CASE 26
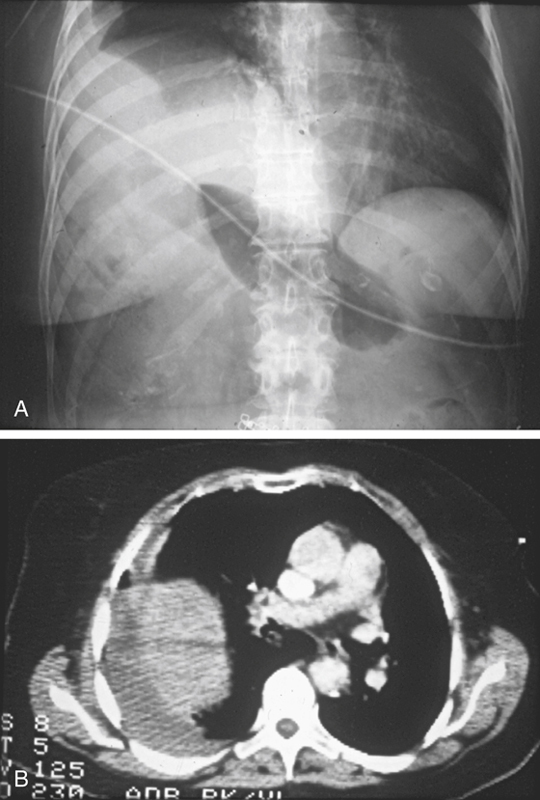
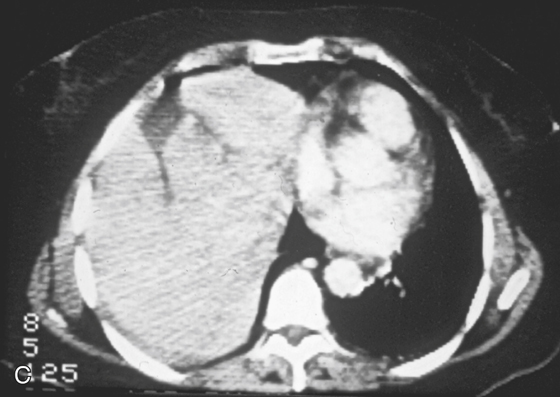
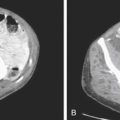
History: A 70-year-old woman was injured in a motor vehicle accident.
1. Which of the following should be included in the differential diagnosis of the dominant imaging finding on figure A? (Choose all that apply.)
D. Traumatic diaphragmatic hernia
2. What other abdominal or pelvic injury is most commonly involved with this abnormality?
C. Hepatic and splenic laceration
3. What is the most commonly herniated organ in patients with traumatic diaphragmatic injury?
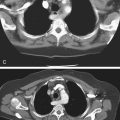
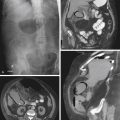
4. What is the most common sign of a diaphragmatic hernia on CT (including coronal and sagittal reformats)?
A. Abdominal viscera in the thorax
C. The collar sign, a waistlike constriction of viscera at the level of the diaphragm
D. Discontinuity of the diaphragm
ANSWERS
CASE 26
Traumatic Diaphragmatic Injury
1. A, B, D, and E
2. B
3. A
4. D
References
Eren S, Kantarci M, Okur A. Imaging of diaphragmatic rupture after trauma. Clin Radiol. 2006;61:467–477.
Cross-Reference
Gastrointestinal Imaging: THE REQUISITES, 3rd ed, p 193.
Comment
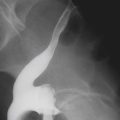
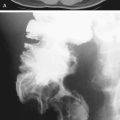
Most traumatic diaphragmatic ruptures are associated with high-velocity, high-impact motor vehicle accidents (85%), and the remainder are usually associated with falling from ladders and roofs or from penetrating trauma. Diagnosis of diaphragmatic trauma is often delayed or missed, even with the current advances in imaging. This is often the case with penetrating injuries. The more severe the diaphragmatic trauma, the easier the diagnosis. However, the more severe the trauma, the less likely is survival. This is especially true of right-sided trauma because of the increased incidence of aortic tears associated with it. The size of the diaphragmatic tear can vary from 1 cm to almost the entire diaphragm (about 15 cm), such as in this case (see figures).