CHAPTER 67 Peripheral Nerve Blocks
3 What are the risks of performing a peripheral nerve block?
 There may be inadvertent damage to anatomic structures by the advancing needle. Examples include direct trauma to the nerve or spinal cord by intraneural injection of local anesthetic, nerve laceration, vascular injury with resulting hematoma formation, or pneumothorax.
There may be inadvertent damage to anatomic structures by the advancing needle. Examples include direct trauma to the nerve or spinal cord by intraneural injection of local anesthetic, nerve laceration, vascular injury with resulting hematoma formation, or pneumothorax. The drugs that are injected may have undesirable local and systemic effects. Allergic reactions to local anesthetics are rare. Ester local anesthetics are derivatives of para-aminobenzoic acid, a known allergen, and therefore more likely to cause allergic reactions than the amide local anesthetics. Any local anesthetic injected intravascularly has the potential for systemic reactions, including seizures and cardiovascular collapse.
The drugs that are injected may have undesirable local and systemic effects. Allergic reactions to local anesthetics are rare. Ester local anesthetics are derivatives of para-aminobenzoic acid, a known allergen, and therefore more likely to cause allergic reactions than the amide local anesthetics. Any local anesthetic injected intravascularly has the potential for systemic reactions, including seizures and cardiovascular collapse.8 When using ultrasound guidance, what is the difference between an in-plane and an out of-plane approach?
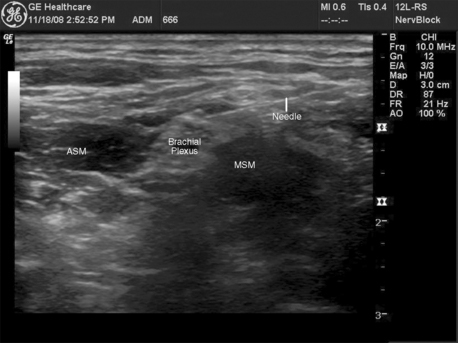
The in-plane approach means that the shaft of the needle is visualized while the needle is advanced (Figure 67-1). This technique allows the operator to observe the tip of the needle as it advances through the different anatomic structures. The out-of-plane approach relies on known anatomic relationships and careful injection (which can be observed in real time) to evaluate the adequacy of needle placement. In the out-of-plane approach the short axis (transverse cut) of the needle is visualized.
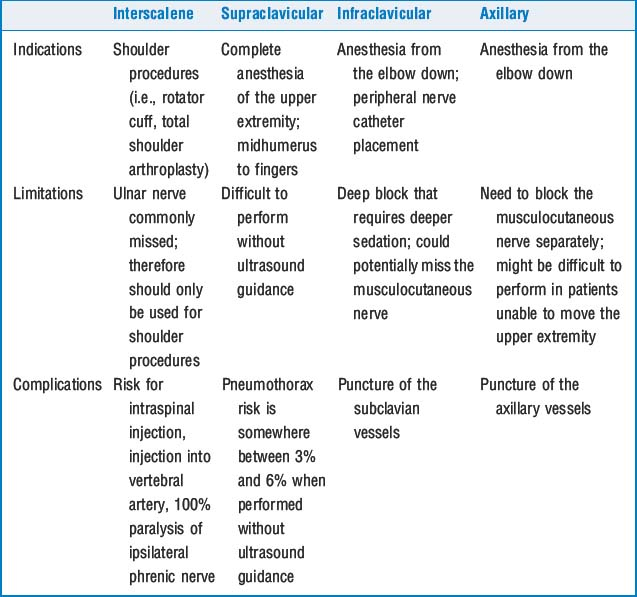
9 Review upper-extremity nerve blocks, including their indications, limitations, and complications
See Table 67-1. The volumes of local anesthetic solutions for an adult are between 20 and 30 ml.
11 How is local anesthetic toxicity avoided when performing a Bier block?
KEY POINTS: Peripheral Nerve Blocks 
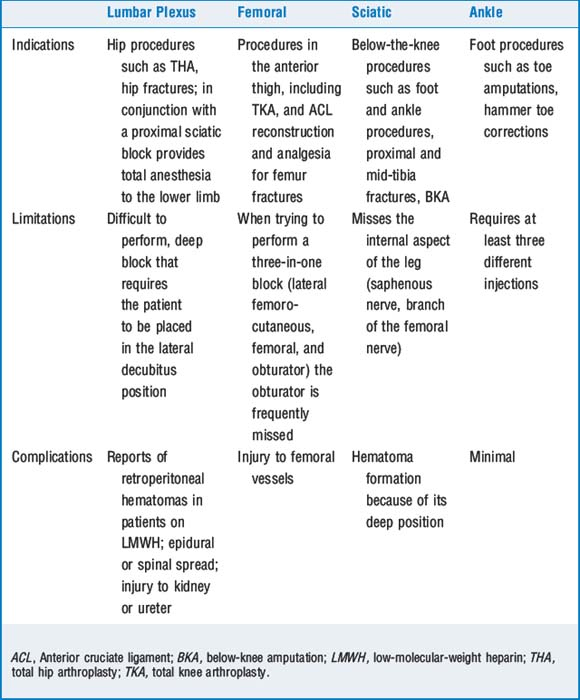
12 What peripheral nerve block can be performed for surgery of the lower extremity?
The first step in deciding what block is indicated for anesthesia or analgesia is appreciating the innervation of the lower extremity and the requirements of the proposed procedure. The lumbar plexus (L1-L4) gives origin to the ilioinguinal, genitofemoral, obturator, femoral, and lateral femorocutaneous nerves and mainly innervates the inguinal region and the anterior aspect of the thigh. The rest of the lower extremity is innervated by the sacral plexus. This includes the posterior aspect of the thigh and all the area distal to the knee except for the medial aspect, which is the territory of the saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve. The main nerve arising from the sacral plexus is the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve is actually formed by union of the tibial and peroneal nerves. These two nerves separate in or slightly above the cephalad region of the popliteal fossa. Table 67-2 describes the most common indications, limitations, and complications of the most commonly performed PNB to the lower extremity.
14 What peripheral nerve block can be used to provide anesthesia or analgesia to the anterior abdominal wall?
1. Brull R., McCartney C.J., Chan V.W., et al. Neurological complications after regional anesthesia: contemporary estimates of risk. Anesth Analg. 2007;104:965-974.
2. De Tran Q.H., Clemente A., Doan J., et al. Brachial plexus blocks: a review of approaches and techniques. Can J Anaesth. 2007;54:662-674.
3. Koscielniak-Nielsen Z.J. Ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks: what are the benefits? Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008;52:727-737.
4. McDonnell J.G., O’Donnell B., Curley G., et al. The analgesic efficacy of transverses abdominis plane block after abdominal surgery: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 2007;104:193-197.
5. Tran D., Clemente A., Finlayson R.J. A review of approaches and techniques for lower extremity nerve blocks. Can J Anaesth. 2007;54:992-1034.
6. Tsai T.P., Vuckovic I., Dilberovic F., et al. Intensity of the stimulating current may not be a reliable indicator of intraneural needle placement. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2008;33:207-210.