CASE 35
History: A 48-year-old woman presents with 5 days of constipation.
1. Which of the following should be included in the differential diagnosis of the dominant imaging finding on figure A? (Choose all that apply.)
2. After reviewing all the provided images, what is the most likely diagnosis?
3. Which statement about ovarian dermoids is true?
A. The usual clinical presentation is with abdominal pain.
B. It is bilateral in 2% to 3% of cases.
C. Malignant degeneration occurs in 1% to 2%, more commonly during pregnancy.
D. Imaging finding of a fat-fluid level on imaging is diagnostic.
E. Malignant transformation should be suspected if the cyst ruptures spontaneously.
4. A variety of tissues have been recognized in ovarian dermoids. Which of the following elements would you not expect to find in ovarian dermoids?
ANSWERS
CASE 35
Pelvic Ovarian Dermoid
1. B, C, D, and E
2. D
3. D
4. C
References
Dill-Macky MJ, Mostafa A. Ovarian sonography. In: Callen PW, ed. Ultrasonography in Obstetrics and Gynecology. 4th ed Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2000:878–880.
Cross-Reference
Genitourinary Radiology: THE REQUISITES, 2nd ed, pp 288-290.
Comment
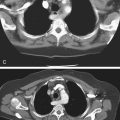
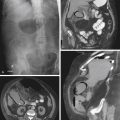
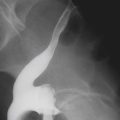
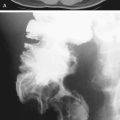
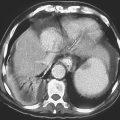
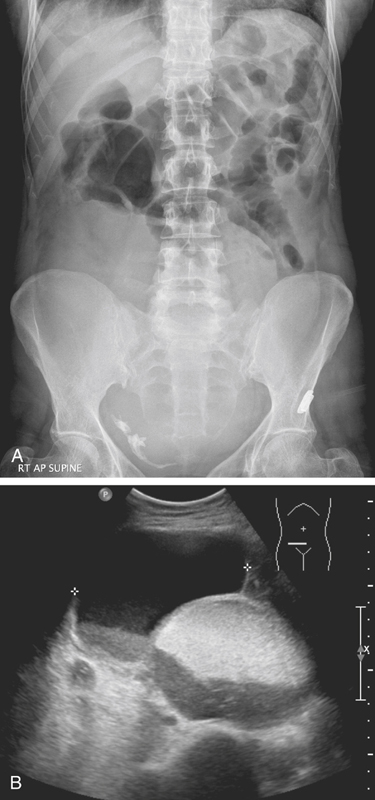
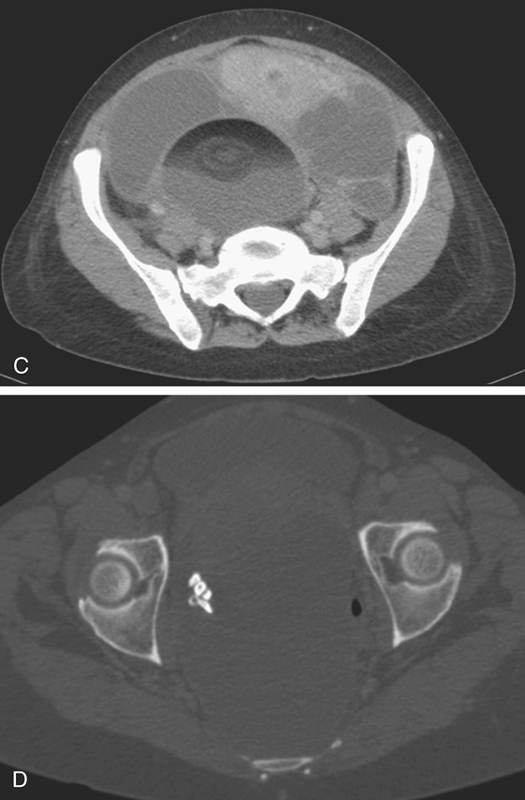
Benign dermoid cysts (also called mature cystic teratomas) are the most common pelvic masses in young women (see figures). They usually produce no symptoms and are bilateral in 10% to 15%, but they cause discomfort in some patients. The reasons are not clear. It might relate to a contiguous position of the lesion or possibly to degrees of torsion. On the other hand, it might also be a sign of possible malignancy. Fatty density is seen in almost 100% of ovarian dermoids along with hair and rudimentary teeth.
CT of the pelvis shows these findings, usually as an incidental finding in most patients (see figures). Extragonadal germ cell tumors, which include dermoid cysts, are not uncommon and are among the important diagnoses in the differential for upper anterior mediastinal masses. Malignant degeneration is rare but increases with the age of the patient. The size of the lesion and the amount of soft tissue and fatty material held by the lesion are variable. Torsion is the most common complication associated with these lesions.