CASE 58
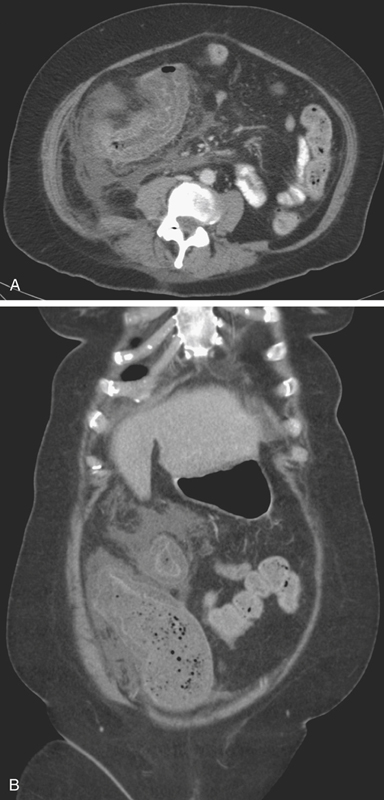
History: An immunocompromised 26-year-old woman presents with pain, rectal bleeding, and diarrhea.
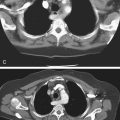
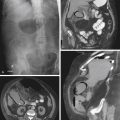
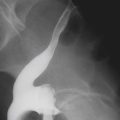
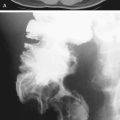
1. Which of the following should be included in the differential diagnosis of the imaging finding shown in figure A? (Choose all that apply.)
2. Which of the following symptoms suggest that diarrhea occurring in a patient with AIDS is due to colitis?
A. Watery, large-volume diarrhea
B. Tenesmus, dyschezia, and urgency
C. Frequent, small-volume, painful stools
D. Bloating, nausea, and epigastric cramps
3. Which of the following statements regarding diarrhea in a patient with AIDS is false?
A. Cytomegalovirus is the most common viral colitis.
B. Cytomegalovirus colitis typically causes large, deep ulceration.
C. Viral infections of the gastrointestinal tract tend to affect the small bowel.
4. When a patient with AIDS presents with diarrhea, what diagnostic study should be performed after history, examination, and routine blood tests?
ANSWERS
CASE 58
AIDS Colitis
1. B, C, D, and E
2. C
3. C
4. A
Reference
Glick S. Other inflammatory conditions of the colon. In: Gore RM, Levine MS, eds. Textbook of Gastrointestinal Radiology. 2nd ed Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2000:993–1008.
Cross-Reference
Gastrointestinal Imaging: THE REQUISITES, 3rd ed, p 297.
Comment
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) colitis is a type of colitis seen in AIDS patients and other immunocompromised patients. Both CT and barium studies can be quite helpful and suggestive. The discovery of large ulcers has been associated with CMV infection in AIDS patients. Ultimately the diagnosis is usually made when the virus is isolated in tissue specimens. Although CMV is probably the most common viral colonic infection seen today, other opportunistic infections are also seen, including Cryptosporidium infection and pseudomembranous colitis, both of which are more common in AIDS patients. Bacterial colitis must be included in the diagnosis; Campylobacter and even tuberculosis must be considered, although tuberculosis tends to affect the ileocecal area, as it would in patients without an impaired immune system.