CASE 27
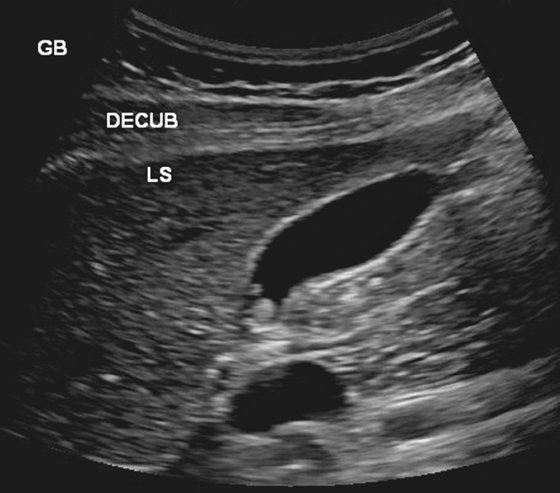
History: A 33-year-old woman, 12 weeks pregnant, underwent routine ultrasound, with an incidentally noted finding in the gallbladder.
1. Which of the following should be included in the differential diagnosis of the imaging finding? (Choose all that apply.)
E. Hematogenous metastatic deposits
2. What is the most common type of gallbladder polyp?
3. What types of tumors can produce multiple mural nodules?
4. What benign condition can produce gallbladder wall nodularity?
B. Emphysematous cholecystitis
D. Intramural pseudodiverticulosis
ANSWERS
CASE 27
Gallbladder Polyps
1. A, B, C, and E
2. C
3. C
4. A
References
Lee KF, Wong J, Li JCM, Lai PBS. Polypoid lesions of the gallbladder. Am J Surg. 2004;188:186–190.
Cross-Reference
Gastrointestinal Imaging: THE REQUISITES, 3rd ed, pp 246-252.
Comment
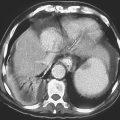
Although calculi are by far the most common cause of filling defects within the gallbladder, several noncalculous lesions can produce filling defects within the gallbladder lumen. One of the more common noncalculous causes is a gallbladder polyp. Polyps in the gallbladder produce echogenic filling defects within the lumen but are fixed, often along the nondependent surface of the gallbladder (see figure). They do not move with changes in position. Polyps of the gallbladder, particularly when they are multiple, are most often cholesterol polyps. The patient with multiple cholesterol polyps is considered to have a type of cholesterolosis. If the polyp is solitary, it could be cholesterol, an adenoma, or a papilloma.
Rarely, other conditions produce multiple mural nodules or protrusions that simulate gallbladder polyps. Adenomyomatosis with prominence of the Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses sometimes results in some mural nodularity. Adherent stones can also produce polyp-like lesions that can be difficult to differentiate from true polyps. Metastases are quite uncommon in the gallbladder, but when they occur, they can produce mural polyps. Melanoma, breast cancer, and lymphoma infiltrating the gallbladder can cause gallbladder metastases. Primary gallbladder carcinoma can result in the formation of a solitary polypoid lesion but rarely results in multiple mural polyps. Potentially, blood clots, hemorrhage, and even varices could produce mural polyps or nodularity, but this is quite uncommon.