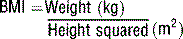CHAPTER 51 Obesity and Sleep Apnea
1 Define obesity
Obesity is defined using the body mass index (BMI) (Table 51-1).
| BMI | |
|---|---|
| 18.5–25 | Normal range |
| 26–30 | Overweight |
| 31–35 | Class I obesity |
| 36–40 | Class II obesity |
| 41+ | Morbid obesity |
BMI, Body mass index.
3 Review some pulmonary and respiratory considerations in the obese patient
Obesity is typically associated with hypoxemia, the mechanisms of which include:
 Increased work of breathing. Because of an increased chest wall mass, decreased chest wall compliance, and abdominal cavity adipose tissue decreasing diaphragmatic excursion, work of breathing is two to four times greater than normal.
Increased work of breathing. Because of an increased chest wall mass, decreased chest wall compliance, and abdominal cavity adipose tissue decreasing diaphragmatic excursion, work of breathing is two to four times greater than normal.5 Discuss the pharmacokinetic changes found in the obese patient
Loading doses of most intravenous agents are based on volume of distribution; maintenance dosing is based on clearance. In obese patients the volume of distribution is usually increased, but clearance approaches normal or is increased compared to a lean patient (Table 51-2).
| Drugs | Dosing Strategy |
|---|---|
| Fentanyl | Loading dose based on TBW; decrease maintenance |
| Sufentanil | Loading dose based on TBW; decrease maintenance |
| Remifentanil | Dose based on IBW |
| Succinylcholine | Dose based on TBW |
| Atracurium | Dose using TBW |
| Vecuronium | Dose using IBW |
| Rocuronium | Dose using IBW |
| Propofol | Loading dose and maintenance based on TBW |
| Thiopental | Reduce loading dose |
| Midazolam | Loading dose based on TBW; adjust maintenance to IBW |
IBW, Ideal body weight; TBW, total body weight.
6 Discuss the appropriate preoperative assessment of this population
See Chapters 8 and 17 for important historical information and airway concerns. As far as laboratory testing is concerned:
 An electrocardiogram should be obtained for all obese patients to evaluate for atrial or ventricular enlargement, arrhythmias, and ischemia. Ventricular arrhythmias are common. Further cardiac testing such as exercise stress tests or chemically induced stress testing may be required. Echocardiography can be used to assess cardiac function and presence of pulmonary hypertension.
An electrocardiogram should be obtained for all obese patients to evaluate for atrial or ventricular enlargement, arrhythmias, and ischemia. Ventricular arrhythmias are common. Further cardiac testing such as exercise stress tests or chemically induced stress testing may be required. Echocardiography can be used to assess cardiac function and presence of pulmonary hypertension. Chest radiographs may not be generally useful unless the history suggests additional information may be gleaned.
Chest radiographs may not be generally useful unless the history suggests additional information may be gleaned. Laboratory analysis should include a complete blood count, electrolytes, blood sugar, blood urea nitrogen, and creatinine. Elevated bicarbonate suggests carbon dioxide retention. Hypokalemia may occur with chronic use of diuretics. A room air arterial blood gas analysis will identify hypoxemia, hypercarbia, and metabolic compensation.
Laboratory analysis should include a complete blood count, electrolytes, blood sugar, blood urea nitrogen, and creatinine. Elevated bicarbonate suggests carbon dioxide retention. Hypokalemia may occur with chronic use of diuretics. A room air arterial blood gas analysis will identify hypoxemia, hypercarbia, and metabolic compensation.10 What extubation criteria would you use for the obese patient?
The patient must be hemodynamically stable. Muscle relaxants should be adequately reversed and verified by peripheral nerve stimulator findings (sustained tetanus and with no post-tetanic facilitation of twitches). The patient should be awake, alert, and able to sustain a head lift for 5 seconds (Table 51-3).
| Respiratory rate | <30 Breaths/min |
| Maximal inspiratory force | −25 to −30 cm H2O |
| Vital capacity | 10–15 ml/kg |
| Tidal volume | 5 ml/kg (lean body weight) |
16 Is bariatric surgery used in the pediatric population?
KEY POINTS: Obesity and Sleep Apnea 
1. American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force. Practice guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Anesthesiology. 2006;104:1081-1093.
2. Brodsky J.B., Lemmens H.J. Regional anesthesia and obesity. Obes Surg. 2007;17:1146-1149.
3. Chung F., Yegneswaran B., Liao P., et al. STOP questionnaire: a tool to screen patients for obstructive sleep apnea. Anesthesiology. 2008;108:812-821.
4. Chung F., Yegneswaran B., Liao Pu, et al. Validation of the Berlin questionnaire and American Society of Anesthesiologists checklist as screening tools for obstructive sleep apnea in surgical patients. Anesthesiology. 2008;108:822-830.
5. Haque A.K., Gadre S., Taylor J., et al. Pulmonary and cardiovascular complications of obesity: an autopsy study of 76 obese subjects. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008;132:1397-1404.
6. Setzer N., Saade E. Childhood obesity and anesthetic morbidity. Paediatr Anaesth. 2007;17:321-326.
7. Soens M.A., Birnbach D.J., Ranasinghe J.S., et al. Obstetric anesthesia for the obese and morbidly obese patient: an ounce of prevention is worth more than a pound of treatment. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008;52:6-19.