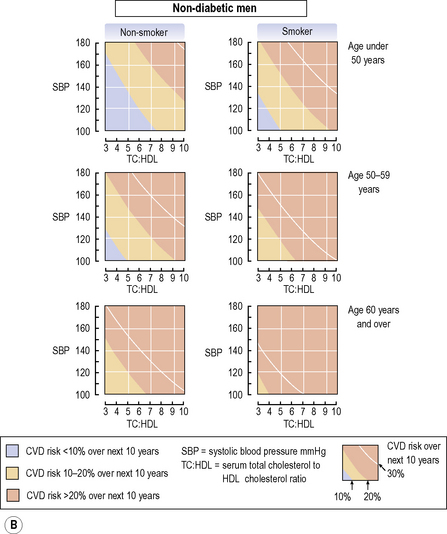
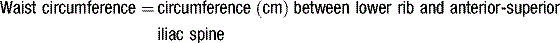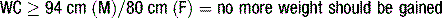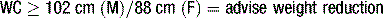TOPIC 3 Preventative cardiology
Diabetes and metabolic syndrome
ESC Guidelines on treatment targets in type 2 diabetes
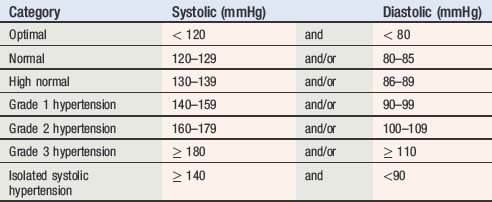
Table 3.3 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Guidelines on treatment targets in type 2 diabetes
| Category | Unit | Target |
|---|---|---|
| HbA1c | HbA1c (%) | ≤ 6.5 |
| Plasma glucose | Fasting/pre-prandial mmol/L (mg/dl) | < 6.0 (110) |
| Blood pressure | mmHg | ≤ 130/80 |
| Total cholesterol | mmol/L (mg/dl) | < 4 (155) |
| LDL cholesterol | mmol/L (mg/dl) | < 2 80 |
International Diabetes Federation (IDF) definition of metabolic syndrome
1. Central obesity (defined by ethnic-specific waist circumference criteria ≥ 94 cm in Europoid men, ≥ 80 cm in Europoid women).
Renal impairment
Cardiovascular risk increases 20–30-fold with the diagnosis of end-stage renal failure.
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP)
The acute phase, C-reactive protein can function as a marker for generalized inflammation which is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. See Table 3.4.
Table 3.4 High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) and risk
| hsCRP level | Risk |
|---|---|
| < 1.0 mg/L | Low |
| 1.0–2.9 mg/dl | Intermediate |
| >3.0 mg/L | High |