Topical Medications
Objectives
1. Identify major categories of medications used topically.
2. Describe specific administration techniques for topical products.
3. List at least three preparations used to treat eye, ear, and skin problems.
Key Terms
anorectal preparations (ā-nō-RĔK-tăl, p. 411)
antiglaucoma agents (ĂN-tĭ-glăw-KŌ-mă, p. 416)
antipsoriatics (ĂN-tĭ-SŌ-rē-ĂT-ĭks, p. 417)
antiseptics (ăn-tĭ-SĔP-tĭks, p. 412)
mydriasis (mĭ-DRī-ă-sĭs, p. 416)
pediculicides (pĕ-DĬK-ū-lĭ-sīdz, p. 417)
scabicides (SKĂB-ĭ-sīdz, p. 417)
vasoconstrictors (vās-ō-kŏn-STRĭK-tŏrz, p. 417)
Overview
![]() http://evolve.elsevier.com/Edmunds/LPN/
http://evolve.elsevier.com/Edmunds/LPN/
This chapter presents a brief overview of the many products that may be used topically somewhere on the skin or mucous membranes. Many of these products are purchased over the counter (OTC). Because hundreds of preparations are available, and new products come onto the market very quickly, only a few selected examples of drugs in the major categories can be presented. The nurse may play a major role in teaching the patient the proper administration of these medications and precautions for their use. Side effects are usually local unless systemic sensitization (allergic reaction) develops or absorption systemically (throughout the body) occurs.
Integumentary System
The integumentary system is made up of the skin, hair, nails, and sweat glands (Figure 23-1). The skin provides the most important barrier to infection and protects the body, regulates temperature, prevents water loss, and produces the chemicals that develop into vitamin D.
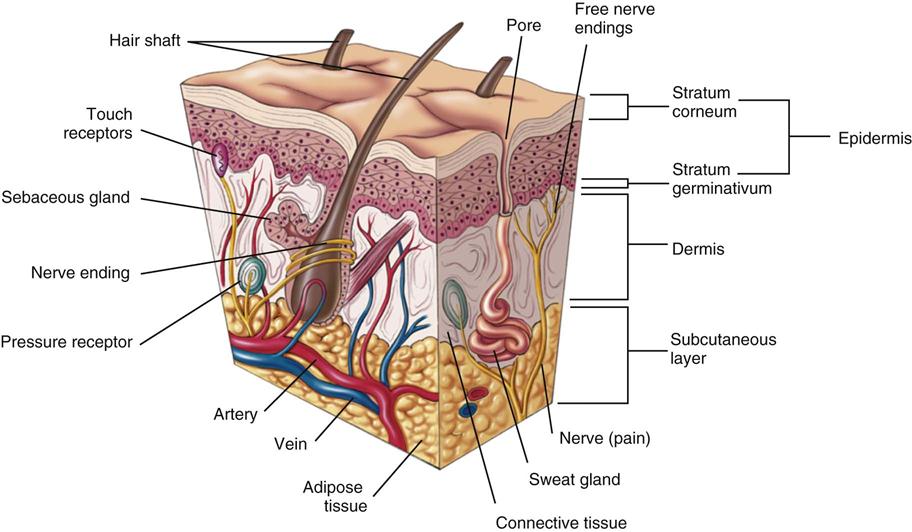
The skin; mucous membranes; and surfaces of the eye, ear, nose, mouth, and vagina are often the sites of minor infections. Medications are frequently used to treat conditions in these areas. For medication to go deep within these tissues, special preparations and procedures are required.
Topical Medications
Anorectal Preparations
Action and Uses
Anorectal preparations include emollients, foams, and gels for topical anesthesia or healing of the rectal area. They are used for symptomatic relief of discomfort from hemorrhoids. They may be used on a long-term basis or briefly for hemorrhoids associated with pregnancy, prolonged sitting, or other temporary problems. Table 23-1 presents a summary of these preparations.
![]() Table 23-1
Table 23-1
| GENERIC NAME | TRADE NAME | COMMENTS |
| dibucaine | Nupercainal (OTC) | Patient should apply ointment morning and night and after each bowel movement. For suppositories, one should be inserted after each bowel movement. |
| hydrocortisone acetate | Anusol-HC | Contains hydrocortisone. |
| zinc sulfate monohydrate | Anusol (OTC) Preparation H (OTC) |
Suppository should be inserted in the morning and at bedtime for 3-6 days or until inflammation subsides; or cream may be applied to anal area and gently rubbed in 3 to 4 times daily for 3-6 days. |
| hydrocortisone foam | ProctoFoam-HC | Steroid used for antiinflammatory treatment of ulcerative proctitis and distal ulcerative colitis. Contains hydrocortisone. Patient should insert one applicator full in rectum daily or twice daily for 2-3 wk, then every other day, decreasing therapy gradually. |
Adverse Reactions
The patient may have sensitization to the product.
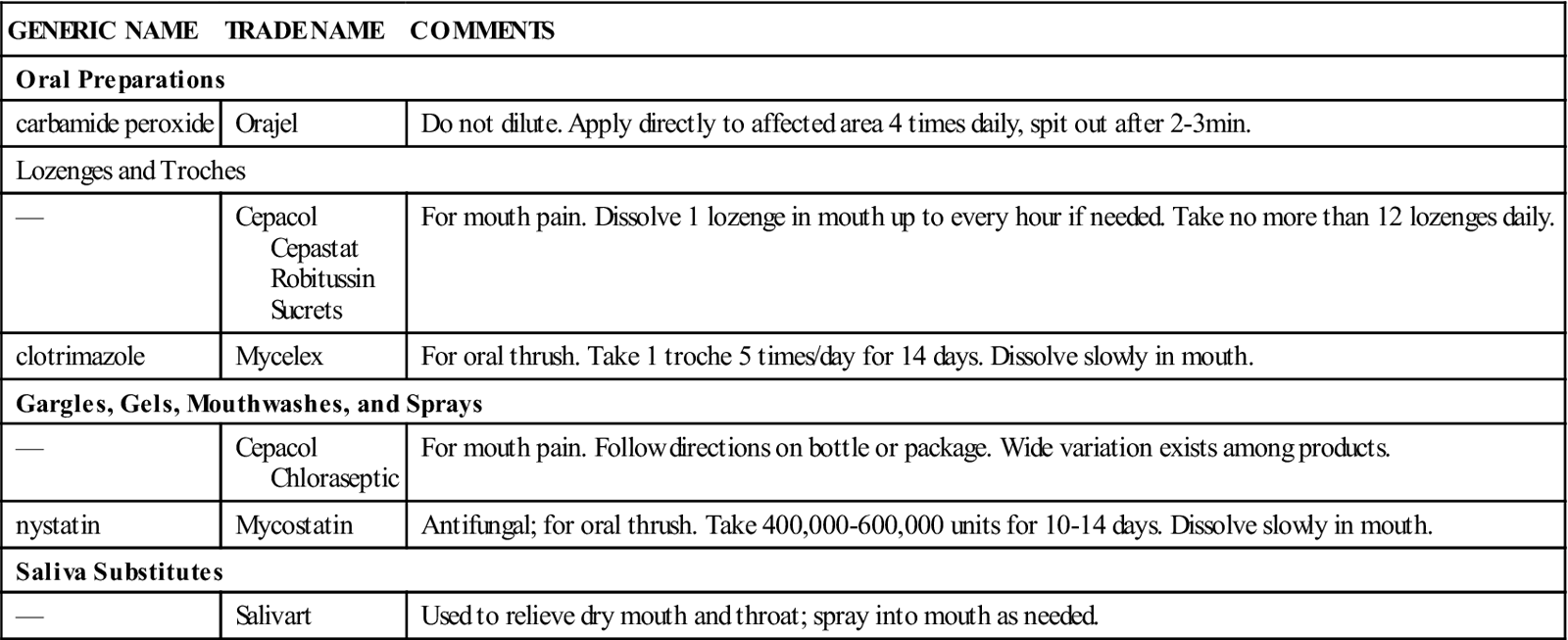
Mouth And Throat Preparations
Action and Uses
Miscellaneous products are used to soothe minor irritation in the mouth and throat. Some release oxygen to provide cleansing, whereas others contain an anesthetic property to reduce pain. These preparations are used for minor oral inflammation, such as canker sores, dental irritation, and pain after dental procedures; for relief of dryness of the mouth and throat; or for treatment of minor sore throat discomfort and control of cough caused by colds.
Products are available in mouthwashes, sprays, solutions, troches, lozenges, and disks. The patient should be taught the appropriate administration technique for the drug form being used. Patients should not take these products for longer than 3 or 4 days for normal therapy. Table 23-2 presents a summary of these products.
![]() Table 23-2
Table 23-2
| GENERIC NAME | TRADE NAME | COMMENTS |
| Oral Preparations | ||
| carbamide peroxide | Orajel | Do not dilute. Apply directly to affected area 4 times daily, spit out after 2-3 min. |
| Lozenges and Troches | ||
| — | Cepacol Cepastat Robitussin Sucrets |
For mouth pain. Dissolve 1 lozenge in mouth up to every hour if needed. Take no more than 12 lozenges daily. |
| clotrimazole | Mycelex | For oral thrush. Take 1 troche 5 times/day for 14 days. Dissolve slowly in mouth. |
| Gargles, Gels, Mouthwashes, and Sprays | ||
| — | Cepacol Chloraseptic |
For mouth pain. Follow directions on bottle or package. Wide variation exists among products. |
| nystatin | Mycostatin | Antifungal; for oral thrush. Take 400,000-600,000 units for 10-14 days. Dissolve slowly in mouth. |
| Saliva Substitutes | ||
| — | Salivart | Used to relieve dry mouth and throat; spray into mouth as needed. |
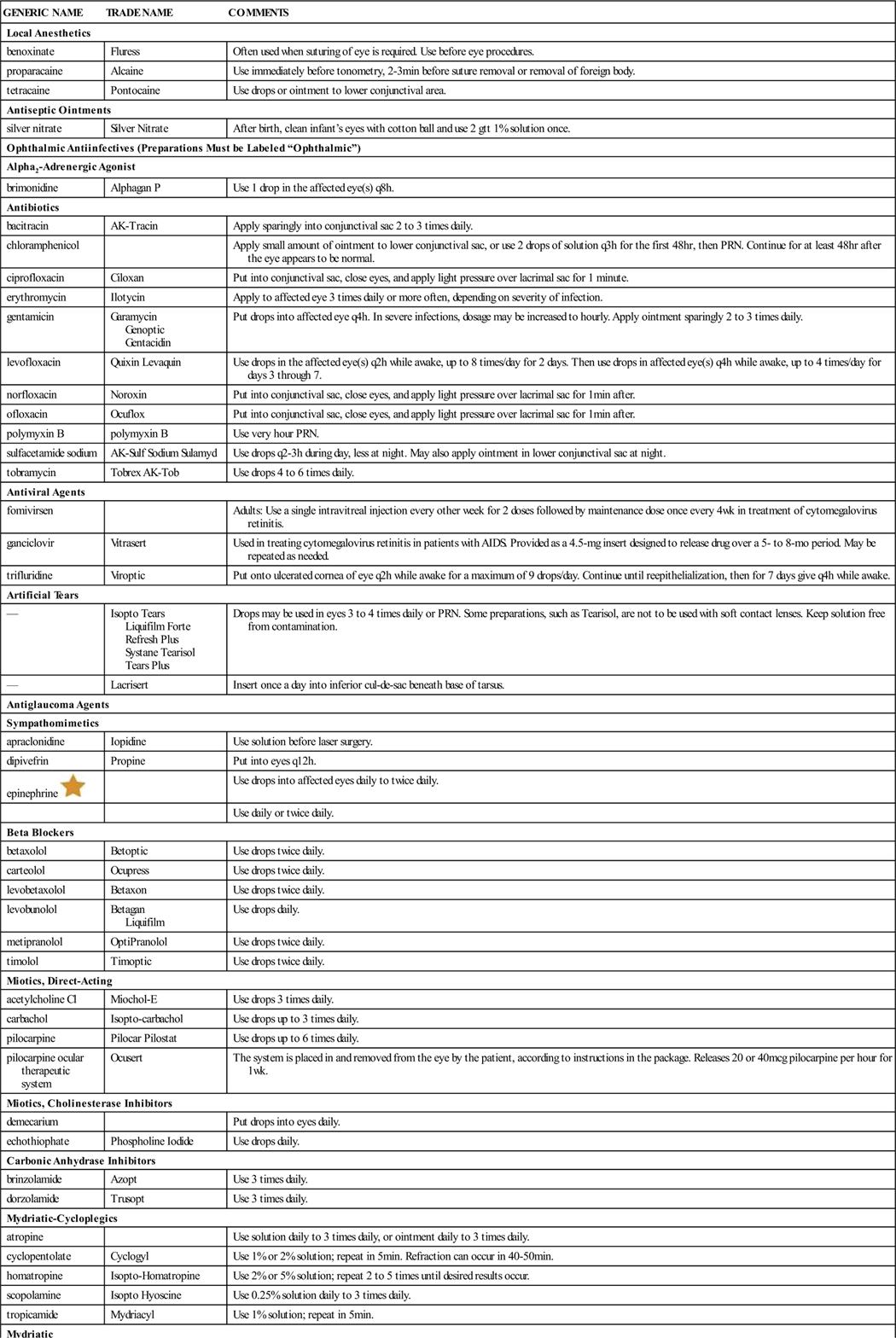
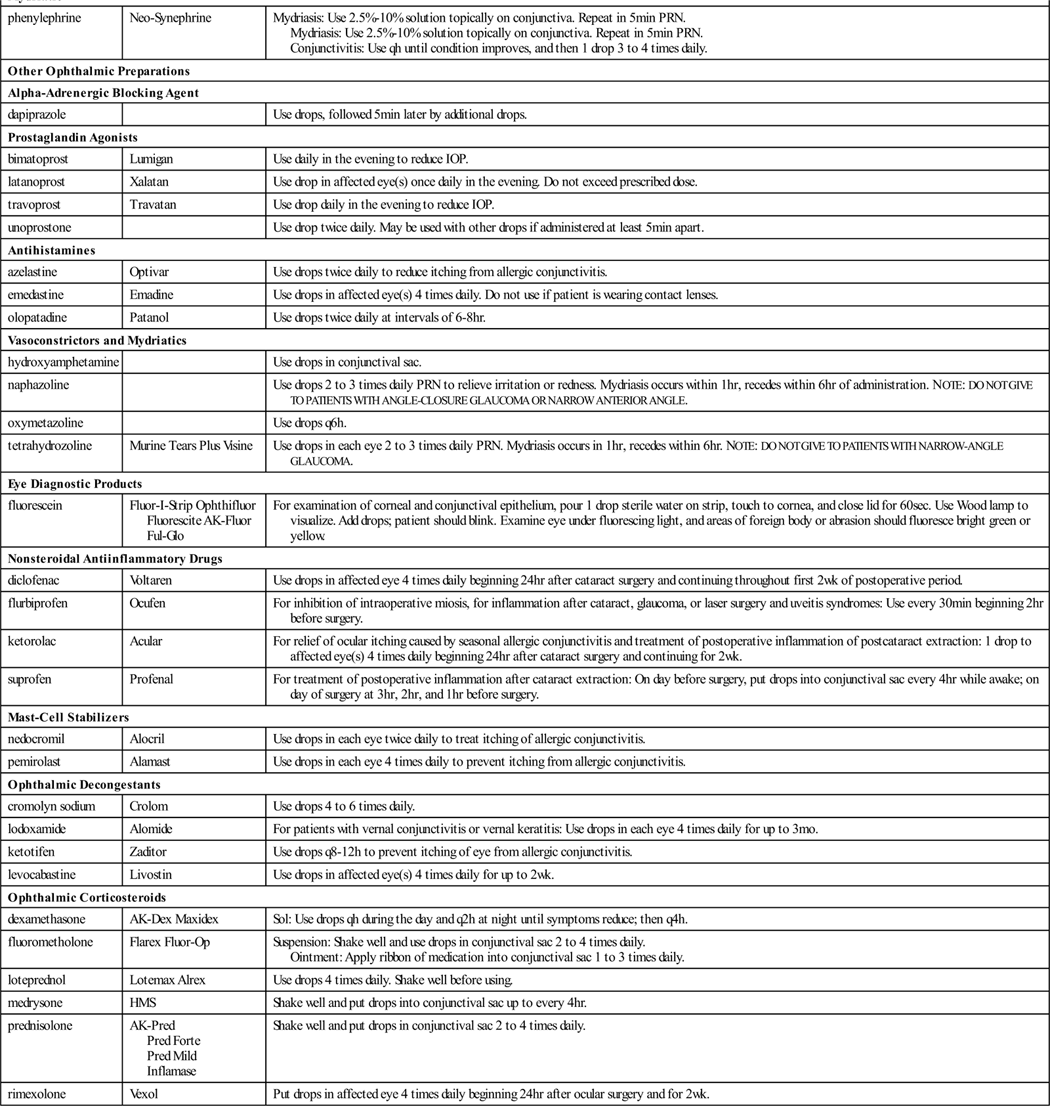
Ophthalmic Drugs
Action and Uses
A wide variety of preparations are used for eye problems (Table 23-3). Local anesthetics are useful in procedures such as tonometry, gonioscopy, cataract surgery, and removal of foreign bodies from the cornea. Antiseptics are compounds capable of preventing infection. They are used for the prevention of gonorrheal ophthalmia neonatorum when babies are born or any time germicidal or astringent (tissue constricting) action is needed. Antiinfectives are used to treat common eye infections caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses. Artificial tears provide lubrication to relieve dry eyes, eye irritation secondary to wearing contact lenses, or deficient tear production caused by a wide variety of disorders. Diagnostic products include topical fluorescein stains, which are used to detect foreign bodies or scratches.
![]() Table 23-3
Table 23-3
| GENERIC NAME | TRADE NAME | COMMENTS |
| Local Anesthetics | ||
| benoxinate | Fluress | Often used when suturing of eye is required. Use before eye procedures. |
| proparacaine | Alcaine | Use immediately before tonometry, 2-3 min before suture removal or removal of foreign body. |
| tetracaine | Pontocaine | Use drops or ointment to lower conjunctival area. |
| Antiseptic Ointments | ||
| silver nitrate | Silver Nitrate | After birth, clean infant’s eyes with cotton ball and use 2 gtt 1% solution once. |
| Ophthalmic Antiinfectives (Preparations Must be Labeled “Ophthalmic”) | ||
| Alpha2-Adrenergic Agonist | ||
| brimonidine | Alphagan P | Use 1 drop in the affected eye(s) q8h. |
| Antibiotics | ||
| bacitracin | AK-Tracin | Apply sparingly into conjunctival sac 2 to 3 times daily. |
| chloramphenicol | Apply small amount of ointment to lower conjunctival sac, or use 2 drops of solution q3h for the first 48 hr, then PRN. Continue for at least 48 hr after the eye appears to be normal. | |
| ciprofloxacin | Ciloxan | Put into conjunctival sac, close eyes, and apply light pressure over lacrimal sac for 1 minute. |
| erythromycin | Ilotycin | Apply to affected eye 3 times daily or more often, depending on severity of infection. |
| gentamicin | Garamycin Genoptic Gentacidin |
Put drops into affected eye q4h. In severe infections, dosage may be increased to hourly. Apply ointment sparingly 2 to 3 times daily. |
| levofloxacin | Quixin Levaquin | Use drops in the affected eye(s) q2h while awake, up to 8 times/day for 2 days. Then use drops in affected eye(s) q4h while awake, up to 4 times/day for days 3 through 7. |
| norfloxacin | Noroxin | Put into conjunctival sac, close eyes, and apply light pressure over lacrimal sac for 1 min after. |
| ofloxacin | Ocuflox | Put into conjunctival sac, close eyes, and apply light pressure over lacrimal sac for 1 min after. |
| polymyxin B | polymyxin B | Use very hour PRN. |
| sulfacetamide sodium | AK-Sulf Sodium Sulamyd | Use drops q2-3h during day, less at night. May also apply ointment in lower conjunctival sac at night. |
| tobramycin | Tobrex AK-Tob | Use drops 4 to 6 times daily. |
| Antiviral Agents | ||
| fomivirsen | Adults: Use a single intravitreal injection every other week for 2 doses followed by maintenance dose once every 4 wk in treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis. | |
| ganciclovir | Vitrasert | Used in treating cytomegalovirus retinitis in patients with AIDS. Provided as a 4.5-mg insert designed to release drug over a 5- to 8-mo period. May be repeated as needed. |
| trifluridine | Viroptic | Put onto ulcerated cornea of eye q2h while awake for a maximum of 9 drops/day. Continue until reepithelialization, then for 7 days give q4h while awake. |
| Artificial Tears | ||
| — | Isopto Tears Liquifilm Forte Refresh Plus Systane Tearisol Tears Plus |
Drops may be used in eyes 3 to 4 times daily or PRN. Some preparations, such as Tearisol, are not to be used with soft contact lenses. Keep solution free from contamination. |
| — | Lacrisert | Insert once a day into inferior cul-de-sac beneath base of tarsus. |
| Antiglaucoma Agents | ||
| Sympathomimetics | ||
| apraclonidine | Iopidine | Use solution before laser surgery. |
| dipivefrin | Propine | Put into eyes q12h. |
| epinephrine |
Use drops into affected eyes daily to twice daily. | |
| Use daily or twice daily. | ||
| Beta Blockers | ||
| betaxolol | Betoptic | Use drops twice daily. |
| carteolol | Ocupress | Use drops twice daily. |
| levobetaxolol | Betaxon | Use drops twice daily. |
| levobunolol | Betagan Liquifilm |
Use drops daily. |
| metipranolol | OptiPranolol | Use drops twice daily. |
| timolol | Timoptic | Use drops twice daily. |
| Miotics, Direct-Acting | ||
| acetylcholine Cl | Miochol-E | Use drops 3 times daily. |
| carbachol | Isopto-carbachol | Use drops up to 3 times daily. |
| pilocarpine | Pilocar Pilostat | Use drops up to 6 times daily. |
| pilocarpine ocular therapeutic system | Ocusert | The system is placed in and removed from the eye by the patient, according to instructions in the package. Releases 20 or 40 mcg pilocarpine per hour for 1 wk. |
| Miotics, Cholinesterase Inhibitors | ||
| demecarium | Put drops into eyes daily. | |
| echothiophate | Phospholine Iodide | Use drops daily. |
| Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors | ||
| brinzolamide | Azopt | Use 3 times daily. |
| dorzolamide | Trusopt | Use 3 times daily. |
| Mydriatic-Cycloplegics | ||
| atropine | Use solution daily to 3 times daily, or ointment daily to 3 times daily. | |
| cyclopentolate | Cyclogyl | Use 1% or 2% solution; repeat in 5 min. Refraction can occur in 40-50 min. |
| homatropine | Isopto-Homatropine | Use 2% or 5% solution; repeat 2 to 5 times until desired results occur. |
| scopolamine | Isopto Hyoscine | Use 0.25% solution daily to 3 times daily. |
| tropicamide | Mydriacyl | Use 1% solution; repeat in 5 min. |
| Mydriatic | ||
| phenylephrine | Neo-Synephrine | Mydriasis: Use 2.5%-10% solution topically on conjunctiva. Repeat in 5 min PRN. Mydriasis: Use 2.5%-10% solution topically on conjunctiva. Repeat in 5 min PRN. Conjunctivitis: Use qh until condition improves, and then 1 drop 3 to 4 times daily. |
| Other Ophthalmic Preparations | ||
| Alpha-Adrenergic Blocking Agent | ||
| dapiprazole | Use drops, followed 5 min later by additional drops. | |
| Prostaglandin Agonists | ||
| bimatoprost | Lumigan | Use daily in the evening to reduce IOP. |
| latanoprost | Xalatan | Use drop in affected eye(s) once daily in the evening. Do not exceed prescribed dose. |
| travoprost | Travatan | Use drop daily in the evening to reduce IOP. |
| unoprostone | Use drop twice daily. May be used with other drops if administered at least 5 min apart. | |
| Antihistamines | ||
| azelastine | Optivar | Use drops twice daily to reduce itching from allergic conjunctivitis. |
| emedastine | Emadine | Use drops in affected eye(s) 4 times daily. Do not use if patient is wearing contact lenses. |
| olopatadine | Patanol | Use drops twice daily at intervals of 6-8 hr. |
| Vasoconstrictors and Mydriatics | ||
| hydroxyamphetamine | Use drops in conjunctival sac. | |
| naphazoline | Use drops 2 to 3 times daily PRN to relieve irritation or redness. Mydriasis occurs within 1 hr, recedes within 6 hr of administration. NOTE: DO NOT GIVE TO PATIENTS WITH ANGLE-CLOSURE GLAUCOMA OR NARROW ANTERIOR ANGLE. | |
| oxymetazoline | Use drops q6h. | |
| tetrahydrozoline | Murine Tears Plus Visine | Use drops in each eye 2 to 3 times daily PRN. Mydriasis occurs in 1 hr, recedes within 6 hr. NOTE: DO NOT GIVE TO PATIENTS WITH NARROW-ANGLE GLAUCOMA. |
| Eye Diagnostic Products | ||
| fluorescein | Fluor-I-Strip Ophthifluor Fluorescite AK-Fluor Ful-Glo | For examination of corneal and conjunctival epithelium, pour 1 drop sterile water on strip, touch to cornea, and close lid for 60 sec. Use Wood lamp to visualize. Add drops; patient should blink. Examine eye under fluorescing light, and areas of foreign body or abrasion should fluoresce bright green or yellow. |
| Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs | ||
| diclofenac | Voltaren | Use drops in affected eye 4 times daily beginning 24 hr after cataract surgery and continuing throughout first 2 wk of postoperative period. |
| flurbiprofen | Ocufen | For inhibition of intraoperative miosis, for inflammation after cataract, glaucoma, or laser surgery and uveitis syndromes: Use every 30 min beginning 2 hr before surgery. |
| ketorolac | Acular | For relief of ocular itching caused by seasonal allergic conjunctivitis and treatment of postoperative inflammation of postcataract extraction: 1 drop to affected eye(s) 4 times daily beginning 24 hr after cataract surgery and continuing for 2 wk. |
| suprofen | Profenal | For treatment of postoperative inflammation after cataract extraction: On day before surgery, put drops into conjunctival sac every 4 hr while awake; on day of surgery at 3 hr, 2 hr, and 1 hr before surgery. |
| Mast-Cell Stabilizers | ||
| nedocromil | Alocril | Use drops in each eye twice daily to treat itching of allergic conjunctivitis. |
| pemirolast | Alamast | Use drops in each eye 4 times daily to prevent itching from allergic conjunctivitis. |
| Ophthalmic Decongestants | ||
| cromolyn sodium | Crolom | Use drops 4 to 6 times daily. |
| lodoxamide | Alomide | For patients with vernal conjunctivitis or vernal keratitis: Use drops in each eye 4 times daily for up to 3 mo. |
| ketotifen | Zaditor | Use drops q8-12h to prevent itching of eye from allergic conjunctivitis. |
| levocabastine | Livostin | Use drops in affected eye(s) 4 times daily for up to 2 wk. |
| Ophthalmic Corticosteroids | ||
| dexamethasone | AK-Dex Maxidex | Sol: Use drops qh during the day and q2h at night until symptoms reduce; then q4h. |
| fluorometholone | Flarex Fluor-Op | Suspension: Shake well and use drops in conjunctival sac 2 to 4 times daily. Ointment: Apply ribbon of medication into conjunctival sac 1 to 3 times daily. |
| loteprednol | Lotemax Alrex | Use drops 4 times daily. Shake well before using. |
| medrysone | HMS | Shake well and put drops into conjunctival sac up to every 4 hr. |
| prednisolone | AK-Pred Pred Forte Pred Mild Inflamase |
Shake well and put drops in conjunctival sac 2 to 4 times daily. |
| rimexolone | Vexol | Put drops in affected eye 4 times daily beginning 24 hr after ocular surgery and for 2 wk. |
AIDS, Acquired immune deficiency syndrome; IOP, intraocular pressure; PRN, as needed; Sol, solution.![]() Indicates “Must-Know Drugs,” or the 35 drugs most prescribers use.
Indicates “Must-Know Drugs,” or the 35 drugs most prescribers use.
Increased intraocular pressure is a sign of the eye condition called glaucoma. This condition results from either excess production or reduced outflow of aqueous humor (ocular fluid). There are three major forms of glaucoma. Primary glaucoma includes narrow-angle glaucoma and wide-angle glaucoma. Patients with narrow-angle glaucoma have a shallow anterior chamber, possibly because of the anatomy or physiologic action they were born with. Drugs are used to control the acute problem before there is a permanent surgical solution. Wide-angle glaucoma has a gradual onset, and its control depends on permanent drug therapy. Secondary glaucoma may result from other eye problems such as cataract extraction; it is treated with medication. Congenital glaucoma is a birth defect requiring surgical correction. Medications for treating glaucoma use a variety of mechanisms to increase outflow of aqueous humor.
Antiglaucoma agents make up a large class of medications with a variety of actions. Mydriatic-cycloplegics block the action of acetylcholine. The sphincter of the iris is paralyzed, causing mydriasis, or abnormal dilation (opening) of the pupil, and the ciliary muscles are paralyzed, blocking accommodation (the ability to switch from near to far vision and back), or adjustment of the focus of the eye. These agents are used in some tests for glaucoma. Atropine and scopolamine are long-acting agents that produce complete cycloplegia, or paralysis. Homatropine, cyclopentolate, and tropicamide have shorter durations of action and are most useful for diagnostic procedures. Long-acting cholinesterase inhibitors include miotic-antiglaucoma agents that inactivate acetylcholinesterase. This provides iris sphincter contraction, leading to miosis (small pupils), and ciliary muscle constriction, which leads to increased aqueous humor outflow. Parasympathomimetic or miotic drugs, such as carbachol, act as cholinergic agonists to reduce intraocular pressure by causing iris sphincter contraction, leading to miosis. This allows an increased outflow of aqueous humor by opening up the anterior chamber angle. Cholinesterase inhibitors such as physostigmine salicylate briefly inactivate acetylcholinesterase to allow acetylcholine to accumulate, which increases parasympathetic tone. This causes iris sphincter contraction, resulting in miosis, increased ciliary muscle constriction, and an increase in aqueous humor outflow. Timolol is a beta blocker that reduces intraocular pressure, probably by reducing the formation of aqueous humor. Sympathomimetic agents such as epinephrine produce vasoconstriction (narrowing of the blood vessels) and decreased intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma, probably as a result of decreased production of aqueous humor. Phenylephrine acts as a mydriatic, causing constriction of the dilator muscles of the pupil, leading to mydriasis and vasoconstriction of the arterioles of the conjunctiva. Vasoconstrictors such as naphazoline cause direct stimulation of the alpha receptors of vascular smooth muscle, leading to vasoconstriction. This action lasts for several hours.
Before administering any ophthalmic agent, it is especially important for the nurse to learn whether the patient has a history of glaucoma. Dilating the pupils of a patient who may have glaucoma could provoke angle closure and lead to a surgical emergency.
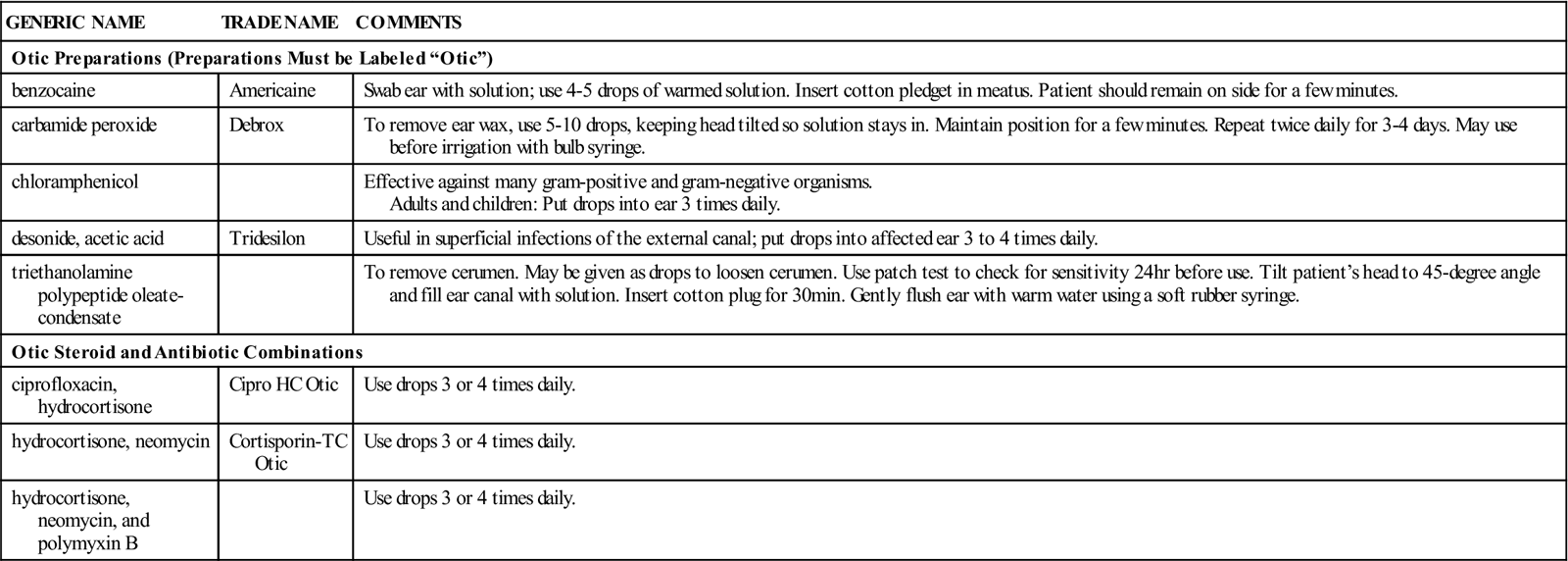
Otic Preparations
Action and Uses
Topical antibiotics are used to control superficial infections of the ear through bactericidal or bacteriostatic mechanisms. Other products may be used for prophylaxis of infections in swimmers and for removing cerumen (earwax) plugs. There are also some steroid products available for ear problems. Check the package inserts of individual products for precautions, contraindications, and adverse effects. Table 23-4 presents a summary of otic preparations.
![]() Table 23-4
Table 23-4
| GENERIC NAME | TRADE NAME | COMMENTS |
| Otic Preparations (Preparations Must be Labeled “Otic”) | ||
| benzocaine | Americaine | Swab ear with solution; use 4-5 drops of warmed solution. Insert cotton pledget in meatus. Patient should remain on side for a few minutes. |
| carbamide peroxide | Debrox | To remove ear wax, use 5-10 drops, keeping head tilted so solution stays in. Maintain position for a few minutes. Repeat twice daily for 3-4 days. May use before irrigation with bulb syringe. |
| chloramphenicol | Effective against many gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. Adults and children: Put drops into ear 3 times daily. |
|
| desonide, acetic acid | Tridesilon | Useful in superficial infections of the external canal; put drops into affected ear 3 to 4 times daily. |
| triethanolamine polypeptide oleate-condensate | To remove cerumen. May be given as drops to loosen cerumen. Use patch test to check for sensitivity 24 hr before use. Tilt patient’s head to 45-degree angle and fill ear canal with solution. Insert cotton plug for 30 min. Gently flush ear with warm water using a soft rubber syringe. | |
| Otic Steroid and Antibiotic Combinations | ||
| ciprofloxacin, hydrocortisone | Cipro HC Otic | Use drops 3 or 4 times daily. |
| hydrocortisone, neomycin | Cortisporin-TC Otic | Use drops 3 or 4 times daily. |
| hydrocortisone, neomycin, and polymyxin B | Use drops 3 or 4 times daily. | |
Topical Skin Preparations
Action and Uses
Topical preparations for the skin may include medicated bar soaps and foams, sulfur preparations, topical antibiotics, and medications used for acne. A wide variety of steroids are also available for topical use in a variety of dermatologic disorders. These preparations come in mild, intermediate, and strong concentrations. Fluorinated products should not be used on the face because they may cause thinning of the skin and leave scars. Steroids should not be used if there is strong indication of bacterial or fungal infection because the steroid may suppress the action of the antibiotic or antifungal and allow the infection to get worse.
Antipsoriatics accelerate scaling and healing of dry lesions in chronic psoriasis. Antiseborrheic shampoos promote shedding and softening of the horny cell layer and inhibit the growth of microorganisms in seborrhea and dandruff. There are now antiviral agents used to treat herpes simplex. These agents help reduce the severity of symptoms and lengthen the time between outbreaks. Scabicides are applied to the skin and in the hair to treat scabies, a condition caused by the microscopic mite Sarcoptes scabiei. Pediculicides are used to treat pediculosis, an infestation with lice seen mostly in children. There are also a variety of burn preparations, cauterizing agents, emollients, keratolytics, and wet dressings and soaks on the market. These agents all have their own individual precautions, adverse reactions, and drug interactions. The specific product information should be consulted. These preparations are summarized in Table 23-5. Any of the chemicals in these products may interact with other medications the patient may be taking.
![]() Table 23-5
Table 23-5
| GENERIC NAME | TRADE NAME | COMMENTS |
| Acne Products | ||
| adapalene | Differin | Wash face then apply a thin film of gel once daily to affected areas. An exacerbation of acne may initially be seen; therapeutic results usually seen in 8-12 wk. |
| azelaic | Azelex | Wash face and dry thoroughly. Then apply thin film twice daily to affected areas and gently massage into skin. Results usually seen in 4 wk. |
| benzoyl peroxide cream and soaps | Clearasil Desquam-X Oxy Oil-Free Acne Wash |
Apply daily to affected areas after cleansing skin. After 3-4 days, if redness, dryness, and peeling do not occur, increase application to twice daily. Use instead of soap. These products promote drying of skin and provide a gentle abrasive action when applied. If undue skin irritation develops, stop use and contact nurse, physician, or other health care provider. Available OTC. |
| isotretinoin | Accutane |
This product must not be taken by women who are pregnant, because severe fetal abnormalities may be produced. Women in childbearing years should be protected by adequate contraception methods during the course of therapy. Cystic acne: Dosage may adjusted for individual weight and severity of disease. |
| sulfur preparations | Liquimat | Thin film of medication should be applied daily or twice daily to clean skin. Used to treat oily skin and mild acne. |
| tazarotene | Tazorac | Wash face and then apply a thin film to affected areas once daily. |
| tretinoin | Retin-A Vesanoid |
Wash face and apply to affected area daily at bedtime. Start with low doses; may irritate skin initially. Makes individuals more sensitive to the sun, necessitating sunscreen. Evidence suggests that this product restores skin collagen and turgor, reversing fine wrinkles. Not for use by pregnant women. |
| Topical Antiinfectives | ||
| bacitracin | Baciguent | Apply small amount to infected area 3 times daily; comes as cream. |
| chloramphenicol | Chloromycetin | Apply small amount to infected area 3 times daily; comes as cream. |
| clindamycin | Cleocin T | Apply small amount to infected area twice daily. |
| erythromycin | Akne-Mycin | Apply small amount to infected area 3 times daily; comes as cream. |
| gentamicin | Apply small amount to infected area 3 times daily; comes as cream. | |
| mupirocin | Bactroban | New topical antibiotic. Used to treat impetigo; may produce superinfection. Apply small amount to affected area 3 times daily. May cover with gauze. Must be reevaluated within 3 days. |
| neomycin sulfate | Apply small amount to infected area 3 times daily; comes as cream. | |
| Combination Products | ||
| polymyxin B, neomycin, and bacitracin | Neosporin | Apply small amount to infected area 3 times daily; comes as ointment. |
| polymyxin B | Polysporin | Apply small amount to infected area 3 times daily; comes as ointment. |
| Topical Corticosteroids | ||
| alclometasone | Aclovate | For relief of inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses. Apply sparingly to affected areas 2 to 4 times daily. |
| amcinonide | Cyclocort | Apply sparingly to affected areas 2 to 4 times daily. |
| betamethasone dipropionate | Diprolene | Fluorinated product, relatively expensive. Comes as cream, lotion, ointment, or topical aerosol. Use sparingly for dermatoses needing antiinflammatory medication. |
| betamethasone valerate | Beta-Val Valisone |
Fluorinated product that may be used with occlusive dressings; comes as cream, lotion, or ointment. Apply sparingly daily to 3 times daily for adults. |
| desonide | Tridesilon | Gently rub in medication 2 to 4 times daily. |
| desoximetasone | Topicort | Do not use near eyes; apply sparingly daily to twice daily. |
| diflorasone | Maxiflor | Apply sparingly to affected areas 2 to 4 times daily. |
| fluocinolone acetonide | Synalar | Rub cream in gently, 2 to 4 times daily. Apply very sparingly; use less frequent applications for children. |
| fluocinonide | Lidex | Comes as cream, gel, or ointment; apply 3 to 4 times daily. |
| flurandrenolide | Cordran | Shake lotion well; protect from light, heat, and freezing. Also comes as a film tape. Apply sparingly 2 to 3 times daily. |
| halcinonide | Halog | Ointment, cream, solution; protect ointment from light. Apply sparingly 2 to 3 times daily. |
| hydrocortisone |
Cortizone Hycort | One of the few steroids that can be used safely on the face, axilla, and groin, and under the breasts. Comes as ointment, cream, or lotion. Apply thin coat once daily to 4 times daily; increase strength as indicated by condition. |
| hydrocortisone acetate | Cortaid Lanacort 5 | This form is more expensive. Apply thin coat of ointment or apply the cream gently and sparingly. Apply once daily to 4 times daily as needed by condition. The lowest doses are available without a prescription. |
| hydrocortisone plus antibiotics | Cortisporin | Comes with neomycin sulfate and polymyxin B. Apply to affected area 2 to 3 times daily; withdraw gradually if medication has been used for a long time. |
| methylprednisolone | Medrol | Very expensive; apply ointment once daily to 4 times daily. |
| triamcinolone acetonide | Aristocort Kenalog |
Fluorinated steroid, highest potency; has many precautions to use. Apply to affected area 2 to 4 times daily. Do not use on face. |
| triamcinolone plus antifungals | Mycolog II | Many precautions and warnings. Apply ointment to affected areas 2 to 3 times daily. Ototoxicity (damage to the ear) and nephrotoxicity (damage to the kidney) have been reported if preparation is overused. |
| Anesthetics for Mucous Membranes and Skin | ||
| benzocaine | Solarcaine Babee Teething lotion | Used for sunburn, wounds, toothaches, mouth ulcers, and lesions of oral mucosa. Apply 20% aerosol or gel to affected areas 2 to 3 times daily. |
| dibucaine | Nupercainal | For abrasions, minor burns, sunburn, and hemorrhoids. Apply ointment or cream sparingly to affected area 2 to 3 times daily. |
| tetracaine | Pontocaine | Used in treating hemorrhoids and minor skin disorders. Apply sparingly 3 to 4 times daily. |
| Antipsoriatics | ||
| acitretin | Soriatane | Systemic psoriasis therapy for severe disease. |
| anthralin | Anthra Forte | Apply thin layer of 0.1% ointment once to twice daily for 2 wk. |
| calcipotriene | Dovonex | Synthetic vitamin D3 derivative indicated for topical treatment of moderate plaque psoriasis. Calcipotriene is similar to vitamin D3 in its effects on keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation, yet it has a less potent effect on calcium metabolism. Also modifies immune activity of monocytes, macrophages, and T lymphocytes. In clinical trials, improvement in psoriasis noted within 2 wk of initiating topical therapy (twice-daily application). Approximately 70% of patients have shown marked improvement after 8 wk of therapy, with 10% showing complete clearing. Apply thin layer twice daily and rub in completely. |
| tazarotene | Tazorac | For topical treatment of patients with stable plaque psoriasis with approximately 20% body surface area involvement. The 0.1% gel also is indicated for mild to moderately severe facial acne vulgaris. |
| Antiseborrheic Products | ||
| povidone-iodine | Betadine | Shampoo with 2 tsp to hair and scalp. Lather with warm water and rinse. Repeat application and allow to remain on scalp 5 min; rinse thoroughly. Use twice weekly until improvement, then once weekly. |
| selenium | Selsun Blue | Massage 1-2 tsp into wet scalp. Allow medicated shampoo to remain on scalp for 2-3 min; rinse thoroughly; repeat application and rinse. Use twice weekly for 2 wk, then weekly for 2 wk. |
| Antiviral Agents | ||
| acyclovir | Zovirax | For treatment of herpes simplex. Cover all lesions q3h, 6 times per day for 6 days. Approximately 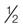 -inch ribbon of ointment per 4 square inches of surface area should be used. Oral forms are available for treatment of herpes labialis (cold sores). -inch ribbon of ointment per 4 square inches of surface area should be used. Oral forms are available for treatment of herpes labialis (cold sores). |
| penciclovir | Denavir | Apply cream q2h while awake for 4 days. Start treatment as early as possible to reduce symptoms. |
| Burn Preparations | ||
| mafenide | Sulfamylon | Apply once or twice daily to a thickness of approximately 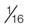 inch. No dressing required. inch. No dressing required. |
| nitrofurazone | Furacin | Soluble dressing: apply directly to lesions daily; topical cream: apply directly to lesion once daily or every few days. |
| silver nitrate | Silver Nitrate | Saturate dressing with warmed solution and apply to burn wound. Mold dressing to body surface and cover with dry dressing. Reapply solution q2h. Change dressing at least once daily. |
| silver sulfadiazine | Silvadene | Apply once or twice daily to a thickness of approximately 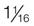 inch. No dressing required. inch. No dressing required. |
| Scabicides and Pediculicides | ||
| crotamiton | Eurax | Used in scabies and very pruritic skin conditions. Massage into skin of the whole body; apply a second coating 24 hr later. Clothing and bed linen should be changed after 24 hr. Bath should be taken 48 hr after the last application. |
| malathion | Ovide | Apply to hair and let hair dry naturally. Wash after 8-12 hr and comb hair. Repeat in 7-9 days, if necessary. |
| permethrin | Elimite Nix Acticin |
Massage into skin from scalp to soles of feet. Wash off after 8-14 hr. For pediculosis capitis in infants, wet hair, shampoo, and then apply medication to hairline, neck, scalp, temple, and forehead, and wash off after 10 min |
| Miscellaneous Skin Preparations | ||
| Cauterizing Agents | ||
| dichloroacetic acid | Bichloracetic Acid | Apply petrolatum to tissue surrounding area to be treated. Solution should then be carefully applied to lesion. A kit is provided with detailed instructions. |
| monochloroacetic acid | Mono-Chlor | Used for removing verrucae or warts. Do not drip solution on normal tissue or mucous membranes. Apply solution with cotton-tipped applicator or capillary tube. Cover with bandage and allow to remain in place for 4-6 days. May require more than one application. |
| podofilox | Condylox | Apply solution or gel to venereal warts morning and evening with a cotton-tipped applicator. |
| podophyllum resin | Podofin Podocon-25 | Applied to venereal warts only by health care provider. Cleanse area and then apply sparingly to lesion. Leave on 30-40 min to check sensitivity, and no longer than 4 hr. Remove with alcohol or soap and water. |
| silver nitrate solution or sticks | Apply to local area as needed. | |
| trichloroacetic acid | Tri-Chlor | Use on débrided skin to remove verruca. Apply to wart, then cover for 5-6 days. Peel off wart tissue. |
| Emollients | ||
| colloidal baths | Alpha Keri Aveeno | Bath additives for treating widespread eruptions. Limit bath time to 30 min; patient should be aware that preparations often make tub slippery. Follow directions on packet or bottle. |
| dexpanthenol | Panthoderm | Stimulates epithelization and granulation. Aids in the healing of skin lesions and relieves pruritus. Apply directly to clean skin once to twice daily. |
| salicylic acid | Mediplast-Salacid Wart-Off | Use creams for corns and calluses. Apply directly to area daily for 2 wk. Cut out piece of plaster to fit callus or apply gels to well-hydrated skin. Check callus q24h; discontinue if irritation develops. |
| urea | Aquacare Nutraplus | Hydrates skin and aids in removing scales and crusts. Apply directly to clean skin 2 to 3 times daily, affected area only. |
| vitamin E | Vite E Cream Vitec | Apply cream or ointment to skin to hydrate. |
| Vitamins A, D, and E | Retinol Clocream | Apply cream or ointment to skin. |
| Smoking Cessation Products | ||
| nicotine transdermal system | Nicoderm CQ Nicotrol | Used to decrease withdrawal symptoms as part of smoking cessation program. No serious side effects. In association with behavior modification programs, use patch daily. Use 2 wk at each of 3 strengths in decreasing order of strength. |
| nicotine gum | Nicorette | Use 2- or 4-mg gum to reduce cravings. Chew gum steadily, and then place gum against buccal membranes. |
| nicotine inhalation system | Nicotrol Inhaler | 4-mg inhaler. Used as part of withdrawal system. |
| nicotine nasal spray | Nicotrol NS | Spray 0.5 mg into nostril to reduce symptoms of withdrawal. |
| Wet Dressings and Soaks | ||
| Burow’s solution | Domeboro | Used for open wet dressings in inflammatory conditions of skin; cool and dry through evaporation, which causes local vasoconstriction. Moisten dressing and apply multiple layers to prevent rapid drying and cooling. Reapply every 15-30 min as indicated for 4-8 hr. |
OTC, Over the counter.![]() Indicates “Must-Know Drugs,” or the 35 drugs most prescribers use.
Indicates “Must-Know Drugs,” or the 35 drugs most prescribers use.
Complementary And Alternative Products
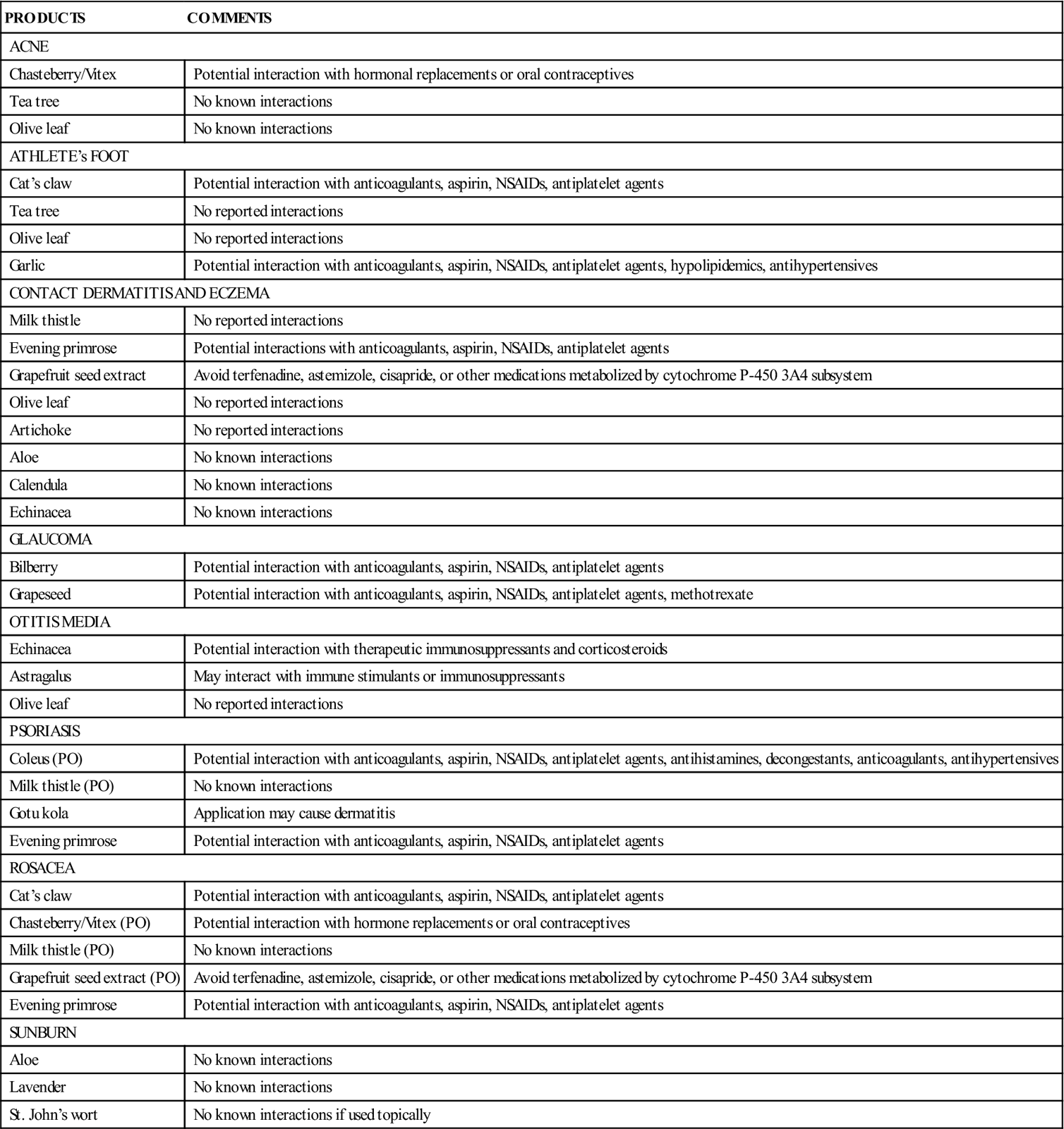
Patients use a wide variety of topical herbal products. The Complementary and Alternative Therapies box summarizes common herbal preparations and their potential for interactions with other medications.