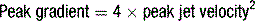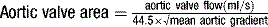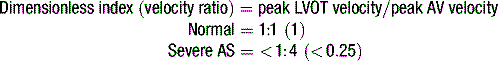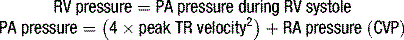TOPIC 6 Cardiac valvular structure and function
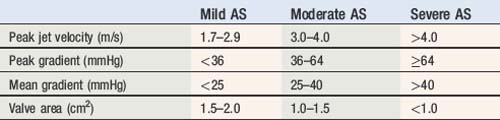
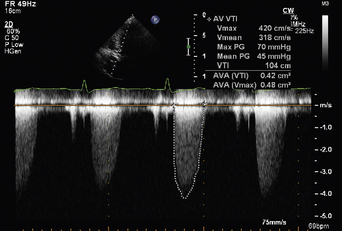
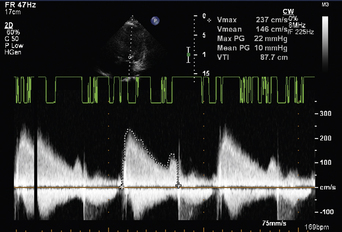
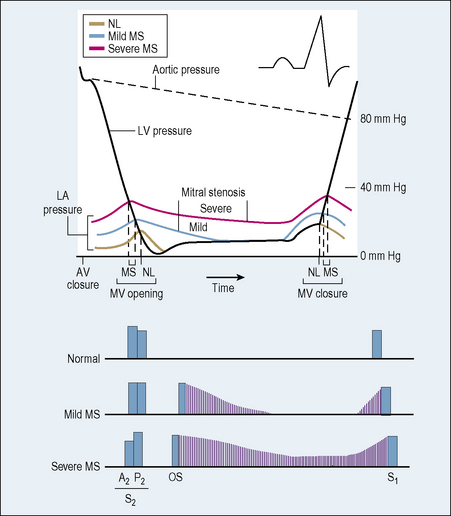
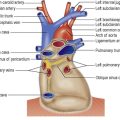
Aortic stenosis
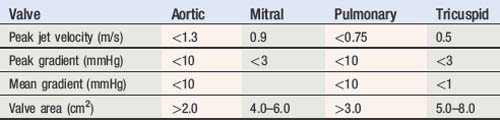
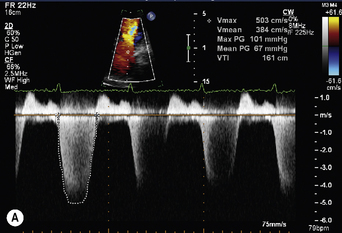
index) is suggestive of significant aortic stenosis, and dobutamine stress echocardiography is indicated.
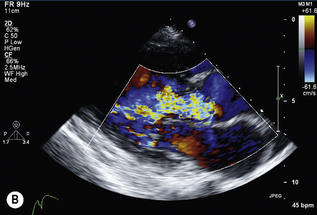
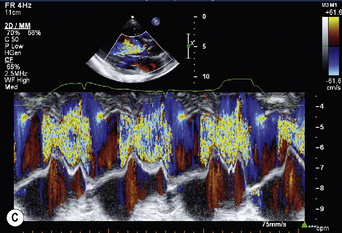
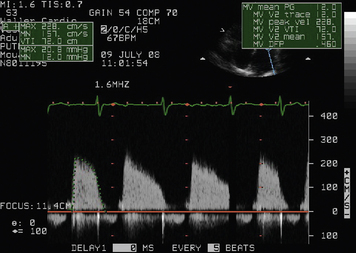
Pulmonary stenosis
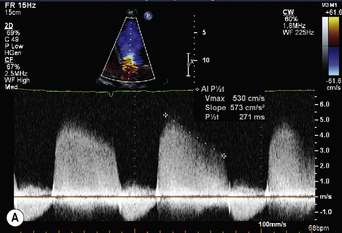
PS is diagnosed when peak jet velocity is >3 m/s, corresponding to a peak PV gradient of 36 mmHg.
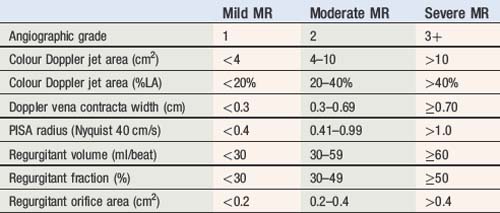
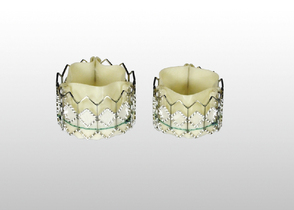
Prosthetic heart valves
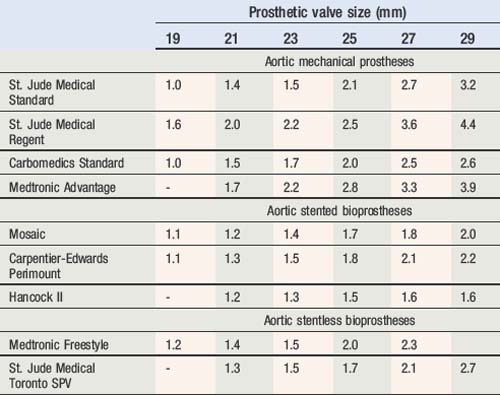
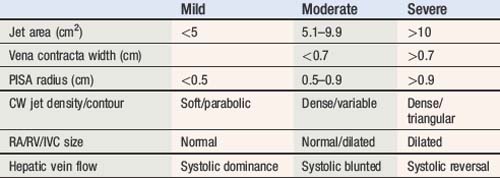
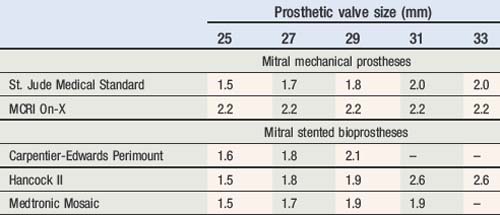
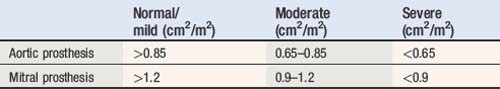
Normal reference values of EOAs are presented in Table 6.8 for aortic valve prostheses, and in Table 6.9 for mitral valve prostheses. Threshold for prosthetic valve ? patient mismatched sizing are presented in Table 6.10.
Table 6.8 Effective orifice area values for the different sizes of commonly used aortic valve prostheses