CASE 65
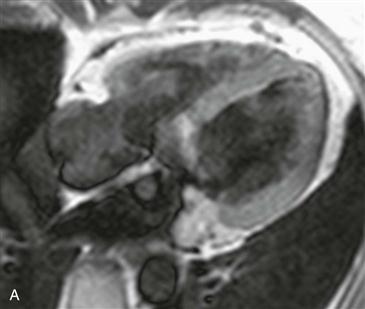
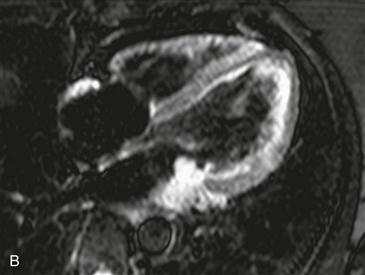
History: A patient presents with arrhythmia.
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis for a T1 hyperintense cardiac mass on a non–contrast-enhanced image? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Lipoma
B. Lipomatous hypertrophy of the interatrial septum
D. Myxoma
2. What is the most useful way to differentiate a fat-containing lesion from a melanin-containing lesion?
A. Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images
B. Fat-suppressed T1-weighted images
C. Cine steady-state free precession
D. Velocity-encoded cine phase contrast
3. What is the most common cardiac tumor?
A. Lipoma
B. Angiosarcoma
C. Myxoma
D. Metastasis
4. What is the most common patient presentation for this entity?
A. Arrhythmia
B. Asymptomatic
C. Chest pain
D. Pneumothorax
ANSWERS
Reference
Tesolin M, Lapierre C, Oligny L, et al. Cardiac metastases from melanoma. Radiographics. 2005;25(1):249–253.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 277–278.
Comment
Epidemiology
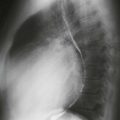
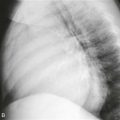
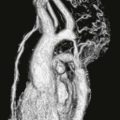
Cardiac metastasis is the most common cardiac tumor. The most frequent metastases are from lung or breast cancer. However, melanoma is more likely to metastasize to the heart; more than 50% of patients with known melanoma have evidence of metastatic disease at autopsy. Melanoma metastases are difficult to diagnose because they are commonly asymptomatic. Most patients who are symptomatic present with arrhythmia.
Differential Diagnosis and Treatment
Melanoma metastases are characteristically hyperintense on T1-weighted images because of the presence of melanin. They are T2 hyperintense and enhance with contrast agent administration, which are important features to differentiate from thrombus. MRI is the test of choice in patients with suspected metastatic disease. Surgery may be performed in select cases to treat an isolated melanoma metastasis.