Mathematical Calculations Used in Pharmacology
Objectives
1. Describe the apothecaries’ and household measure systems and when they might be used.
2. Use the metric system to convert from one measure to another.
3. Use common abbreviations and symbols to interpret and solve medication problems.
4. State the values of common household measures and their equivalents.
5. Compare the units used in the apothecaries’, metric, and household measures systems.
Key Terms
Celsius (SĔL-sē-ěs, p. 80)
Fahrenheit (FĂR-ěn-HĪT, p. 80)
gram (GRĂM, p. 79)
liter (LĒ-těr, p. 79)
meter (MĒ-těr, p. 79)
metric system (MĔ-trĭk, p. 79)
Overview
![]() http://evolve.elsevier.com/Edmunds/LPN/
http://evolve.elsevier.com/Edmunds/LPN/
Giving medicines requires the nurse to use precise weights and measures so each dose is the same. General household measures are often used when medicine is given in the home; unfortunately, it is not very accurate but patients are familiar with it. For example, 1 glass equals 8 ounces. Although one would think that this system is out of date for giving current medications, LPNs/LVNs practice in a wide variety of settings and may need to know this information. It is also important to understand household measures because this may be what patients will use in talking with you about how much medication they take. Household measures you should know are listed in Box 8-1.
Another measuring system is the apothecary system that was used primarily by pharmacists. This system is no longer recommended for use but a few medications have survived that are listed in grains (aspirin, iron, quinidine), and drops (gtts) are used in intravenous calculations. Drams and minims are no longer used. 1 grain = 60 or 64 mg of 0.06 g; 1/60 grain = 1 mg
Metric System
The metric system was developed in France and relies on a decimal system; it is built on multiples of 10 (tens, hundreds, and thousands). The metric system is the most commonly used drug measurement system. The metric system is the main system used internationally to measure weight, length, and volume.
The metric system uses meter (m) for the unit of length, liter (L) for the unit of volume, and gram (g) for the unit of weight. The most common measures used in the metric system are listed in Box 8-2.
Relying on what you know about the decimal system, it is simple to change measures within the metric system. To change milligrams to micrograms, move the decimal point three places to the right (multiply by 1000):
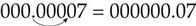
To change micrograms to milligrams, move the decimal point three places to the left (divide by 1000):
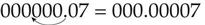
To change grams to milligrams, move the decimal point three places to the right (multiply by 1000):
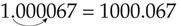
To change milligrams to grams, move the decimal point three places to the left (divide by 1000):
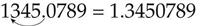
If you have not used the metric system before, you will want to use common sense to see if the dose you calculate seems right. The number you get after doing the calculation may appear abnormally small or tremendously large. As you gain experience, common sense will help you determine whether the answer is correct. As you practice, you will soon learn shortcuts to help with mathematical calculations. You may wish to add these formulas to iPhone, personal digital assistants, or other handheld devices you use all the time. For commonly recognized measures and how they compare with the metric system, see Box 8-3.
Converting Temperature Readings
For years, nurses have used the Fahrenheit (F) scale to take temperatures. In the last 20 years, institutions have placed increasing emphasis on the centigrade, or Celsius (C), scale for hospital use. Although electronic thermometers with digital readouts are used in some hospitals, nurses still use either Fahrenheit or Celsius mercury-based thermometers throughout other parts of the world.
Thermometers used in many hospitals come in either Fahrenheit or Celsius scale. Oral thermometers come with either a long, flat tip or oblong or stubby tips. The oblong or stubby tips may also be used for rectal or axillary temperatures.
On the Fahrenheit scale, 212° is the boiling point and 32° is the freezing point. Outdoor temperature thermometers generally include these points. The Fahrenheit thermometer used for medical measurement ranges from 95° to 105°, with individual divisions representing 0.2°. Because body temperature generally does not vary more than a few degrees, this smaller range is sufficient to measure the normal body temperature range of 97.6° F to 99.4° F and any common variations from normal.
The Celsius scale has a boiling point of 100° and a freezing point of 0°. The Celsius thermometer also has a restricted range for medical use, with each division on the scale representing 0.1°. The normal body range as measured on the Celsius scale varies from 36.5° C to 37.5° C.
Because both Fahrenheit and Celsius scales are commonly used in hospitals, the nurse must understand how to read each thermometer accurately, correctly note changes from normal, and convert from one scale to another. If you need to give a medication to help lower a high temperature, you must clearly understand the variations from normal in either scale.
The formulas for converting from one scale to another are very simple. Because the normal range of temperatures varies so little in individuals, even a little experience in changing temperatures will aid you in rapidly understanding this process.
The formula for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius is as follows:
< ?xml:namespace prefix = "mml" />
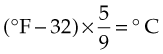
For example:
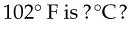
First, Fahrenheit temperature minus 32. Multiply that times 5, then divide by nine:
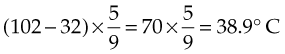
The formula for converting Celsius temperature to Fahrenheit temperature is as follows:
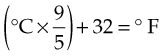
For example:
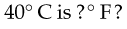
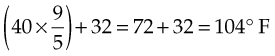
Individuals who dislike working with fractions and find decimal methods easier for temperature conversions must master two other formulas:



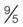 of one degree on the Celsius scale.
of one degree on the Celsius scale.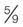 of one degree on the Fahrenheit scale.
of one degree on the Fahrenheit scale.