CASE 60
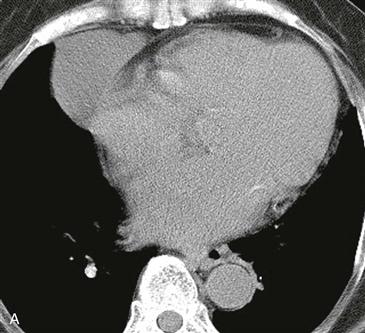
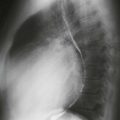
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis based on Fig. A, in which the mass measures 35 HU? (Choose all that apply.)
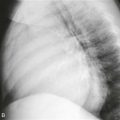
A. Fat pad
C. Metastasis
D. Lymphoma
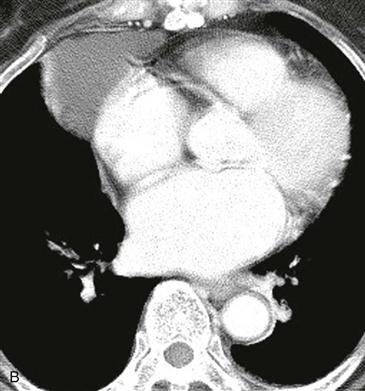
2. What is the most likely diagnosis based on Figs. A and B? The mass measures 35 HU in Fig. A and 36 HU in Fig. B.
A. Fat pad
C. Metastasis
D. Lymphoma
3. What is the most common presentation of a pericardial cyst?
A. Asymptomatic
B. Pain
D. Fever
4. What is the most appropriate management of this mass?
A. No treatment
B. Chemotherapy
D. Surgery
ANSWERS
References
Kim JS, Kim HH, Yoon Y. Imaging of pericardial diseases. Clin Radiol. 2007;62(7):626–631.
Wang ZJ, Reddy GP, Gotway MB, et al. CT and MR imaging of pericardial disease. Radiographics. 2003;23(Spec No):S167–S180.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 78–79.
Comment
Etiology and Pathology
A pericardial cyst is a benign developmental lesion that is formed when a portion of the embryonic pericardium is pinched off and isolated. It has a thin wall, contains clear fluid, and is well circumscribed. The two most common locations are the right and left cardiophrenic angles. When a pericardial cyst is located in another area of the mediastinum, it can be difficult to differentiate from a bronchogenic, esophageal duplication, neuroenteric, or thymic cyst. Pericardial cysts are usually homogeneous and well circumscribed. Often they contain simple fluid, but they can contain complex hemorrhagic or proteinaceous fluid.
Imaging Features and Diagnosis
On CT and MRI, pericardial cysts are round or ovoid and are contiguous with the normal pericardium. CT shows a well-circumscribed mass (Figs. A and B). The density may be in the range of simple fluid, in which case the diagnosis is straightforward. If the density is higher, non-contrast and contrast-enhanced CT scans can be performed to assess for enhancement (Figs. A and B). Pericardial cysts do not enhance, in contrast to neoplasms. Alternatively, MRI can be performed. On MRI, these lesions typically exhibit signal characteristics consistent with simple cysts found elsewhere in the body. They appear as low to intermediate signal masses on T1-weighted images (Fig. B) and high signal intensity lesions on T2-weighted images.