CASE 61
1. What lesions are likely present in this patient? (Choose all that apply.)
B. Hypoplastic right pulmonary artery
C. Hypoplastic right main bronchus
2. What is the most common shunt lesion in this anomaly?
D. Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection
3. Where do the anomalous pulmonary veins drain?
D. Portal vein
4. What is the most likely diagnosis?
ANSWERS
Reference
Biyyam DR, Chapman T, Ferguson MR, et al. Congenital lung abnormalities: embryologic features, prenatal diagnosis, and postnatal radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2010;30(6):1721–1738.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 334–336.
Comment
Primary Anomalies
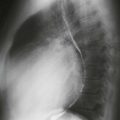
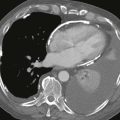
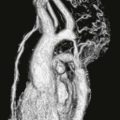
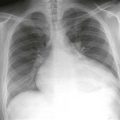
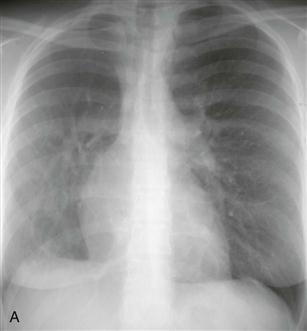
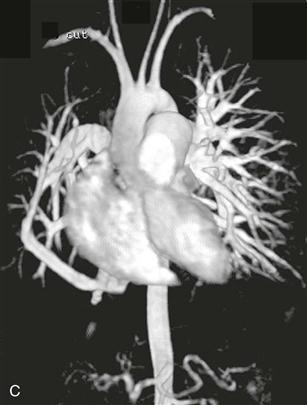
The scimitar syndrome, also known as hypogenetic lung syndrome or venolobar syndrome, is a complex anomaly characterized by four components: right lung hypoplasia; hypoplastic right pulmonary artery; systemic arterial supply (from the abdominal aorta) of right lower lobe; and partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection from the right lung, most commonly into the inferior vena cava or occasionally into the right atrium, portal vein, azygos vein, or a hepatic vein. All four components need not be present to make the diagnosis. The name scimitar syndrome arises from the anomalous pulmonary vein, which can have the appearance of a scimitar, a curved Turkish sword.
Associated Anomalies
Associated findings include hypoplastic right bronchus or other abnormalities of the tracheobronchial tree and cardiac anomalies such as atrial septal defect. The partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection in scimitar syndrome is a left-to-right shunt at the atrial level, with physiology similar to an atrial septal defect. The severity of the shunt has a substantial effect on the clinical course.
Imaging
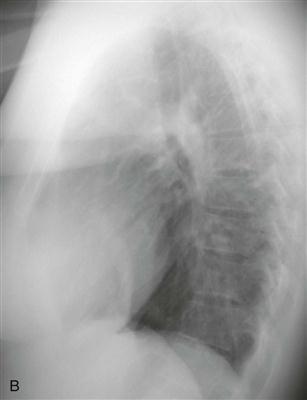
Chest radiography (Figs. A and B), echocardiography, and cineangiography have been used to establish the diagnosis. In recent years, MRI has been used as a noninvasive means of diagnosis. Gadolinium-enhanced MRA can be used to demonstrate the anomalous venous drainage, the hypoplastic ipsilateral pulmonary artery, and the systemic arterial supply to the right lung base (Fig. C). Velocity-encoded phase contrast cine MRI can be used to assess cardiac function in scimitar syndrome by quantifying the degree of left-to-right shunting and by differentiating left and right pulmonary arterial blood flow.