Extubation/Decannulation (Assist)
Extubation/Decannulation (Assist)
PREREQUISITE NURSING KNOWLEDGE
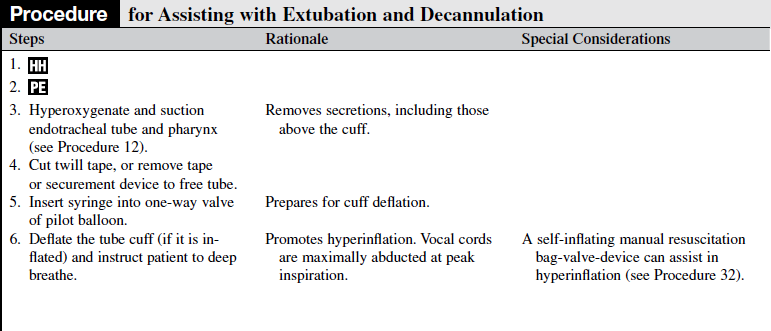
• Extubation refers to removal of an endotracheal tube, and decannulation refers to removal of a tracheostomy tube.
• Indications for extubation and decannulation include the following3–5:
v. The underlying condition that led to the need for an artificial airway is reversed or improved.
v. Hemodynamic stability is achieved, with no new reasons for continued artificial airway support.
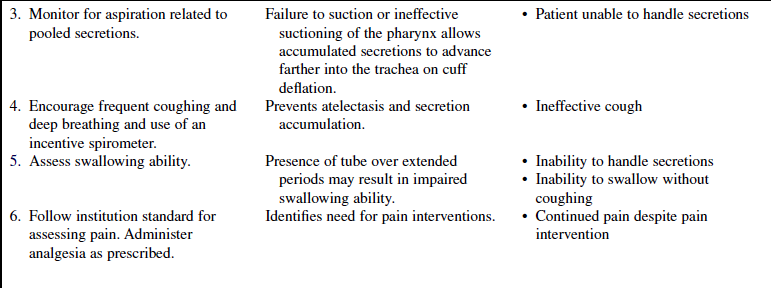
v. The patient is able to effectively clear pulmonary secretions.
v. Airway problems have resolved; minimal risk for aspiration exists.
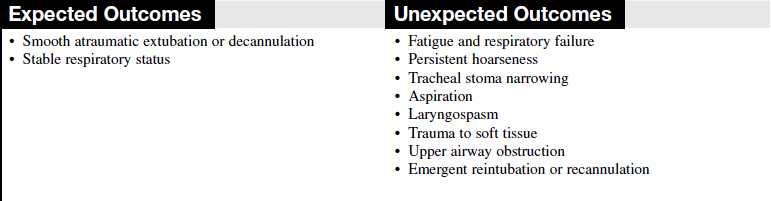
• Most extubations or decannulations are planned. Planning allows for preparation of the patient physically and emotionally and decreases the likelihood of reintubation and hypoxic sequelae. Unintentional or unplanned extubation complicates a patient’s overall recovery.1
• Extubation may occur in a rapid fashion when the previous indications are met, whereas decannulation generally occurs in a stepwise fashion. A patient with a tracheostomy tube may be weaned gradually from the tracheostomy tube, possibly with a combination of techniques, including downsizing the tube diameter, using tubes and inner cannulas with fenestrations, and capping the tracheostomy. The tracheostomy tube is removed when the patient is able to breathe comfortably, maintain adequate ventilation and oxygenation, and manage secretions, through the normal anatomic airway.
EQUIPMENT
• Personal protective equipment
• Sterile suction catheter or suction kit
• Self-inflating manual resuscitation bag-valve-device connected to 100% oxygen source
• Supplemental oxygen with aerosol
Additional equipment, to have available as needed, includes the following:
PATIENT AND FAMILY EDUCATION
• Explain the procedure and the reason the endotracheal tube or tracheostomy tube is no longer needed.  Rationale: This process identifies patient and family knowledge deficits concerning the patient’s condition, procedure, and expected benefits and allows time for questions to clarify information and voice concerns. Explanations decrease patient anxiety and enhance cooperation.
Rationale: This process identifies patient and family knowledge deficits concerning the patient’s condition, procedure, and expected benefits and allows time for questions to clarify information and voice concerns. Explanations decrease patient anxiety and enhance cooperation.
• Explain the purpose and necessity of extubation or decannulation.  Rationale: Communication and explanation for therapy encourage cooperation and minimize anxiety.
Rationale: Communication and explanation for therapy encourage cooperation and minimize anxiety.
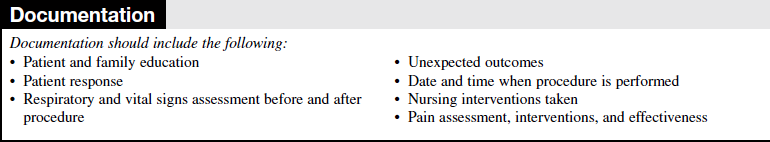
• Discuss the suctioning process and the importance of coughing and deep breathing.  Rationale: Understanding therapy encourages cooperation with the follow-up procedures necessary to maintain a patent airway.
Rationale: Understanding therapy encourages cooperation with the follow-up procedures necessary to maintain a patent airway.
• Explain that the patient’s voice may be hoarse after extubation or decannulation. With removal of a tracheostomy tube, occlusion of the stoma may be necessary to facilitate normal speech and coughing.  Rationale: Knowledge minimizes patient and family fear and anxiety.
Rationale: Knowledge minimizes patient and family fear and anxiety.
• Explain that the patient may need continued oxygen or humidification support.  Rationale: Many patients continue to need oxygen support for some time after extubation. Continued humidification often helps to decrease hoarseness and liquefies secretions.
Rationale: Many patients continue to need oxygen support for some time after extubation. Continued humidification often helps to decrease hoarseness and liquefies secretions.
PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND PREPARATION
Patient Assessment
• Desired level of consciousness has been achieved (in most cases, the patient is awake and able to follow commands).5
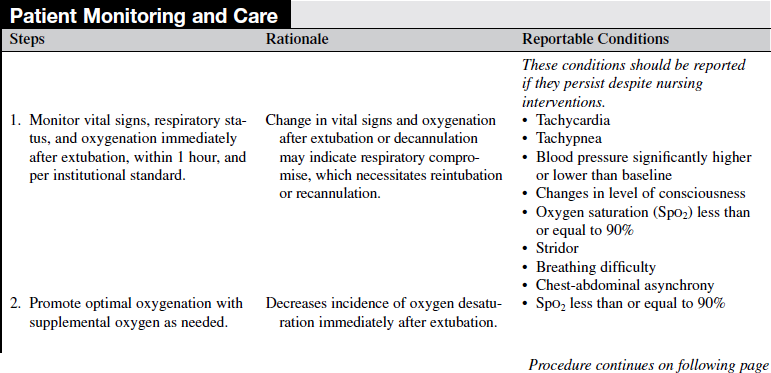
• Assess the stability of the patient’s respiratory status2,4,5:
• Stable respiratory rate of less than 25 breaths/min
• Absence of accessory muscle use
• Negative inspiratory pressure less than or equal to ?20 cm H2O
• Positive expiratory pressure greater than or equal to +30 cm H2O
• Spontaneous tidal volume greater than or equal to 5 mL/kg
• Vital capacity greater than or equal to 10 to 15 mL/kg
• Minute ventilation greater than or equal to 10 L/min
• Fraction of inspired oxygen less than or equal to 50%
• Stable pulse and blood pressure and absence of serious cardiac dysrhythmias  Rationale: Evaluation of the patient’s respiratory status identifies that intubation is no longer necessary. Signs and symptoms associated with independent breathing are as follows.2,4,5
Rationale: Evaluation of the patient’s respiratory status identifies that intubation is no longer necessary. Signs and symptoms associated with independent breathing are as follows.2,4,5
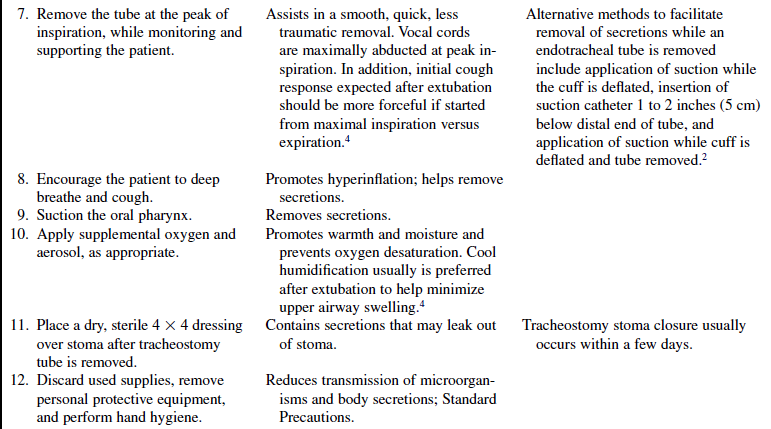
• Assess the patient’s ability to cough.  Rationale: The ability to cough and clear secretions is important for successful airway management after extubation.
Rationale: The ability to cough and clear secretions is important for successful airway management after extubation.
Patient Preparation
• Verify correct patient with two identifiers.  Rationale: Prior to performing a procedure, the nurse should ensure the correct identification of the patient for the intended intervention.
Rationale: Prior to performing a procedure, the nurse should ensure the correct identification of the patient for the intended intervention.
• Ensure that the patient understands preprocedural teachings. Answer questions as they arise, and reinforce information as needed.  Rationale: This process evaluates and reinforces understanding of previously taught information.
Rationale: This process evaluates and reinforces understanding of previously taught information.
• Place the patient in a semi-Fowler’s position.  Rationale: Respiratory muscles are more effective in an upright position versus a supine position. This position facilitates coughing and minimizes the risk of vomiting and consequent aspiration.
Rationale: Respiratory muscles are more effective in an upright position versus a supine position. This position facilitates coughing and minimizes the risk of vomiting and consequent aspiration.
References
![]() 1. O’Meade, M, Guyatt, G, Cook, D, Weaning from mechanical ventilation. the evidence from clinical research. Respir Care 2001; 12:78–83.
1. O’Meade, M, Guyatt, G, Cook, D, Weaning from mechanical ventilation. the evidence from clinical research. Respir Care 2001; 12:78–83.
2. Pierce, L, Airway maintenance. In Management of the mechanically ventilated patient. ed 2. Saunders, St Louis, 2007.
3. Scales, K, Pilsworth, J. A practical guide to extubation. Nurs Stand. 2007; 22(2):44–48.
4. St John, RE, Seckel, MA, Airway managementBurns SM, ed.. AACN protocols for practice . care of mechanically ventilated patients. ed 2. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Sudbury, MA, 2007:1–57.
![]() 5. Twibel, R, Siela, D, Mahmoodi, M. Subjective perceptions in physiological variables during weaning from mechanical ventilation. Am J Crit Care. 2003; 12:12–101.
5. Twibel, R, Siela, D, Mahmoodi, M. Subjective perceptions in physiological variables during weaning from mechanical ventilation. Am J Crit Care. 2003; 12:12–101.
American Association for Respiratory Care, Clinical practice guideline. removal of the endotracheal tube. Respir Care. 2007; 52(1):81–93.
Burns, SM, Weaning from mechanical ventilationBurns SM, ed.. AACN protocols for practice. care of mechanically ventilated patients. ed 2. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Sudbury, MA, 2007:97–160.
Ead, H, Post anesthesia tracheal extubation . CACCN. 2004; 15(3):20–25.
Henneman, E. Liberating patients from mechanical ventilation. a team approach. Crit Care Nurse 2001; 21:25–33.