CASE 45
Mary, a 3-year-old girl, had her spleen removed after a motor vehicle accident, in which both parents died. When she was transferred to the emergency department of a nearby hospital, it became apparent that her spleen had ruptured and the surgeon had no option but to remove it. Mary recovered well from the surgery, but her next of kin, who knows that the spleen is important in immune responses, wants to know how removal of the spleen will affect her immunologically, and so you arrange for a consultation with an immunologist.
QUESTIONS FOR GROUP DISCUSSION
RECOMMENDED APPROACH
Implications/Analysis of Clinical History
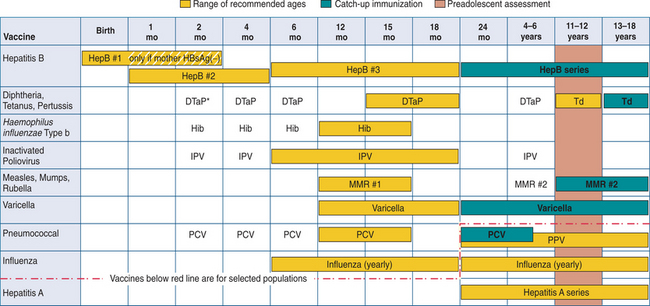
Childhood immunization is important, particularly if we are to maintain what is referred to as herd immunity (protection from spread of disease within a group because most members are immunized). However, in asplenic patients, immunization is recommended for their own protection. Mary’s medical files indicated that she had received most of the recommended pediatric vaccines and boosters. These included vaccines for DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus toxoids, and acellular pertussis), MMR (measles, mumps, rubella), hepatitis, and the inactivated poliovirus (IPV).
ETIOLOGY: STREPTOCOCCAL INFECTIONS AND IMMUNIZATION
Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccines
The major components of the pneumococcal capsules are T cell–independent antigens. As the term implies, these antigens can activate B cells in the absence of cognate interaction with T cells. The predominant antibody isotype produced in response to T cell– independent antigens is IgM. As such the response is not long lasting and memory B cells are not generated. Therefore, protection is not long lasting. The Pneumovax 23 vaccine is a mixture of purified capsular polysaccharides from the 23 most prevalent S. pneumoniae serotypes causing infection in North America. Included in the vaccine are the seven serotypes in the Prevnar vaccine (see later). Protective antibodies are usually detectable 3 to 4 weeks after immunization. This vaccine is recommended for the elderly, the immunocompromised, and children older than the age of 2 who are congenitally asplenic or have had a splenectomy.