CASE 74
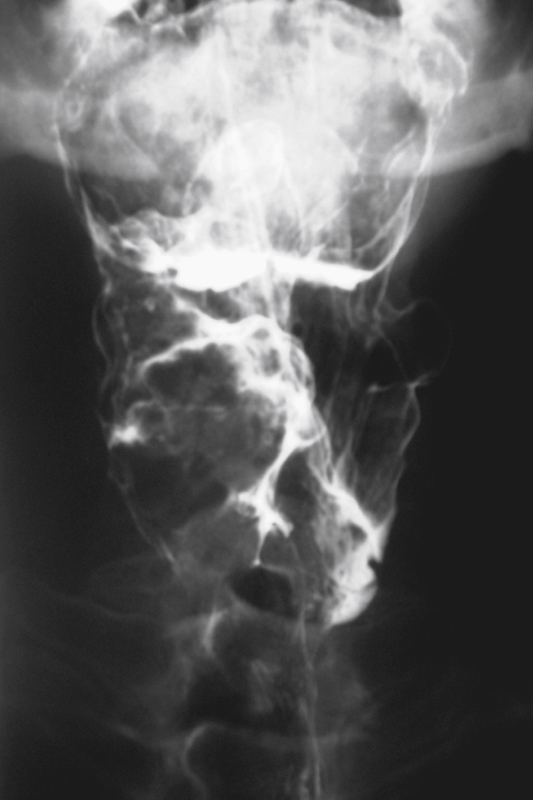
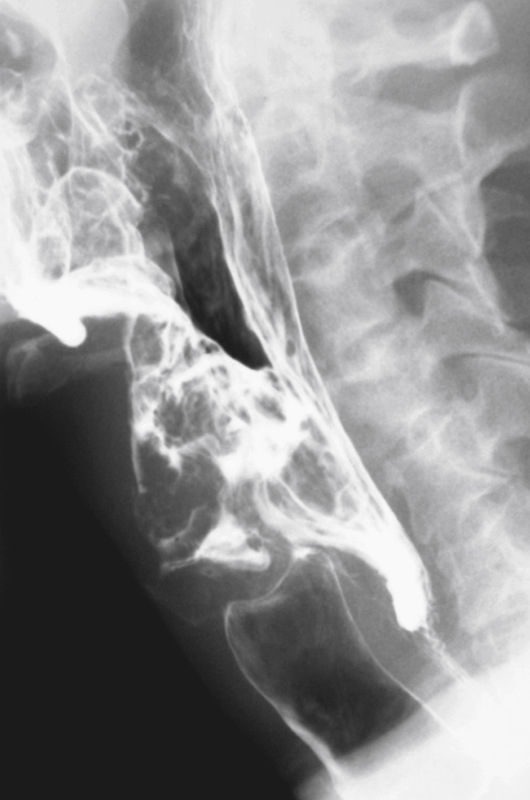
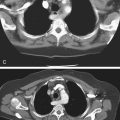
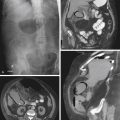
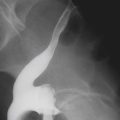
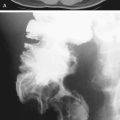
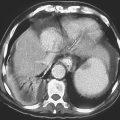
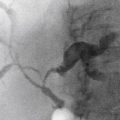
History: A 50-year-old man presents with right neck swelling but no dysphagia or dysphonia.
1. Which of the following should be included in the differential diagnosis of the imaging finding shown in the figures? (Choose all that apply.)
E. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor
2. What is the most common tumor of the pharynx?
3. What is the most common risk factor for the development of pharyngeal cancer?
4. Which of the following statements relevant to imaging of pharyngeal cancers is true?
A. Pharyngeal cancers usually manifest early.
B. In staging pharyngeal tumors, T2 describes primary tumor between 2 and 4 cm in diameter.
C. In staging pharyngeal tumors, N2 describes lymph nodes between 2 and 4 cm in diameter.
ANSWERS
CASE 74
Squamous Carcinoma of the Pharynx
1. A, B, C, and D
2. D
3. A
4. B
References
Dammann F, Horger M, Mueller-Berg M, et al: Rational diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck region: comparative evaluation of CT, MRI, and 18FDG PET. Am J Roentgenol. 2005;184:1326–1331.
Cross-Reference
Gastrointestinal Imaging: THE REQUISITES, 3rd ed, p 5.
Comment
The majority of tumors involving the pharynx are squamous in origin. These tumors are seen radiologically as small nodules or masses or sometimes as a thickening or obliteration of the normal structures. Laryngoscopy is the method of choice for identification, but with the increase in swallowing studies being performed to diagnose conditions causing dysphagia, the radiologist may be the first to encounter these tumors.
The pharynx and hypopharynx are repositories of a substantial amount of lymph tissue. Thus it is to be expected that patients with lymphoma might develop neoplastic infiltration of these structures. In patients with lymphoma and dysphagia, the hypopharynx must be studied closely. Squamous tumors of the hypopharynx typically arise in the vallecula, piriform sinuses, or epiglottis.
Lymphomas more commonly involve the posterior or lateral wall and may be submucosal, producing subtle changes. If a tumor is substantially posterior, lymphoma must be strongly considered. Potentially, all tumors can metastasize to this region. However, it is a rare event, given the number of patients with malignancies. Two common cancers—breast and lung—are known to metastasize to the pharynx on occasion. Also, cancers of the skin, such as melanoma and Kaposi’s sarcoma, seem to metastasize to the hypopharynx relatively commonly.
Patients with Plummer-Vinson syndrome have anemia associated with cervical esophageal webs. Although it is controversial, some authors believe that the syndrome is a premalignant condition and that affected patients have a higher incidence of pharyngeal and esophageal carcinoma.