CHAPTER 45 Increased Intracranial Pressure and Traumatic Brain Injury
4 Summarize the conditions that commonly cause elevated intracranial pressure
| Increased CSF Volume | Increased Blood Volume | Increased Brain Tissue Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Communicating hydrocephalus | Intracerebral hemorrhage (aneurysm or AVM) | Neoplasm |
| Obstructing hydrocephalus | Epidural or subdural hematoma | Cerebral edema (CVA, encephalopathic, metabolic, traumatic) |
| Malignant hypertension | Cysts |
AVM, Arteriovenous malformation; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; CVA, cerebrovascular accident; ICP, intracranial pressure.
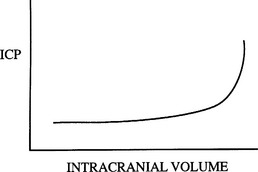
8 What is intracranial elastance? Why is it clinically significant?
Intracranial elastance, commonly misnamed intracranial compliance, refers to the variation in ICP in accordance with intracranial volume. Because intracranial components can shift their volumes to an extent (e.g., CSF movement from the intracranial compartment to the spinal compartment), ICP remains somewhat constant over a certain range of volume. However, when compensatory mechanisms are exhausted, ICP rises rapidly with further increases in volume (Figure 45-1).
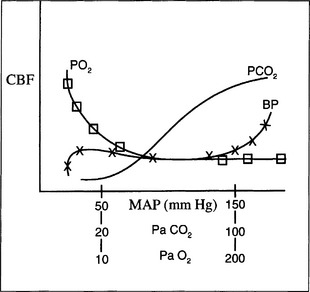
9 How is cerebral blood flow regulated?
CBF is coupled to cerebral metabolic rate by an uncharacterized mechanism but may involve potassium, hydrogen, calcium ions, adenosine, nitric oxide, and prostaglandins. In general, increases in the cerebral metabolic rate for oxygen (CMRO2) lead to increases in CBF, although the increase in flow is delayed by 1 to 2 minutes. Several other parameters influence flow. Specifically an increase in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood (PaCO2) is a powerful cerebral vasodilator, with CBF increasing/decreasing 1 to 2 ml/100g/min with a 1-mm Hg change in PaCO2. Similarly, a decrease in the partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) in arterial blood below 50 mm Hg greatly increases flow. Variations in MAP also may result in large increases or decreases in flow, but over a broad range (50 to 150 mm Hg) flow is nearly constant. This constancy of flow over a range of pressures is known as autoregulation. Chronic hypertension shifts the autoregulation curve to the right. Following a brain injury such as stroke, tumor accompanied by edema, or trauma, autoregulation may be disrupted, and flow becomes pressure dependent (Figure 45-2).
15 Which intravenous fluids are used during surgery to minimize intracranial pressure?
19 If the previously mentioned measures fail to control intracranial pressure, what other measures are available?
20 What are the mechanisms behind traumatic brain injury?
The damage to the brain after traumatic injury can be divided into two categories:
22 In a patient with traumatic head injury, how should fluid resuscitation be prioritized and what fluids are beneficial?
1. Bedell E., DS Prough D.S. Anesthetic management of traumatic injury. Anesthesiol Clin North Am. 2002;20:417-439.
2. Bendo A., et al. Anesthesia for neurosurgery. In: Barash P.G., Cullen B.F., Stoelting R.K., editors. Clinical anesthesia. ed 5. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005:746-789.
3. Moppett I.K. Traumatic brain injury: assessment, resuscitation and early management. Br J Anaesth. 2007;99:18-37.