Anticoagulants and Hematinics
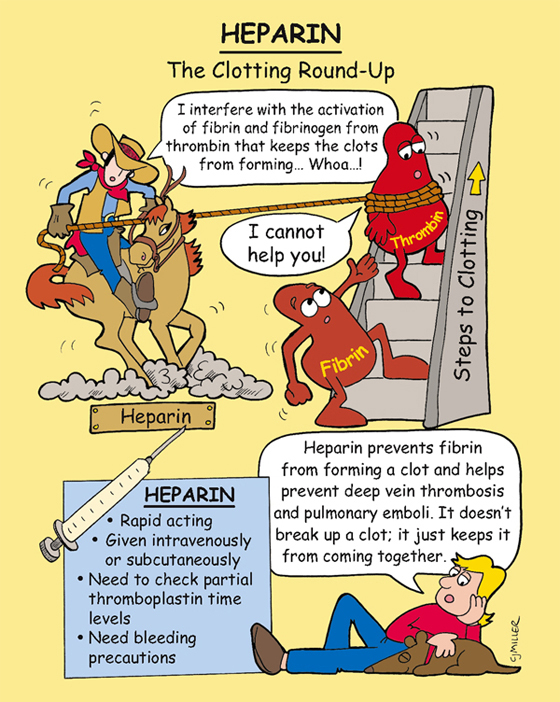
Heparin
ACTION
Anticoagulant exerts direct effect on blood coagulation by enhancing the inhibitory actions of antithrombin on several factors essential to normal blood clotting, thereby blocking the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin and fibrinogen to fibrin.
USES
• Prevents and treats deep-vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism, and emboli in atrial fibrillation.
• Treats disseminated intravascular coagulation.
• Is preferred anticoagulant during pregnancy.
PRECAUTIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Bleeding tendencies—hemophilia, dissecting aneurysm, peptic ulcer
• Thrombocytopenia, uncontrollable bleeding, threatened abortion
SIDE EFFECTS
• Injection site reactions and †heparin-induced thrombocytopenia† may develop.
• Large doses may suppress renal function.
• May result in †spontaneous bleeding.†
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Monitor partial thromboplastin time (PTT) and activated PTT (aPTT)—should be 1½ to 2 times the normal range.* †Watch for bleeding.†
2. *Protamine sulfate is the antidote.*
4. Administered either intravenously (IV) or †subcutaneously; apply firm pressure for 1 to 2 minutes; do not massage site after injection.†
Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
ACTIONS
Low–molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) with a great affinity for factor Xa in providing anticoagulation action; provides a predictable anticoagulant response.
USES
Treats and prevents postoperative deep-vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, unstable angina, or non–Q-wave myocardial infarction (MI).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Presence of any active bleeding
• Increased risk of hematoma in patients with spinal or epidural anesthesia
• Not to be used concurrently with other anticoagulants or aspirin
• †Not to be used in presence of thrombocytopenia†
SIDE EFFECTS
• Immune-mediated thrombocytopenia
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. Medication is only administered subcutaneously.
2. *Protamine sulfate is antidote.*
3. *Always double check—cannot be given to a patient receiving heparin.*
4. *Injections in abdomen should be 2 inches from umbilicus or any incisional area.*
5. ‡Advise patient not to take any over-the-counter (OTC) medications, especially aspirin.‡
6. Check complete blood count (CBC), especially platelet count.
• *Guaiac stools for occult blood*
Warfarin Sodium (Coumadin)
ACTIONS
Anticoagulant that antagonizes vitamin K, which is necessary for the synthesis of clotting factors VII, IX, X, and prothrombin. As a result, it disrupts the coagulation cascade.
USES
• Long-term prophylaxis of thrombosis; is not useful in emergency because of delayed onset of action.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Bleeding disorders (hemophilia, thrombocytopenia)
• Vitamin K deficiency; severe hypertension
• Pregnancy—category X; breast-feeding (crosses into breast milk)
• Renal or liver disease, alcoholism
SIDE EFFECTS
• Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., dermatitis, fever, pruritus, urticaria)
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Monitor prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR) as ordered (2 to 3 is usually an acceptable INR for anticoagulation).*
2. *Interacts with a large number of medications; consequently, monitor for drug interactions before initiating therapy.*
3. *Monitor for bleeding tendencies.*
4. *Vitamin K is an antidote.*
5. ‡Teach patient to decrease intake of green, leafy vegetables.‡
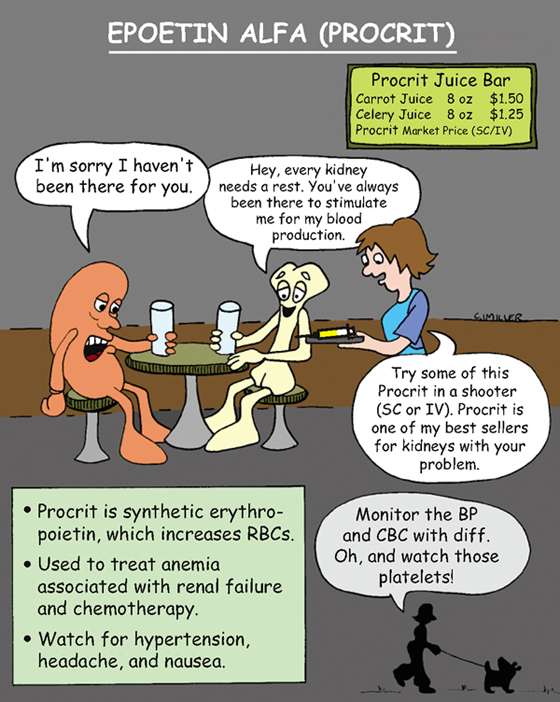
Epoetin Alfa (Procrit)
ACTION
Erythropoietic growth factor stimulates red blood cell production.
USES
• Patients with anemia as a result of chronic renal failure, chemotherapy
• Patients infected with human immunodeficiency (HIV) and taking zidovudine (Retrovir)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
PRECAUTIONS
• Patients with cancers of myeloid origin
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Monitor blood pressure before erythropoietin therapy.*
2. *Do not shake solution; it may denature the glycoprotein. Do not mix with other medications.*
3. Discard remaining contents because erythropoietin does not contain a preservative.
4. Monitor hematocrit (Hct), hemoglobin (Hb), serum iron, and fluid and electrolyte balance.
5. *Monitor for seizures* (rapid increase in Hct increases risk of hypertensive encephalopathy).
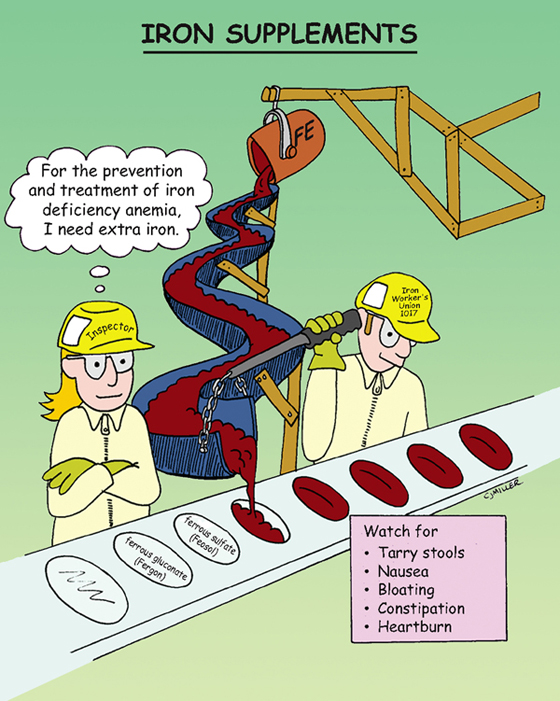
Iron Supplements
ACTION
Hematinic agent used in the production of normal hemoglobin and red blood cells for transportation and utilization of oxygen.
USES
• Prophylactic use in pregnancy and childhood
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
• All anemias other than iron-deficiency anemia
• Peptic ulcers, regional enteritis, colitis
SIDE EFFECTS
• Gastrointestinal (GI) disturbances—**nausea** (usually transient), heartburn, bloating, **constipation**
• Tarry stools or dark-green discoloration (not associated with bleeding)
• †Anaphylaxis† (parenteral preparation only)
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Do not give with antacids or tetracyclines or crush or chew sustained-release medications.*
2. ‡Take between meals to maximize uptake.‡
3. *Take vitamin C to promote the absorption of the iron.*
4. ‡Because liquid preparations stain teeth, use a straw or dilute; follow with rinsing the mouth.‡
5. ‡Teach patient that oral iron supplements differ from one another and should not be interchanged.‡
6. ‡Diet teaching to include iron-rich food—liver, eggs, meat, fish, and fowl.‡
7. †Assess for anaphylaxis with parenteral iron dextran, as well as hypotension headache, fever, urticaria, and arthralgia.†
8. ‡Teach to store iron out of reach and in childproof containers;‡ †iron poisoning can be fatal to young children.†
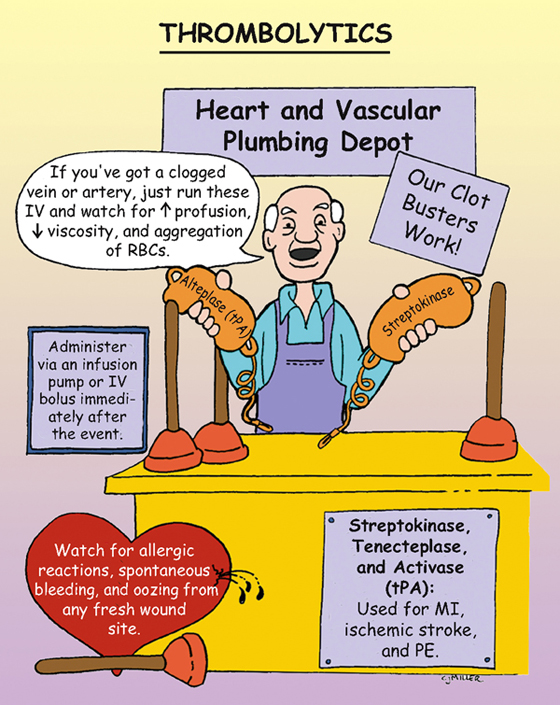
Thrombolytics
ACTIONS
Work to directly or indirectly convert plasminogen to plasmin, an enzyme that acts to digest the fibrin matrix of clots. Dissolve existing thrombi rather than prevent them from occurring.
USES
• Treatment of acute myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, thrombotic strokes, and deep vein thrombosis
• Treatment of arteriovenous cannula occlusion
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
• Cerebrovascular disease and pregnancy
• Active bleeding, aortic dissection, pericarditis
• History of intracranial hemorrhage
• History of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding
SIDE EFFECTS
Streptokinase
• †Hemorrhage (intracranial of greatest concern)† and anemia
• Allergic reactions—itching, urticaria, headache, †anaphylaxis†
Activase (tPA) and tenectoplase
• Risk of †intracranial hemorrhage is higher.†
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Administer immediately after the event for better outcome, preferably within 4 to 6 hours.*
2. Monitor intake and output and hematocrit during treatment.
3. *Monitor patient for bleeding and anaphylactic reactions.*
4. While receiving the medication, maintain patient on bed rest.
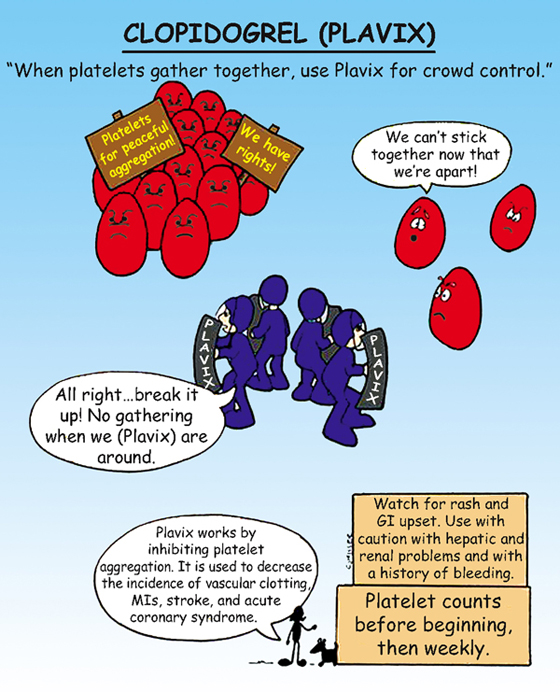
Clopidogrel (Plavix)
CLASSIFICATION
Antiplatelet
ACTION
Suppresses platelet aggregation in arterial circulation; antiplatelet action occurs within 2 hours of administration.
USES
• Secondary prevention of myocardial infarction (MI), ischemic stroke, and other vascular events
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Administer with food to diminish gastrointestinal (GI) upset.*
2. ‡Teach patient to report any unusual bleeding or bruising.‡
3. ‡Teach patient that if surgery is scheduled, medication may be held 3 to 7 days before surgery.‡
4. Platelet counts may be monitored.
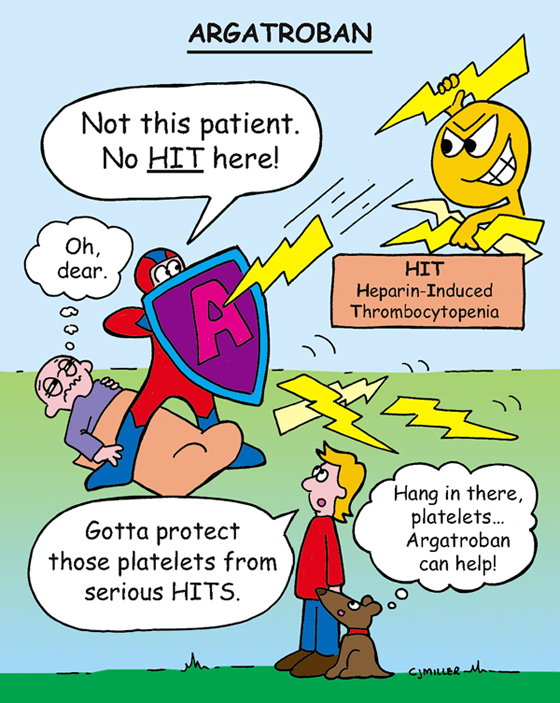
Argatroban
CLASSIFICATION
Anticoagulant
ACTION
Directly inhibits the action of thrombin in the clotting mechanism.
USES
Prevents and treats heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT); prevents HIT during coronary procedures.
CONTRAINDICATION
• Any evidence of overt bleeding
PRECAUTIONS
• Severe hypertension, hepatic impairment
• Spinal anesthesia or lumbar puncture
• History of any bleeding disorders
SIDE EFFECTS
• †Allergic reactions: dyspnea, cough, rash†—primarily in patients receiving other thrombolytic drugs or contrast media
• **Hypotension, fever, diarrhea**
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Carefully monitor patient for any evidence of bleeding.*
3. Administer only intravenously (IV); reconstitute for final solution of 1 mg/ml.
4. Dose and rate of administration are based on body weight.
5. *Activated partial prothrombin time (aPTT) is used to monitor treatment. The aPTT returns to base level in 2 to 4 hours after medication is stopped.*