CHAPTER 49 Diabetes Mellitus
1 Describe the principal types of diabetes mellitus
 Type 1 diabetes mellitus: An autoimmune disorder in which destruction of the pancreatic islet cells results in the inability to produce insulin. Onset is more common in children and young adults.
Type 1 diabetes mellitus: An autoimmune disorder in which destruction of the pancreatic islet cells results in the inability to produce insulin. Onset is more common in children and young adults. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A disorder in the body’s ability to use insulin. Early in the course of the disease the patient may be able to make sufficient insulin, but cell-receptor impairment results in hyperglycemia despite normal or high insulin levels. Type 2 diabetes is usually a disease of older adults; onset in the sixth decade and beyond is common. As obesity increases in the population type 2 diabetes also increases. Type 2 diabetes is now commonly seen in adolescents and young adults with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A disorder in the body’s ability to use insulin. Early in the course of the disease the patient may be able to make sufficient insulin, but cell-receptor impairment results in hyperglycemia despite normal or high insulin levels. Type 2 diabetes is usually a disease of older adults; onset in the sixth decade and beyond is common. As obesity increases in the population type 2 diabetes also increases. Type 2 diabetes is now commonly seen in adolescents and young adults with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle.3 What comorbidities are frequently observed in patients with diabetes mellitus and to what significance?
 Hypertension is seen in 40% of patients with poorly controlled diabetes who undergo surgery. Hypertension is a risk factor for coronary artery disease and cardiac failure. If these patients are treated with potassium-wasting diuretic agents, there is often significant total body loss of potassium.
Hypertension is seen in 40% of patients with poorly controlled diabetes who undergo surgery. Hypertension is a risk factor for coronary artery disease and cardiac failure. If these patients are treated with potassium-wasting diuretic agents, there is often significant total body loss of potassium. Coronary artery disease is common, occurs in younger patients, and may be silent or present atypically.
Coronary artery disease is common, occurs in younger patients, and may be silent or present atypically. Autonomic neuropathy may compromise neuroreflexic control of cardiovascular and gastrointestinal function, manifesting as orthostatic hypotension, gastroparesis (increased risk of aspiration), ileus, and urinary retention. Peripheral neuropathies are common.
Autonomic neuropathy may compromise neuroreflexic control of cardiovascular and gastrointestinal function, manifesting as orthostatic hypotension, gastroparesis (increased risk of aspiration), ileus, and urinary retention. Peripheral neuropathies are common.4 What oral medications are currently used in type 2 diabetes?
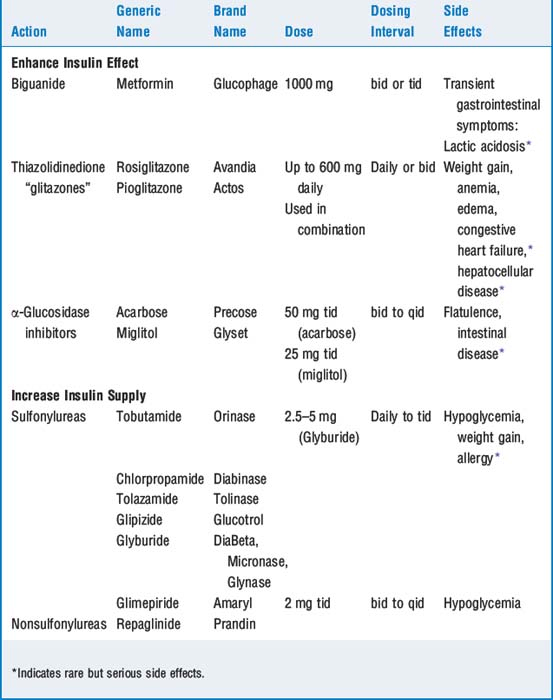
There are two categories of drugs used in treating type 2 diabetes: those that enhance the effectiveness of insulin and those that increase the supply of insulin to the cells. These drugs are outlined in Table 49-1.
5 What insulins are in current use?
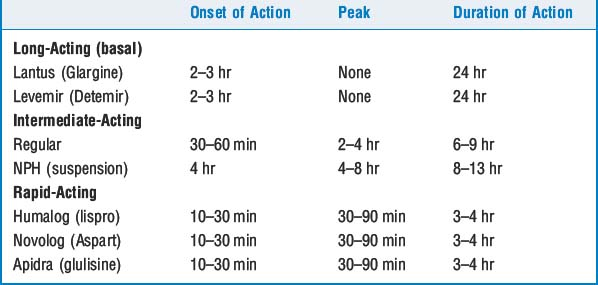
Modern intensive insulin therapy relies on newly designed insulin analogs. Insulin therapy is given using a basal-bolus construct: long-acting (24-hour) insulin is used to provide a steady basal platform, and rapid-acting insulin is used to provide boluses for carbohydrate intake in meals and snacks. This necessitates giving at least four injections per day or the use of an insulin pump. The specific insulins are outlined in Table 49-1.
6 Is there an advantage to the use of insulins that are in solution as opposed to insulin that is in a suspension?
9 What are the complications of hyperglycemia in the perioperative setting?
11 What is the significance of autonomic neuropathy? How can it be assessed?
 An intact sympathetic nervous system can be assessed by the following: A normal response in diastolic pressure (from lying to standing) is a change of at least 16 mm Hg; an affected patient has a response of <10 mm Hg. Autonomic neuropathy is also evidenced by a large change in systolic blood pressure when changing from lying to standing posture. A normal decrease is <10 mm Hg; an affected patient has a decrease of at least 30 mm Hg.
An intact sympathetic nervous system can be assessed by the following: A normal response in diastolic pressure (from lying to standing) is a change of at least 16 mm Hg; an affected patient has a response of <10 mm Hg. Autonomic neuropathy is also evidenced by a large change in systolic blood pressure when changing from lying to standing posture. A normal decrease is <10 mm Hg; an affected patient has a decrease of at least 30 mm Hg. An intact parasympathetic nervous system can be assessed by observing heart rate response to breathing. Normal patients increase heart rate by at least 15 beats/min. Affected patients have an increase of 10 or fewer beats/min. Finally, concurrent with electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring, the R-R ratio can be measured during a Valsalva maneuver. A normal ratio is >1.2; an abnormal response is <1.1.
An intact parasympathetic nervous system can be assessed by observing heart rate response to breathing. Normal patients increase heart rate by at least 15 beats/min. Affected patients have an increase of 10 or fewer beats/min. Finally, concurrent with electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring, the R-R ratio can be measured during a Valsalva maneuver. A normal ratio is >1.2; an abnormal response is <1.1.14 How should the patient with diabetes be prepared before surgery? Should all patients with diabetes receive insulin intraoperatively?
20 Describe the management of patients with diabetes requiring urgent surgery
If at all possible, electrolyte and glucose imbalance should be corrected before surgery. Sufficient rehydration, electrolyte replacement, and insulin treatment can be achieved in 4 to 6 hours, improving hyperglycemia, ketosis, and acidosis. Rehydration is initiated with 10 to 20 ml/kg of normal saline (NS). Infuse insulin at 0.1 unit/kg/hr using 0.45 NS (or D10 in 0.45 NS if glucose is <150 mg/dl). Patients in ketoacidosis requiring emergency surgery may receive insulin therapy according to the guidelines in Table 49-2.
21 Are regional anesthetics helpful in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes? Can epinephrine be added to local anesthetic solutions?
22 Is it possible to achieve continuous monitoring of glucose levels in the operating room and in the perioperative period?
Key Points: Diabetes Mellitus 
1. Burant C.F., editor. Medical management of type 2 diabetes. Alexandria: American Diabetes Association. 2004;ed 5:52-59.
2. Davidson M.B. Standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(Suppl):S4-S36.
3. Ferrari L.R. New insulin analogues and insulin delivery devices for the perioperative management of diabetic patients. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2008;21(3):401-405.
4. Fonseca V.A. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2008. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(Suppl):S12-S54.
5. van den Berghe G., Wouters P., Weekers F., et al. Intensive insulin therapy in the critically ill patients. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1359-1367.
6. Wiener R.S., Wiener D.C., Larson R.J. Benefits and risks of tight glucose control in critically ill adults: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2008;300(8):933-944.