TOPIC 5 Peripheral nervous system
Neuromuscular block monitor
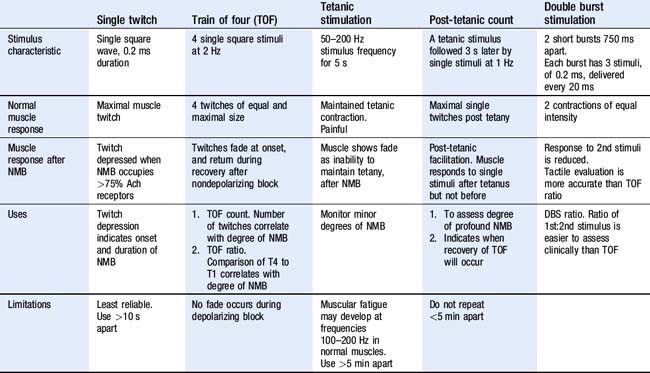
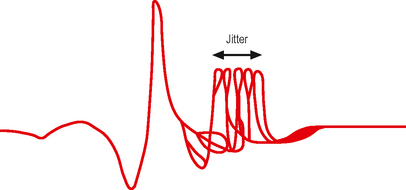
Test: Train of four (TOF) stimulation
How it is done
• Application of a supramaximal stimulus to a peripheral nerve, followed by measurement of the associated muscular response.
• The nerve stimulator device should generate a monophasic square wave constant current up to 80 mA, and last between 0.1 and 0.5 ms.
• The nerve chosen must be close to the skin, have a motor element and muscular contraction must be visible or accessible to monitoring.
• The negative electrode should be placed directly over the superficial part of the nerve and positive electrode placed proximally to avoid direct muscular stimulation.
• The generation of single, train of four, double burst and 50-Hz patterns of stimulation is necessary. Polarity of output should be marked, and battery powered for safety.
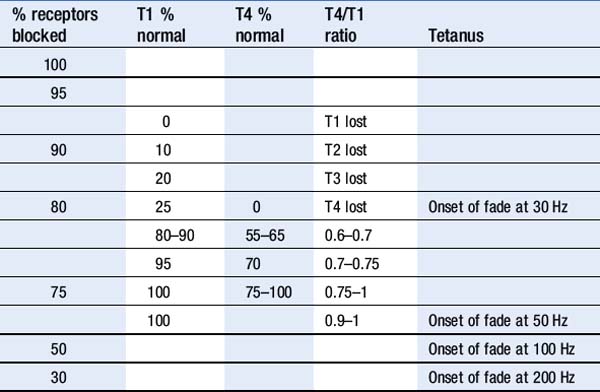
Interpretation
Management principles
• The most accurate muscle to monitor during NMB onset and maintenance is the orbiclaris oculi as it will reflect the conditions of the central larynx and diaphragm muscles.
• It is best to monitor a peripheral muscle such as adductor pollicis during reversal as it has a longer recovery time than respiratory muscles and will provide a greater margin of safety.
Limitations and complications
• Visual and tactile evaluation of muscular contractile response is unreliable. More accurate methods include mechanomyography (MMG), electromyography (EMG) and accelerometry (AMG) but they remain research tools.
• When monitoring is not performed up to 45% of patients are inadequately reversed on arrival to recovery room.
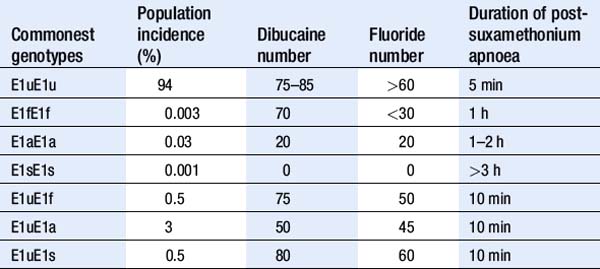
Investigation of suxamethonium apnoea
| Genetic variants | Acquired causes |
|---|---|
| Atypical A | Pregnancy |
| Fluoride resistant F | Liver disease |
| Silent S | Carcinomatosis |
| H (10% reduced concentration) | Cardiac failure |
| J (33% reduced concentration) | Uraemia |
| K (66% reduced concentration) | Myxoedema |
| Burns | |
| Poor nutrition | |
| Drugs: procaine, lithium, magnesium, ketamine, OCP, ecothiopate, tacrine |
OCP, Oral Contraceptive Pill
Test: Dibucaine and fluoride number
Test: Molecular genetic testing
• The gene that codes for the ChE enzyme is located at the E1 locus on the long arm of chromosome 3.
• More than 20 mutations have been identified in the plasma cholinesterase gene. They include: normal plasma ChE (u); atypical hydrolyzing activity (a), fluoride resistant (f), silent (s).
Myasthenia gravis (MG) testing
Indications
Test: Edrophonium (tensilon) test
• The tensilon (edrophonium) test can be performed at the bedside, but is neither sensitive nor specific for MG. It should only be performed when the diagnosis is required urgently. Full cardiac monitoring and atropine is required in case of cardiovascular side effects. Initially 2 mg (max 10 mg) edrophonium is administered IV.
Test: Serum anti-acetylcholinesterase receptor antibody test
Test: Repetitive nerve stimulation (RNS)
Peripheral motor and nerve function assessment
Test: Nerve conduction studies and electromyography (EMG)
To evaluate the integrity and function of the peripheral nervous system.
Indications
Diagnosis and assessment of the following:
• Neuropathy – metabolic (diabetes mellitus, uraemia, hypothyroid, hepatic, HIV immune causes, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus), traumatic, entrapment, idiopathic mononeuropathies, clinical suspicion of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), inflammatory (e.g. post polio, Guillain Barré syndrome), hereditary (e.g. Charcot Marie Tooth)
How it is done
• The selected nerve is stimulated using a current that will excite all the axons in the nerve trunk. The electric output is a rectangular wave, duration 0.1–0.2 ms. Needle electrodes may be required when stimulating a deep nerve. Stimulation should be performed at two or more sites along the nerve.
Interpretation
• Latency. The time between stimulus and response includes nerve conduction time and neuromuscular transmission time.
Abnormalities
• In normal muscle no electrical activity occurs at rest, motor neurons discharge on voluntary contraction, and responses can be recorded. (MUAP).
Management principles
Limitations and complications
• Absence of a sensory nerve AP may be due to Na channel dysfunction, not necessarily peripheral nerve degeneration.