Diuretics
ACTIONS
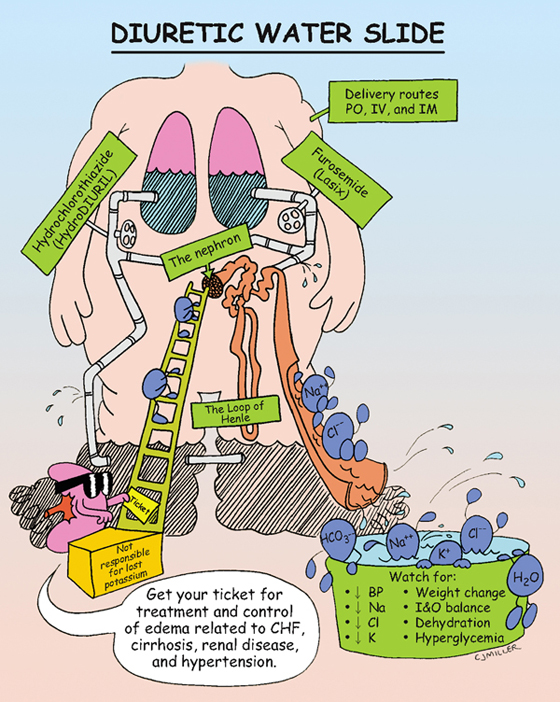
Loop diuretics inhibit sodium (Na) and chloride (Cl) reabsorption through direct action primarily in the ascending loop of Henle but also in the proximal and distal tubules. Thiazide diuretics act primarily on the distal tubules, inhibiting Na and Cl reabsorption.
USES
• To treat edema that involves fluid volume excess resulting from a number of disorders of the heart, liver, or kidney
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Severe adrenocortical impairment
PRECAUTIONS
• Fluid and electrolyte depletion, gout
SIDE EFFECTS
• **Dehydration, hyponatremia, hypochloremia, hypokalemia**
• **Unusual tiredness, weakness,** dizziness
• Irregular heart beat, weak pulse, **orthostatic hypotension**
• Tinnitus, **hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia,** hearing loss (Lasix)
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Monitor for adequate intake and output and potassium loss.*
2. *Monitor patient’s weight and vital signs.*
3. *Monitor for signs and symptoms of hearing loss, which may last from 1 to 24 hours.*
4. ‡Teach patient to take medication early in the day to decrease nocturia.‡
5. ‡Teach patient to report any hearing loss or signs of gout.‡
Spironolactone (Aldactone)
CLASSIFICATION
Potassium-sparing diuretic
ACTIONS
Has a direct effect on the distal tubules in the kidney. Competes with aldosterone for cell-receptor sites in the distal tubules while inducing urinary excretion of sodium and reducing excretion of potassium and hydrogen ions.
USES
• Treats hypertension and edema.
• Reduces edema in patients with severe heart failure.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Hypersensitivity or renal failure
PRECAUTIONS
SIDE EFFECTS
• **Hyperkalemia,** hyponatremia
• Hyperglycemia, hirsutism, menstrual irregularities, gynecomastia
• Impotence, deepening of voice
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Monitor intake and output,* and †watch for cardiac dysrhythmias.†
2. *Monitor levels of electrolytes (e.g., potassium, sodium).*
3. Teach patient to report cramps, weakness, fatigue, or nausea.
4. ‡Teach patient to restrict intake of potassium-rich foods (e.g., nuts, dried fruits, spinach, citrus fruits, bananas).‡
5. ‡Teach patient to take medication with or after meals if gastrointestinal (GI) upset occurs.‡
6. ‡Have patient notify health care provider if menstrual irregularities, gynecomastia, or impotence occurs.‡