CHAPTER 30 Cardiac Dysrhythmias
2 A postoperative patient develops light-headedness with sinus bradycardia and a heart rate of 36. Systolic blood pressure is 83 mm Hg. What treatment should be undertaken?
Atropine, 0.5 mg intravenously, may be effective in increasing heart rate. In addition, search for clues to the etiology of the bradycardia such as those listed in Question 1.
4 Describe the types of second-degree atrioventricular block
 Mobitz type I (Wenckebach): Involves progressive lengthening of the PR interval followed by a nonconducted P wave, followed by a conducted P wave with a shorter PR interval. When lengthening of the PR is difficult to identify, comparing the PR duration before and after the blocked P wave may confirm Wenckebach. The level of block is usually in the atrioventricular (AV) node with Mobitz I.
Mobitz type I (Wenckebach): Involves progressive lengthening of the PR interval followed by a nonconducted P wave, followed by a conducted P wave with a shorter PR interval. When lengthening of the PR is difficult to identify, comparing the PR duration before and after the blocked P wave may confirm Wenckebach. The level of block is usually in the atrioventricular (AV) node with Mobitz I. Mobitz type II: Far less common than Wenckebach. With Mobitz II block there is no progressive prolongation of the PR interval, which for the first conducted beat is the same as the PR interval before the nonconducted beat. The level of the AV block is generally below the AV node with Mobitz II, as suggested by a wide QRS complex. Permanent pacing is usually indicated in patients with Mobitz II block.
Mobitz type II: Far less common than Wenckebach. With Mobitz II block there is no progressive prolongation of the PR interval, which for the first conducted beat is the same as the PR interval before the nonconducted beat. The level of the AV block is generally below the AV node with Mobitz II, as suggested by a wide QRS complex. Permanent pacing is usually indicated in patients with Mobitz II block.6 In addition to complete heart block, what are some other causes of atrioventricular dissociation?
Other causes include accelerated junctional rhythm and ventricular tachycardia (VT).
7 What are some of the causes of atrioventricular block?
 Extrinsic causes: include medications, electrolyte abnormalities, hypothyroidism, hypoxia, and increased vagal tone
Extrinsic causes: include medications, electrolyte abnormalities, hypothyroidism, hypoxia, and increased vagal tone Intrinsic conduction abnormalities: may arise in a patient with coronary artery disease (sometimes as a complication of acute myocardial infarction), ventricular hypertrophy, myocarditis, sarcoidosis, recent cardiac surgery (especially valve surgery), or calcific degeneration of the conduction system
Intrinsic conduction abnormalities: may arise in a patient with coronary artery disease (sometimes as a complication of acute myocardial infarction), ventricular hypertrophy, myocarditis, sarcoidosis, recent cardiac surgery (especially valve surgery), or calcific degeneration of the conduction system8 Your patient exhibits transient evidence of both sinoatrial node and atrioventricular node dysfunction with simultaneous slowing of the sinus rate and second-degree atrioventricular block, type I. What is going on?
9 Which antihypertensive agents are to be avoided in patients with significant bradycardia or heart block?
12 What is meant by the term paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia?
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) is a regular tachycardia with sudden onset and offset that usually has a narrow complex. It may be aborted with vagal maneuvers such as carotid sinus massage or Valsalva. Generally PSVT is responsive to agents such as adenosine, β-blockers, or verapamil if the rhythm is AV nodal dependent. PSVT is actually a family of specific rhythms that fit these characteristics, including AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT), AV reentrant tachycardia (AVRT), and some types of atrial tachycardia. Other causes of narrow-complex tachycardia are listed in Table 30-1.
TABLE 30-1 Differential Diagnosis for a Narrow-Complex Tachycardia
| Sinus tachycardia | Atrial tachycardia |
| Atrial flutter | Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) |
| Atrial fibrillation | Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT) |
| Multifocal atrial tachycardia | Junctional tachycardia |
15 A patient suddenly develops an irregular rhythm with heart rate of 170. A 12-lead electrocardiogram shows no P waves. What is the likely rhythm? How should it be managed?
17 What should be done to reduce the risk of stroke in a patient with chronic or paroxysmal atrial fibrillation?
19 A 60-year-old man with a history of prior anterior myocardial infarction develops a monomorphic wide complex tachycardia after noncardiac surgery. What is the most likely diagnosis, and which treatments would be appropriate or inappropriate?
20 What characteristics of a wide-complex tachycardia suggest ventricular tachycardia rather than supraventricular tachycardia with aberrancy?
 The ability of a P wave to conduct to the ventricle and capture the rhythm with a narrow QRS complex is diagnostic for VT.
The ability of a P wave to conduct to the ventricle and capture the rhythm with a narrow QRS complex is diagnostic for VT. Concordance (QRS entirely above the baseline in all precordial leads or below the baseline in all precordial leads) is seen in a minority of cases of VT. When present, concordance strongly suggests VT. However, the absence of concordance is common with VT and does not imply that a wide-complex tachycardia is SVT with aberrancy.
Concordance (QRS entirely above the baseline in all precordial leads or below the baseline in all precordial leads) is seen in a minority of cases of VT. When present, concordance strongly suggests VT. However, the absence of concordance is common with VT and does not imply that a wide-complex tachycardia is SVT with aberrancy. When the interval from the beginning of the QRS to the nadir of the S wave is greater than 100 milliseconds in any precordial lead, VT is suggested.
When the interval from the beginning of the QRS to the nadir of the S wave is greater than 100 milliseconds in any precordial lead, VT is suggested.21 Why is it important to distinguish between polymorphic and monomorphic ventricular tachycardia?
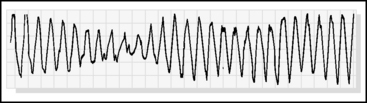
The differential diagnosis and treatment for each are somewhat different. Monomorphic VT is common in patients with structural heart disease (such as a previous Q wave myocardial infarction), but it is generally not caused by acute ischemia. Polymorphic VT may be seen in a variety of settings. Patients may have a long QT interval associated with polymorphic VT, commonly referred to as torsades de pointes. This may arise from medications, electrolyte derangements, a congenital predisposition (long QT syndrome), severe bradycardia, or myocardial ischemia (Figure 30-1).
22 How is torsades de pointes treated?
 If an offending drug (such as procainamide) is suspected as the cause, the drug should be discontinued immediately.
If an offending drug (such as procainamide) is suspected as the cause, the drug should be discontinued immediately.25 Do all patients with an accessory pathway have a delta wave (WPW pattern) on their baseline electrocardiogram?
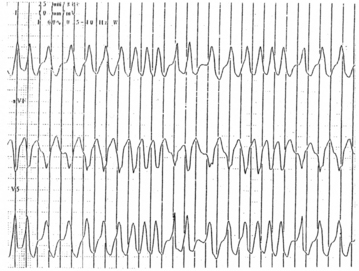
26 A 25-year-old patient presenting with palpitations is noted to have a wide-complex, irregular tachycardia at a rate of 260. The upstroke of the QRS is slurred. The blood pressure is normal, and the patient appears well. What is the most likely diagnosis? What treatments are indicated? What treatments are potentially harmful?
This is probably a case of atrial fibrillation with WPW syndrome (Figure 30-2). The wide QRS is a result of conduction down the accessory pathway from the atrium to the ventricular myocardium. In an unstable patient electrical cardioversion is warranted. In a stable patient amiodarone or procainamide would be reasonable. In these patients avoid using digoxin, calcium blockers, adenosine, and β-blockers. Heart rate may actually increase, and ventricular fibrillation has been reported from AV nodal blocking agents. Elective radiofrequency ablation of the pathway is indicated. This is a percutaneous catheter-based approach that is performed by a cardiac electrophysiologist.
1. ACLS Committee. Management of symptomatic tachycardia and bradycardia. Circulation. 2005;112(Suppl):67-77.
2. Atwood S., Stanton C., Storey-Davenport J. Introduction to basic cardiac dysrhythmias, ed 4. St. Louis: Mosby-Elsevier, 2008.
3. Goldenberg I., Moss A.J. Long QT syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:2291-2300.
4. Lip G.Y., Tse H.F. Management of atrial fibrillation. Lancet. 2007;370:604-618.
5. Surawicz B., Kailans T.K. Chou’s electrocardiography in clinical practice: adult and pediatric, ed 6. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2008.
6. Wagner G.S. Marriott’s practical electrocardiography, ed 11. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, 2007.
7. Reising S., Kusumoto F., Goldschlager N. Life-threatening arrhythmias in the intensive care uni. J Intensive Care Med. 2007;22:3-13.
8. Olgin J.E., Zipes D.P. Specific arrhythmias: diagnosis and treatment. In Libby P., et al, editors: Braunwald’s heart disease: a textbook of cardiovascular medicine, ed 8, Philadelphia: Saunders, 2004.