CASE 24
MM, a 3-year-old white monozygotic twin boy was brought to the emergency department by his mother after suffering from a viral-like illness for nearly 3 weeks. Previously, she had taken MM to the family physician, but he had reassured her that the symptoms would resolve with acetaminophen (Tylenol). At the present time her son is not eating well; his urine output has been diminished for over 24 hours; he is quite listless with sunken eyes, and he is feverish.
QUESTIONS FOR GROUP DISCUSSION
RECOMMENDED APPROACH
Implications/Analysis of Family History
Individuals with type 1 DM and their relatives are at increased risk for a number of autoimmune disorders, including celiac disease, Addison’s disease, pernicious anemia, and autoimmune thyroid dysfunction. About 14% of children with type 1 DM (without celiac disease) have IgA anti-tissue transglutaminase (tTG) autoantibodies. These tTG autoantibodies are also present in about 7% of nondiabetic first-degree relatives (without celiac disease). We would expect, therefore, that a family history would reveal autoimmune disorders in immediate or related family members.
THERAPY
In the past, most patients, irrespective of the source of insulin, developed anti-insulin antibodies. With the human insulin and insulin analogs, development of anti-insulin antibodies is not common.
ETIOLOGY: TYPE 1A DIABETES MELLITUS
Metabolic Complications
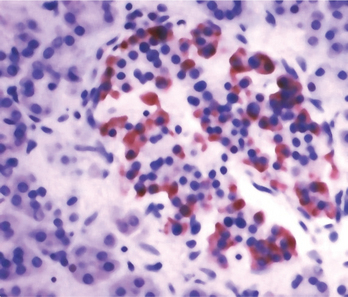
In the nondisease state, insulin is synthesized and stored within cytosolic granules of β cells of the pancreatic islets (Fig. 24-1) and released into circulation when there is a rise in blood glucose concentration. Insulin increases the rate at which glucose is transported into cells, where it plays a role in several anabolic processes. In type 1 DM, glucose generated from simple or complex dietary carbohydrates is unable to enter cells and so the cells are, in effect, starving. Under these conditions, fatty acids are oxidized in the liver and one of the products (acetyl CoA) is converted to ketone bodies, which can serve as a metabolic fuel. However, elevated levels of ketone bodies in the blood lead to a condition known as ketosis.
Breakdown in Tolerance: Stimulation of TLR4
Much of the progress in our understanding of type 1 DM has come from studies with rodents that have served as models for human studies. One pilot study with a heat shock protein (hsp) peptide addressed the relevance of toll-like receptors (TLR) recognition in the immunopathogenesis of type 1 DM. Hsps play an important role, functioning as chaperones for newly synthesized or aberrantly folded proteins. From an evolutionary point of view, hsps are highly conserved in all organisms ranging from bacteria to humans. Hsp60, one of the most studied hsps, has also been shown to activate macrophages and dendritic cells (antigen-presenting cells) after binding to TLR4 on these cells. Peripheral blood cells of both type 1 DM patients and a diabetes-susceptible nonobese diabetic (NOD) strain of mice have a greater number of T cell clones that are specific for hsp60 than do normal populations. In one study, immunization of NOD mice with an hsp60 (amino acids 437 to 460) peptide, prior to the development of overt symptoms of diabetes, led to protection from diabetes. This immunization was associated with a shift from Th1 to Th2 cells specific for the hsp60 peptide. This is consistent with other studies that showed that infusion of Th2 cytokines, particularly IL-4, could ameliorate disease.
Role of Autoantibodies
The role of antibodies in the initiation of disease is controversial, although, once generated, they can certainly contribute to the pathogenesis. It is difficult to rationalize a role for antibody in the initiation of disease given reports of type 1 DM in a patient with X-linked agammaglobulinemia (see Case 3). Not surprising, this patient did not have autoantibodies, which are the diagnostic marker of type 1A DM. Rather, involvement of the immune system was shown to be the in vitro proliferation of T cells to islet-specific autoantigens. Additionally, the patient’s class II MHC haplotype was consistent with that for the highest risk susceptibility (see earlier).