CHAPTER 7 ENDOCRINOLOGY
DIABETES
Diagnosis
Patients are often asymptomatic and may be diagnosed during routine or opportunistic screening.
Management
Referral.
Admit all children and pregnant women.
General management.
Practice nurses and diabetes specialist nurses have a valuable role in sharing the management of the diabetic patient. Diabetes UK is the national association for diabetes (see p. 356) and offers excellent on-line advice to both patients and professionals.
Education
Routine review.
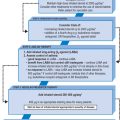
Therapeutic management of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Consider other antidiabetic agents:
If control remains poor despite attention to diet and tablets, insulin therapy should be considered.
THYROID DISORDERS
HYPOTHYROIDISM
Diagnosis
HYPERTHYROIDISM
OBESITY
Obesity is defined in terms of body mass index (BMI) (see p. 152):