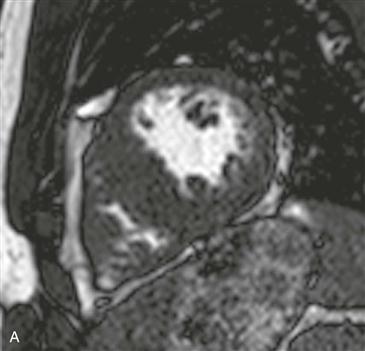
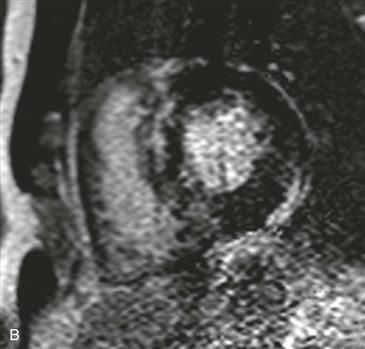
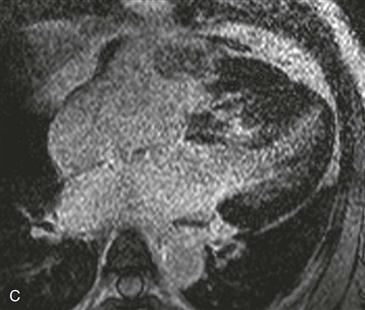
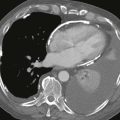
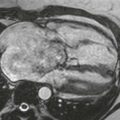
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis for the pattern of late gadolinium enhancement shown in Figs. B and C? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Myocarditis
2. Based on the images, what is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Sarcoidosis
B. Amyloidosis
D. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)
3. What is the distribution of hypertrophy in this patient?
A. Concentric
B. Septal
D. Apical
4. Which of the following is the least appropriate treatment for this patient?
C. Surgery
ANSWERS
References
Harris SR, Glockner J, Misselt AJ, et al. Cardiac MR imaging of nonischemic cardiomyopathies. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2008;16(2):165–183.
Soler R, Rodriguez E, Remuinan C, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of primary cardiomyopathies. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2003;27(5):724–734.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 53, 284–288.
Comment
Etiology and Clinical Features
HCM is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait with variable penetrance. Patients may be asymptomatic, or they may present with atrial fibrillation, heart failure, syncope, or sudden cardiac death, which is the leading cause of mortality in these patients. Asymmetric hypertrophy of the ventricular septum is the most common distribution, seen in 90% of patients with HCM. Other patterns of hypertrophy are right ventricular, left ventricular, septal, apical, midventricular, and concentric. Patients with heart failure secondary to significant septal hypertrophy and left ventricular outflow obstruction can be treated with septal myectomy or percutaneous transluminal septal myocardial ablation with ethanol.
MRI
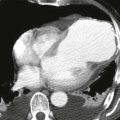
MRI can provide anatomic and functional information in HCM and can be most useful when the diagnosis is in question, when invasive therapy is being considered, or when clinical concern requires more thorough assessment than that provided by echocardiography. MRI can be used to identify the distribution of thickened myocardium, to evaluate for systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve, and to calculate left ventricular mass (Fig. A). Late gadolinium enhancement MRI characteristically shows patchy midmyocardial enhancement (Figs. B and C). MRI also can be used for functional evaluation of left ventricular outflow tract obstruction.