CASE 25

1. What vessels lie in the left atrioventricular groove? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Right coronary artery (RCA)
B. Posterior descending coronary artery
2. Which coronary artery has diagonal and septal perforator branches?
A. Right
B. Left main
3. Which coronary artery lies in the inferior interventricular groove?
D. Right
4. Which coronary artery travels in the right atrioventricular groove?
A. Right
B. Left main
ANSWERS
Reference
Young PM, Gerber TC, Williamson EE, et al. Cardiac imaging: part 2, normal, variant, and anomalous configurations of the coronary vasculature. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(4):816–826.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 110–115.
Comment
Imaging
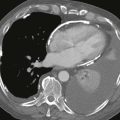
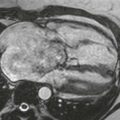
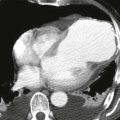
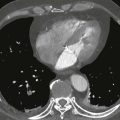
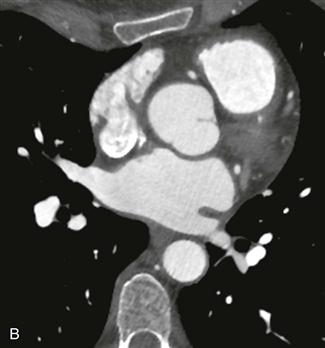
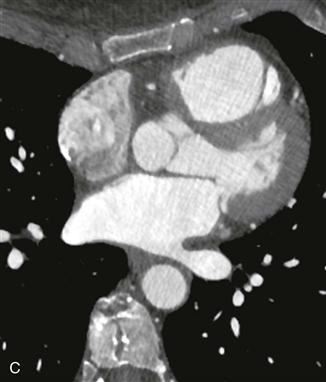
This case illustrates normal coronary artery anatomy (Figs. A–C). The arteries are named according to where the blood flow goes (i.e., the RCA supplies the morphologic right ventricle).
Right Coronary Artery
The RCA originates from the right sinus of Valsalva and travels in the right atrioventricular groove. Its first branch, the conus branch, arises from the RCA in 50% of patients and supplies the right ventricular outflow tract. Other early branches of the RCA include the sinoatrial nodal and atrioventricular nodal arteries. The largest branches of the RCA are the acute marginal arteries, which supply the free wall of the right ventricle. The RCA is “dominant” in most patients (approximately 70–85%), supplying the inferior left ventricular myocardium and septum through the posterior descending coronary artery and posterolateral left ventricular branch.
Left Coronary Artery System
The left main coronary artery originates from the left sinus of Valsalva and is usually about 1 cm in length. It quickly divides into the left anterior descending and left circumflex coronary arteries. In 15% of patients, there is a trifurcation with the ramus intermedius being the named middle branch. The left circumflex coronary artery travels in the left atrioventricular groove and supplies the left ventricular free wall through obtuse marginal branches. The left circumflex coronary artery is dominant in about 10% of patients where it supplies the inferior wall of the left ventricle. Approximately 15% to 20% of patients have codominance of the RCA and left circumflex arteries. The left anterior descending coronary artery lies in the interventricular groove and gives off septal branches that supply the interventricular septum and diagonal branches that supply the anterior left ventricular wall.