CASE 70
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis for this patient history? (Choose all that apply.)
C. Pneumonia
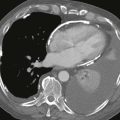
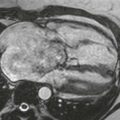
2. What imaging finding is shown in Figs. A–C?
B. Superior vena cava thrombus
C. Saphenous vein graft occlusion
3. Which of the following vascular conduits is the most robust for use in CABG surgery?
A. Left internal mammary artery (LIMA)
4. What is a major advantage of a saphenous vein graft over the LIMA graft?
ANSWERS
Reference
Frazier AA, Qureshi F, Read KM, et al. Coronary artery bypass grafts: assessment with multidetector CT in the early and late postoperative settings. Radiographics. 2005;25(4):881–896.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 229–231.
Comment
Imaging
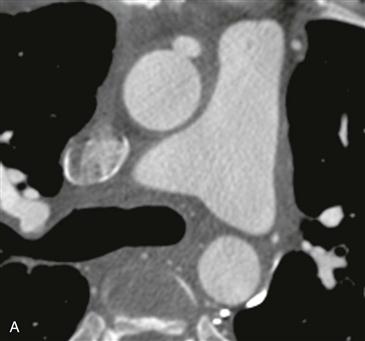
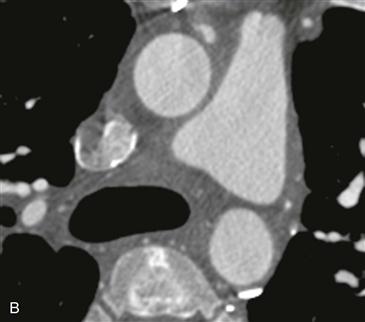
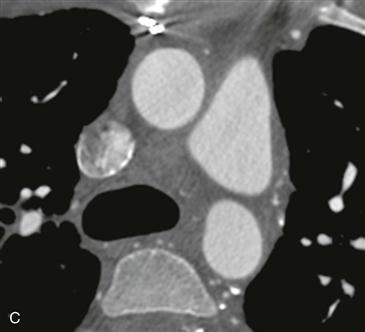
Figs. A–C from a coronary CT angiogram (extending caudal to cranial) show a proximally patent saphenous vein graft arising from the anterior ascending aorta. Fig. C shows near-complete occlusion of the graft.
Complications of CABG
CT angiography is useful in the evaluation of symptomatic patients after CABG surgery. CT angiography is able to diagnose accurately both early and late complications of surgery. Early complications (<1 month after surgery) include saphenous vein graft thrombosis, sternal infection, pericardial or pleural effusion, and pulmonary embolism. Late complications (>1 month after surgery) include graft stenosis or occlusion or graft aneurysm. CT angiography is also useful in preoperative planning before repeat CABG surgery. The main goal of imaging in these patients is to depict the course of the LIMA and saphenous vein graft with respect to the sternum to avoid injury with repeat sternotomy.