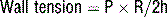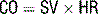CHAPTER 34 Heart Failure
3 Describe the classification of heart failure
 Stage A: Patients with coronary artery disease, hypertension, or diabetes mellitus who do not yet demonstrate impaired left ventricular (LV) function, LV hypertrophy, or geometric chamber distortion
Stage A: Patients with coronary artery disease, hypertension, or diabetes mellitus who do not yet demonstrate impaired left ventricular (LV) function, LV hypertrophy, or geometric chamber distortion Stage B: Patients who are asymptomatic but demonstrate LV hypertrophy, geometric chamber distortion, and/or impaired LV systolic or diastolic function
Stage B: Patients who are asymptomatic but demonstrate LV hypertrophy, geometric chamber distortion, and/or impaired LV systolic or diastolic function Stage C: Patients with current or past symptoms of HF associated with underlying structural heart disease
Stage C: Patients with current or past symptoms of HF associated with underlying structural heart disease4 How is the severity of heart failure classified?
 Class I: Ordinary physical activity does not cause symptoms. Dyspnea occurs with strenuous or prolonged exertion at work or with recreation.
Class I: Ordinary physical activity does not cause symptoms. Dyspnea occurs with strenuous or prolonged exertion at work or with recreation. Class II: Ordinary physical activity results in symptoms. Dyspnea is occurring while walking or climbing stairs rapidly or walking uphill. Walking more than two blocks on the level and climbing more than one flight of ordinary stairs at a normal pace results in symptoms.
Class II: Ordinary physical activity results in symptoms. Dyspnea is occurring while walking or climbing stairs rapidly or walking uphill. Walking more than two blocks on the level and climbing more than one flight of ordinary stairs at a normal pace results in symptoms.5 What major alterations in the heart occur in patients with heart failure?
where P = intracavity pressure, R = the radius of the chamber, and h = the thickness of the chamber wall.
7 How is cardiac output calculated? What is a normal cardiac output and index?
where CO = arterial pressure/ total peripheral resistance, SV = stroke volume and HR = heart rate.
9 What is systolic dysfunction?
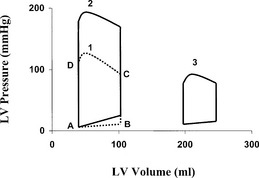
Systolic dysfunction leads to decreased ejection of blood from the left ventricle. The EF is diminished, the end-systolic and end-diastolic volume are enlarged, and the left ventricle is dilated. The stroke volume can be normal, but it is generated by a dilated ventricle with higher wall tension and oxygen consumption. In this pathologic condition the left ventricle has less reserve capacity to overcome pressure or volume load, which manifests in decreased exercise capacity (Figure 34-1, Loop 3).
10 What is diastolic dysfunction?
Diastolic dysfunction can occur with normal LV EF in many patients. Impaired LV relaxation or compliance or both are the major characteristic features of LV diastolic dysfunction. Early diastolic filling depends on the rapidity of ventricular relaxation, characterized by an energy-dependent reuptake of calcium from the cytosol into the sarcoplasmic reticulum of the myocytes. Late diastolic filling (atrial contraction) depends on LV compliance, which is the ratio of change in ventricular volume to change in ventricular diastolic pressure. In diastolic dysfunction the size of the LV cavity can be normal but ischemia, myocardial hypertrophy, pericardial constriction, fibrosis, or myocardial diseases alter the diastolic filling process. Systolic dysfunction with dilated left ventricle and high LV end-diastolic pressure accompanies significant diastolic dysfunction because of decreased LV relaxation and compliance (see Figure 34-1, Loop 2).
13 What physical signs suggest heart failure?
Key Points: Heart Failure
15 What treatment strategies are used in the different stages of heart failure?
 Stage B: Patients with cardiac structural abnormalities or remodeling who have not developed HF symptoms
Stage B: Patients with cardiac structural abnormalities or remodeling who have not developed HF symptoms
16 What should be considered in preparing to conduct an anesthetic on patients with heart failure?
 Patients with stages A or B heart failure have good functional status; thus they can go for surgery after routine preoperative evaluation.
Patients with stages A or B heart failure have good functional status; thus they can go for surgery after routine preoperative evaluation. In stage C heart failure the NYHA functional status should be evaluated, and signs of decompensated HF should be checked. Patients with dyspnea, worsening dyspnea, or other change in clinical status are reasonable candidates to undergo preoperative noninvasive evaluation of LV function and postpone elective surgery until compensation.
In stage C heart failure the NYHA functional status should be evaluated, and signs of decompensated HF should be checked. Patients with dyspnea, worsening dyspnea, or other change in clinical status are reasonable candidates to undergo preoperative noninvasive evaluation of LV function and postpone elective surgery until compensation.1. Crawford M.H. Current Diagnosis and Treatment in Cardiology, ed 2. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2003.
2. Fleisher L.A. Anesthesia and Uncommon Diseases, ed 5. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2006.
3. Fleisher L.A., Beckman J.A., Brown K.A., et al. ACC/AHA Guidelines on perioperative cardiovascular evaluation and care for noncardiac surgery: Executive summary. Circulation. 2007;116:1971-1996.
4. Hunt S.A., Abraham W.T., Chin M.H., et al. ACC/AHA Guideline update for the diagnosis and management of chronic heart failure in the adult: Task force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2005;112:e154-e235.