TOPIC 8 Adult congenital heart disease
Genetic and non-genetic associations with congenital heart disease
Genetic
Table 8.1 Genetic syndromes associated with congenital heart disease
| Syndrome | Typical genetic defect | Typical cardiac defects |
|---|---|---|
| Down syndrome | Trisomy 21 | Atrioventricular septal defect, VSD, ASD, PDA |
| Holt–Oram syndrome | 12q2 | ASD, VSD |
| Turner syndrome | XO | Aortic coarctation, bicuspid aortic valve |
| Noonan syndrome | 12q | Pulmonary stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
| Di George syndrome | 22q11 deletion | Truncus arteriosus, tetralogy of Fallot, interrupted aortic arch |
| Williams syndrome | 7q11 deletion | Supravalvular aortic stenosis, peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis |
Non-genetic
Table 8.2 Non-genetic associations with congenital heart disease (known or suspected maternal factors)
| Infective | Rubella, toxoplasmosis, Coxsackie B virus |
| Environmental | Trichloroethylene, dichloroethylene, chromium |
| Iatrogenic | Antiepileptics, lithium, thalidomide, warfarin, isotretinoin |
| Lifestyle | Alcohol and illicit drug use, low folate intake |
| Medical | Diabetes mellitus, phenylketonuria |
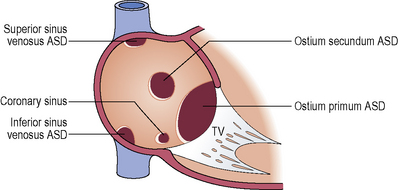
Atrial septal defect (ASD)
Communication between the atrial chambers allowing mixing of blood.
Clinical features
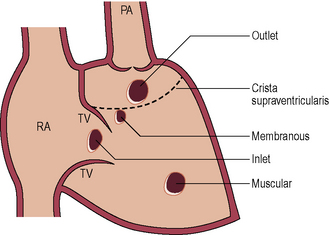
Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
Clinical features
Small: Pressure ratio < 0.3 and flow ratio < 1.4
Moderate: Pressure ratio > 0.3 and flow ratio 1.4 to 2.2
Large: Pressure ratio > 0.3 and flow ratio > 2.2
Aortic regurgitation due to aortic cusp prolapse (outlet VSD and membranous VSD).
Indications for adult intervention include:
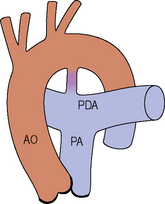
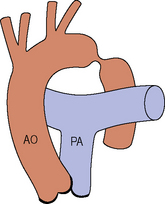
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
Clinical features
After birth the shunt direction reverses with changes in systemic and pulmonary pressures.
Large isolated PDAs are characterized by heart failure in infancy.
A PDA may be clinically silent throughout life or may not present till adulthood.
If the PDA is very small or operated early in childhood, normal survival can be expected.
Coarctation of the aorta
Subvalvular aortic stenosis
Associated lesions include VSD, bicuspid aortic valve and aortic coarctation.
Subvalvular stenosis is often progressive and not uncommonly recurs after surgical repair.
Supravalvular aortic stenosis
Pulmonary stenosis
Indications for intervention include:
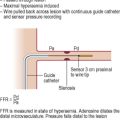
Pullback gradient at catheterization of > 50 mmHg
Presence of right to left shunt (e.g. associated ASD)
Double chambered right ventricle with mid cavity gradient at catheterization > 50 mmHg
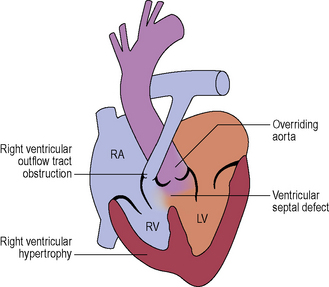
Tetralogy of Fallot
Palliative procedures
Anastomosis of systemic to pulmonary circulation to increase pulmonary blood flow and include:
Corrective surgery
Outcome
Late complications in repaired patients include:
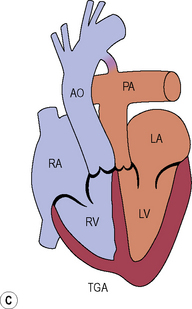
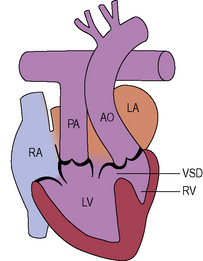
Transposition of the great arteries (D-transposition of the great arteries)
Subsequent surgical strategies
Long term complications
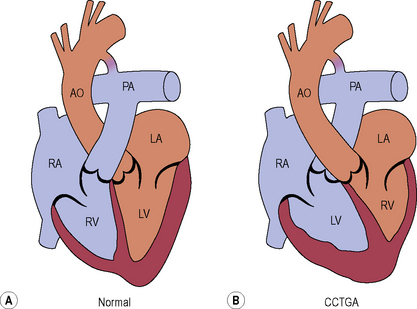
Congenitally corrected transposition of the great arteries (L-transposition of the great arteries)
Management
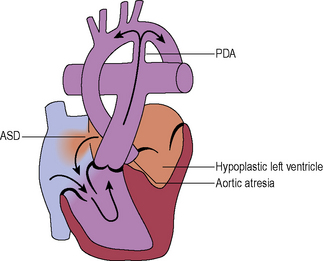
Cyanotic congenital heart disease
Cyanosis occurs in the presence of right to left shunting, with or without pulmonary hypertension.
Complications of cyanotic congenital heart disease include the following:
Univentricular physiology
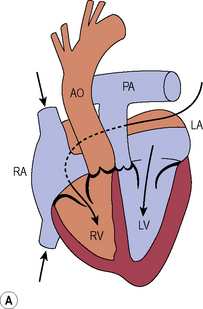
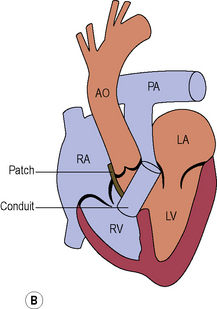
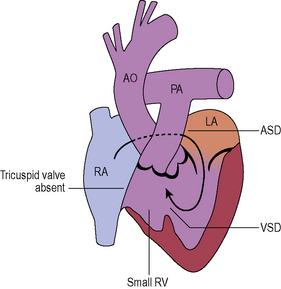
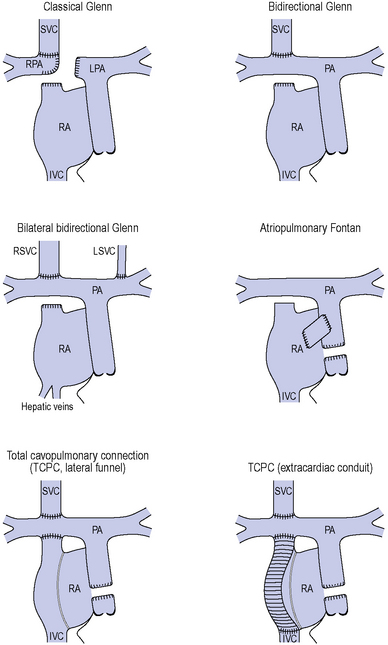
Tricuspid atresia (see Figure 8.8)
The tricuspid valve is not formed and there is an obligatory right to left shunt at atrial level.
Double inlet left ventricle
Complications of the Fontan/TCPC circulation
Characterized by low cardiac output, poor effort tolerance and chronic venous hypertension.