CHAPTER 55 The Burned Patient
2 What are the three main factors that correlate with increased mortality with burn injury?
Advanced age, burn size, and presence of inhalation injury correlate with increased mortality.
4 How are burns classified?
The severity of the burn is graded by its depth, which depends on the extent of tissue destruction.
 Superficial burns involve the upper layers of the epidermis; the skin is painful and appears red and slightly edematous, much like a sunburn.
Superficial burns involve the upper layers of the epidermis; the skin is painful and appears red and slightly edematous, much like a sunburn. Superficial partial-thickness burns occur when tissue damage extends into the superficial layer of the dermis, which is still lined with intact epithelium that proliferates and regenerates new skin. These burns develop blisters and have red or whitish areas that are very painful.
Superficial partial-thickness burns occur when tissue damage extends into the superficial layer of the dermis, which is still lined with intact epithelium that proliferates and regenerates new skin. These burns develop blisters and have red or whitish areas that are very painful. Deep partial-thickness burns extend downward into the deeper layer of the dermis. Edema is marked, and sensation is altered.
Deep partial-thickness burns extend downward into the deeper layer of the dermis. Edema is marked, and sensation is altered. Full-thickness and subdermal burns affect every body system and organ. A full-thickness burn extends through the epidermis and dermis and into the subcutaneous tissue layer. A subdermal burn damages muscle, bone, and interstitial tissue. Some centers are now using laser Doppler imaging to better determine burn depth.
Full-thickness and subdermal burns affect every body system and organ. A full-thickness burn extends through the epidermis and dermis and into the subcutaneous tissue layer. A subdermal burn damages muscle, bone, and interstitial tissue. Some centers are now using laser Doppler imaging to better determine burn depth.20 How do you calculate the percent of total body surface burned?
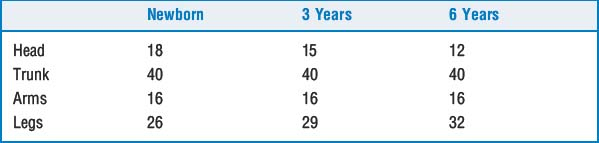
The severity of a burn injury is based on the amount of surface area covered in deep partial-thickness, full-thickness, and subdermal burns. The rule of nines method allows reasonable estimation (Table 55-1). Because of the difference in body habitus (particularly head and neck), the rule of nines must be altered in children (Table 55-2).
| Head and neck | 9% |
| Upper extremities | 9% each |
| Chest (anterior and posterior) | 9% each |
| Abdomen | 9% |
| Lower back | 9% |
| Lower extremities | 18% |
| Perineum | 1% |
21 Early surgical burn wound intervention has recently been shown to be one of the major reasons for the improved outcome in burn patients. What are the four categories of operations that are common for the burn-injured patient?
28 What induction drugs are good for burn patients?
KEY POINTS: The Burned Patient 
1. Cone J.B. What’s new in general surgery: burns and metabolism. J Am Coll Surg. 2005;200:607-615.
2. Johnson A. Hyperbaric oxygen for carbon monoxide poisoning: a systematic review and critical analysis of the evidence. Toxicol Rev. 2005;24:75-92.
3. Klein M.B., Hayden D., Elson C., et al. The association between fluid administration and outcome following major burn: a multicenter study. Ann Surg. 2007;245:622-628.
4. Pham T.N., Cancio L.C., Gibran N.S. American Burn Association practice guidelines for burn shock resuscitation. J Burn Care Res. 2008;29:257-266.