Immunologic Medications
Objectives
1. Define common terms used in immunology.
2. Explain the differences between the three different types of immunity.
3. Outline typical immunization plans for children and adults.
4. List the major adverse reactions of common immunologic drugs.
Key Terms
antigen-antibody response (ĂN-tĭ-jĕn-ĂN-tĭ-bŏ-dē, p. 400)
antiserums (ĂN-tĭ-sĭ-rŭmz, p. 404)
artificially acquired active immunity (ĭ-MŪ-nĭ-tē, p. 400)
immunity (ĭ-MŪ-nĭ-tē, p. 400)
naturally acquired active immunity (ĭ-MŪ-nĭ-tē, p. 400)
passive immunity (PĂ-sĭv ĭ-MŪ-nĭ-tē, p. 404)
toxoid (TŎKS-ŏyd, p. 404)
vaccines (văk-SĒNZ, p. 400)
![]() http://evolve.elsevier.com/Edmunds/LPN/
http://evolve.elsevier.com/Edmunds/LPN/
Overview
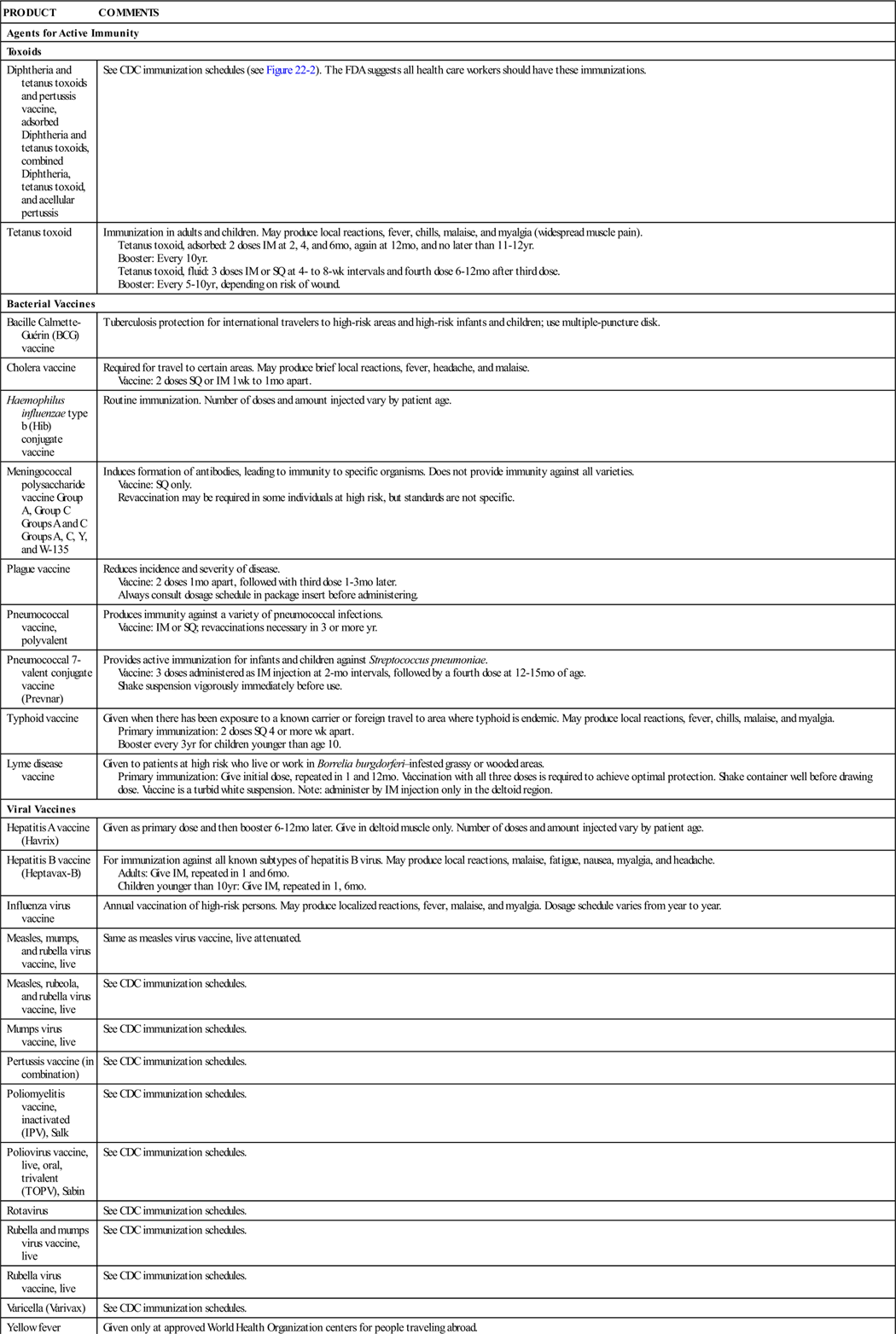
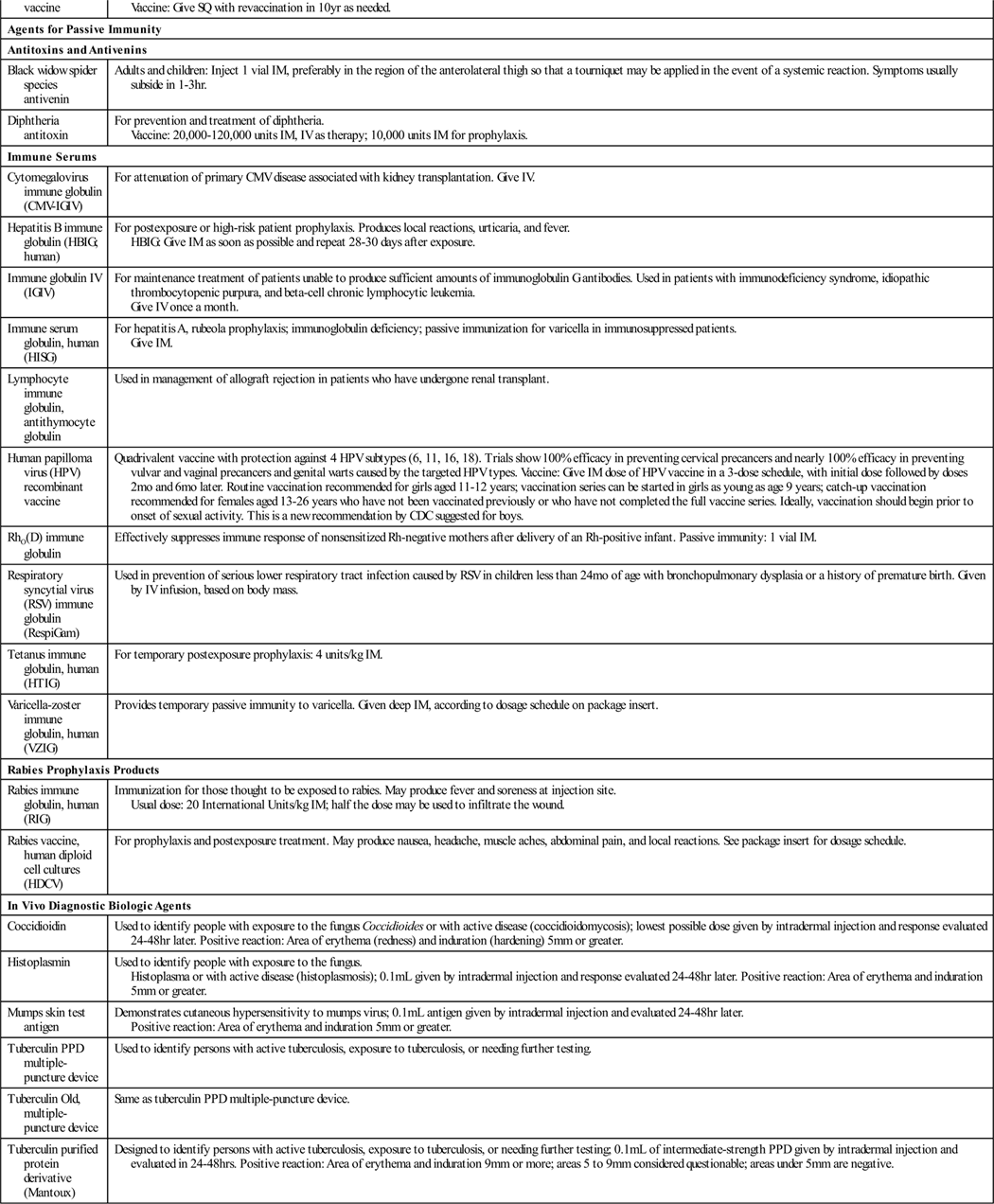
Immunologic agents are biologic preparations such as vaccines, toxoids, and other serologic agents used primarily to prevent or modify disease in an otherwise healthy person. Depending on the formulation of the biologic agents, they provide active or passive immunity to specific diseases. These different mechanisms are discussed in general, with specific product information presented later in Table 22-1.
![]() Table 22-1
Table 22-1
| PRODUCT | COMMENTS |
| Agents for Active Immunity | |
| Toxoids | |
| Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and pertussis vaccine, adsorbed Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids, combined Diphtheria, tetanus toxoid, and acellular pertussis |
See CDC immunization schedules (see Figure 22-2). The FDA suggests all health care workers should have these immunizations. |
| Tetanus toxoid | Immunization in adults and children. May produce local reactions, fever, chills, malaise, and myalgia (widespread muscle pain). Tetanus toxoid, adsorbed: 2 doses IM at 2, 4, and 6 mo, again at 12 mo, and no later than 11-12 yr. Booster: Every 10 yr. Tetanus toxoid, fluid: 3 doses IM or SQ at 4- to 8-wk intervals and fourth dose 6-12 mo after third dose. Booster: Every 5-10 yr, depending on risk of wound. |
| Bacterial Vaccines | |
| Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine | Tuberculosis protection for international travelers to high-risk areas and high-risk infants and children; use multiple-puncture disk. |
| Cholera vaccine | Required for travel to certain areas. May produce brief local reactions, fever, headache, and malaise. Vaccine: 2 doses SQ or IM 1 wk to 1 mo apart. |
| Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine | Routine immunization. Number of doses and amount injected vary by patient age. |
| Meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine Group A, Group C Groups A and C Groups A, C, Y, and W-135 |
Induces formation of antibodies, leading to immunity to specific organisms. Does not provide immunity against all varieties. Vaccine: SQ only. Revaccination may be required in some individuals at high risk, but standards are not specific. |
| Plague vaccine | Reduces incidence and severity of disease. Vaccine: 2 doses 1 mo apart, followed with third dose 1-3 mo later. Always consult dosage schedule in package insert before administering. |
| Pneumococcal vaccine, polyvalent | Produces immunity against a variety of pneumococcal infections. Vaccine: IM or SQ; revaccinations necessary in 3 or more yr. |
| Pneumococcal 7-valent conjugate vaccine (Prevnar) | Provides active immunization for infants and children against Streptococcus pneumoniae. Vaccine: 3 doses administered as IM injection at 2-mo intervals, followed by a fourth dose at 12-15 mo of age. Shake suspension vigorously immediately before use. |
| Typhoid vaccine | Given when there has been exposure to a known carrier or foreign travel to area where typhoid is endemic. May produce local reactions, fever, chills, malaise, and myalgia. Primary immunization: 2 doses SQ 4 or more wk apart. Booster every 3 yr for children younger than age 10. |
| Lyme disease vaccine | Given to patients at high risk who live or work in Borrelia burgdorferi–infested grassy or wooded areas. Primary immunization: Give initial dose, repeated in 1 and 12 mo. Vaccination with all three doses is required to achieve optimal protection. Shake container well before drawing dose. Vaccine is a turbid white suspension. Note: administer by IM injection only in the deltoid region. |
| Viral Vaccines | |
| Hepatitis A vaccine (Havrix) | Given as primary dose and then booster 6-12 mo later. Give in deltoid muscle only. Number of doses and amount injected vary by patient age. |
| Hepatitis B vaccine (Heptavax-B) | For immunization against all known subtypes of hepatitis B virus. May produce local reactions, malaise, fatigue, nausea, myalgia, and headache. Adults: Give IM, repeated in 1 and 6 mo. Children younger than 10 yr: Give IM, repeated in 1, 6 mo. |
| Influenza virus vaccine | Annual vaccination of high-risk persons. May produce localized reactions, fever, malaise, and myalgia. Dosage schedule varies from year to year. |
| Measles, mumps, and rubella virus vaccine, live | Same as measles virus vaccine, live attenuated. |
| Measles, rubeola, and rubella virus vaccine, live | See CDC immunization schedules. |
| Mumps virus vaccine, live | See CDC immunization schedules. |
| Pertussis vaccine (in combination) | See CDC immunization schedules. |
| Poliomyelitis vaccine, inactivated (IPV), Salk | See CDC immunization schedules. |
| Poliovirus vaccine, live, oral, trivalent (TOPV), Sabin | See CDC immunization schedules. |
| Rotavirus | See CDC immunization schedules. |
| Rubella and mumps virus vaccine, live | See CDC immunization schedules. |
| Rubella virus vaccine, live | See CDC immunization schedules. |
| Varicella (Varivax) | See CDC immunization schedules. |
| Yellow fever vaccine | Given only at approved World Health Organization centers for people traveling abroad. Vaccine: Give SQ with revaccination in 10 yr as needed. |
| Agents for Passive Immunity | |
| Antitoxins and Antivenins | |
| Black widow spider species antivenin | Adults and children: Inject 1 vial IM, preferably in the region of the anterolateral thigh so that a tourniquet may be applied in the event of a systemic reaction. Symptoms usually subside in 1-3 hr. |
| Diphtheria antitoxin | For prevention and treatment of diphtheria. Vaccine: 20,000-120,000 units IM, IV as therapy; 10,000 units IM for prophylaxis. |
| Immune Serums | |
| Cytomegalovirus immune globulin (CMV-IGIV) | For attenuation of primary CMV disease associated with kidney transplantation. Give IV. |
| Hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG; human) | For postexposure or high-risk patient prophylaxis. Produces local reactions, urticaria, and fever. HBIG: Give IM as soon as possible and repeat 28-30 days after exposure. |
| Immune globulin IV (IGIV) | For maintenance treatment of patients unable to produce sufficient amounts of immunoglobulin G antibodies. Used in patients with immunodeficiency syndrome, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, and beta-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Give IV once a month. |
| Immune serum globulin, human (HISG) | For hepatitis A, rubeola prophylaxis; immunoglobulin deficiency; passive immunization for varicella in immunosuppressed patients. Give IM. |
| Lymphocyte immune globulin, antithymocyte globulin | Used in management of allograft rejection in patients who have undergone renal transplant. |
| Human papilloma virus (HPV) recombinant vaccine | Quadrivalent vaccine with protection against 4 HPV subtypes (6, 11, 16, 18). Trials show 100% efficacy in preventing cervical precancers and nearly 100% efficacy in preventing vulvar and vaginal precancers and genital warts caused by the targeted HPV types. Vaccine: Give IM dose of HPV vaccine in a 3-dose schedule, with initial dose followed by doses 2 mo and 6 mo later. Routine vaccination recommended for girls aged 11-12 years; vaccination series can be started in girls as young as age 9 years; catch-up vaccination recommended for females aged 13-26 years who have not been vaccinated previously or who have not completed the full vaccine series. Ideally, vaccination should begin prior to onset of sexual activity. This is a new recommendation by CDC suggested for boys. |
| RhO(D) immune globulin | Effectively suppresses immune response of nonsensitized Rh-negative mothers after delivery of an Rh-positive infant. Passive immunity: 1 vial IM. |
| Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) immune globulin (RespiGam) | Used in prevention of serious lower respiratory tract infection caused by RSV in children less than 24 mo of age with bronchopulmonary dysplasia or a history of premature birth. Given by IV infusion, based on body mass. |
| Tetanus immune globulin, human (HTIG) | For temporary postexposure prophylaxis: 4 units/kg IM. |
| Varicella-zoster immune globulin, human (VZIG) | Provides temporary passive immunity to varicella. Given deep IM, according to dosage schedule on package insert. |
| Rabies Prophylaxis Products | |
| Rabies immune globulin, human (RIG) | Immunization for those thought to be exposed to rabies. May produce fever and soreness at injection site. Usual dose: 20 International Units/kg IM; half the dose may be used to infiltrate the wound. |
| Rabies vaccine, human diploid cell cultures (HDCV) | For prophylaxis and postexposure treatment. May produce nausea, headache, muscle aches, abdominal pain, and local reactions. See package insert for dosage schedule. |
| In Vivo Diagnostic Biologic Agents | |
| Coccidioidin | Used to identify people with exposure to the fungus Coccidioides or with active disease (coccidioidomycosis); lowest possible dose given by intradermal injection and response evaluated 24-48 hr later. Positive reaction: Area of erythema (redness) and induration (hardening) 5 mm or greater. |
| Histoplasmin | Used to identify people with exposure to the fungus. Histoplasma or with active disease (histoplasmosis); 0.1 mL given by intradermal injection and response evaluated 24-48 hr later. Positive reaction: Area of erythema and induration 5 mm or greater. |
| Mumps skin test antigen | Demonstrates cutaneous hypersensitivity to mumps virus; 0.1 mL antigen given by intradermal injection and evaluated 24-48 hr later. Positive reaction: Area of erythema and induration 5 mm or greater. |
| Tuberculin PPD multiple-puncture device | Used to identify persons with active tuberculosis, exposure to tuberculosis, or needing further testing. |
| Tuberculin Old, multiple-puncture device | Same as tuberculin PPD multiple-puncture device. |
| Tuberculin purified protein derivative (Mantoux) | Designed to identify persons with active tuberculosis, exposure to tuberculosis, or needing further testing; 0.1 mL of intermediate-strength PPD given by intradermal injection and evaluated in 24-48 hrs. Positive reaction: Area of erythema and induration 9 mm or more; areas 5 to 9 mm considered questionable; areas under 5 mm are negative. |
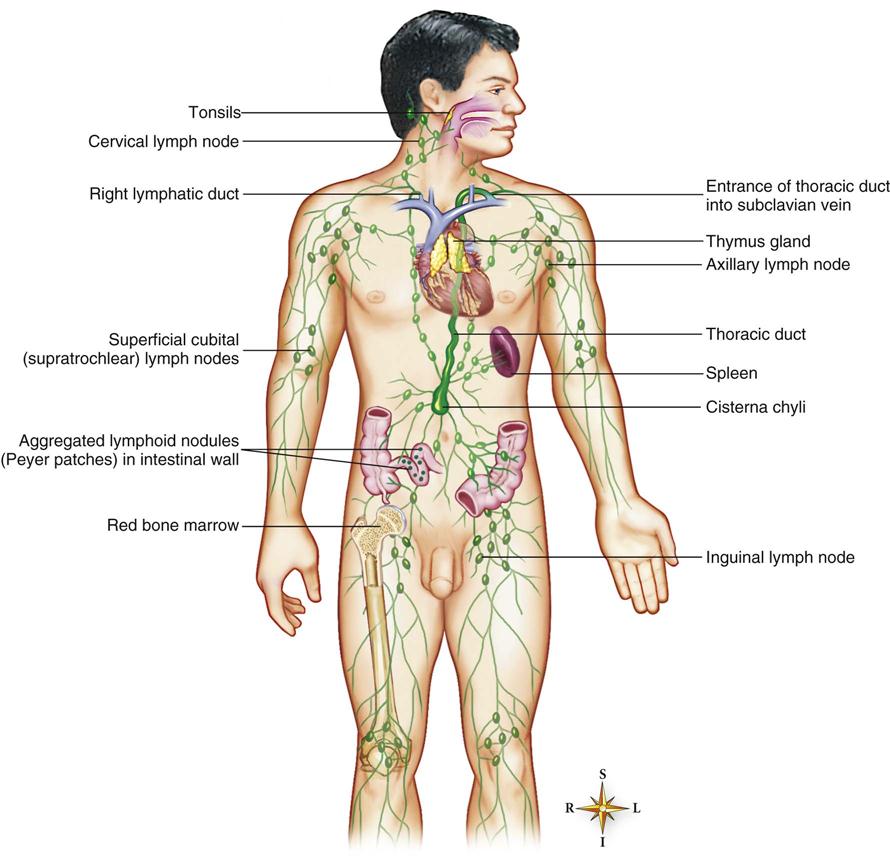
Immune System
The immune system is part of the lymphatic system, which is made up of the lymph vessels, lymph nodes, and other lymph organs (Figure 22-1). This system removes foreign substances from the blood and lymph, combats disease, maintains tissue fluid balance, and absorbs fats. It moves lymph from its source, the body tissues, to the point where it reenters the bloodstream. The structures of the lymphatic system are of two kinds: those concerned with the transport of lymph (lymph capillaries, lymph vessels, and lymph ducts) and those composed mostly of lymphatic tissue but serving other specific functions (lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, and thymus—together these structures are called lymph organs).
The lymphatic system produces the T cells that help provide immunity and moves them throughout the lymphatic system.
Action 
A bacterium, virus, or foreign protein that invades the body is called an antigen. The body senses the foreign antigen and responds by making antibodies. Antibodies are special proteins made by the lymphatic tissue and the reticuloendothelial system; they are designed to help neutralize or resist the effects of invading foreign proteins. In this antigen-antibody response, a specific antigen causes the body to produce an antibody that reacts specifically with that antigen. Some antibodies keep circulating for the life of the person, providing constant active immunity to certain antigens. Other antibodies are active for only a short period, providing passive immunity.
The antigen-antibody response results in immunity, or resistance to invading proteins and diseases. One way a person can develop immunity is by having a disease and recovering from it. An example is when a child develops chickenpox, and the body develops antibodies to the chickenpox virus. These antibodies travel around in the bloodstream for the rest of the person’s lifetime, providing naturally acquired active immunity.
The lymphoid tissue and the reticuloendothelial system tissues will also produce antibodies to a live but weakened antigen (known as a live, attenuated antigen) or an antigen that has been killed. Laboratories can produce vaccines that contain either attenuated or killed antigens, and people can be immunized to prevent them from getting some diseases. This is called artificially acquired active immunity. Whether a weak or dead antigen is given depends on the disease and on what the research has shown is the best way to protect patients. Rubeola (measles) vaccine is an example of a vaccine made from live, attenuated measles antigen. A person who is vaccinated against measles develops a very mild case of measles. The immune system then produces antibodies that protect the person from getting a full infection with measles. Some diseases may require periodic booster injections of vaccine to keep the antibody level high enough to protect the patient from disease.
Some disease-causing proteins that come from invading bacteria are called toxins. Toxins act like antigens to stimulate the immune system to produce antitoxins, which act to neutralize the toxins in the same way antibodies neutralize antigens. When a toxin is attenuated, or weakened, it is called a toxoid. A toxoid can be used to produce immunity because the body cannot distinguish between the toxin and the toxoid. The most common example is the use of tetanus toxoid to protect patients from Clostridium tetani.
Once a person has had an antigen-antibody response, the antibodies are stored in the body. Immune globulins are specific types of protein antibodies that are stored in blood serum and plasma. Concentrated immune globulins are also called antiserums; they may be collected from human or animal sources. A common example is the hepatitis B immune globulin. These antibodies can be injected into a person who does not have immunity to the antigen. The antibodies then circulate to immediately protect this person, but the protection lasts for only a short time. This form of protection is called artificially acquired passive immunity. A type of temporary immunity can also occur when antibodies pass from the mother to the fetus through the placenta or to the nursing infant through breast milk. This is known as naturally acquired passive immunity.
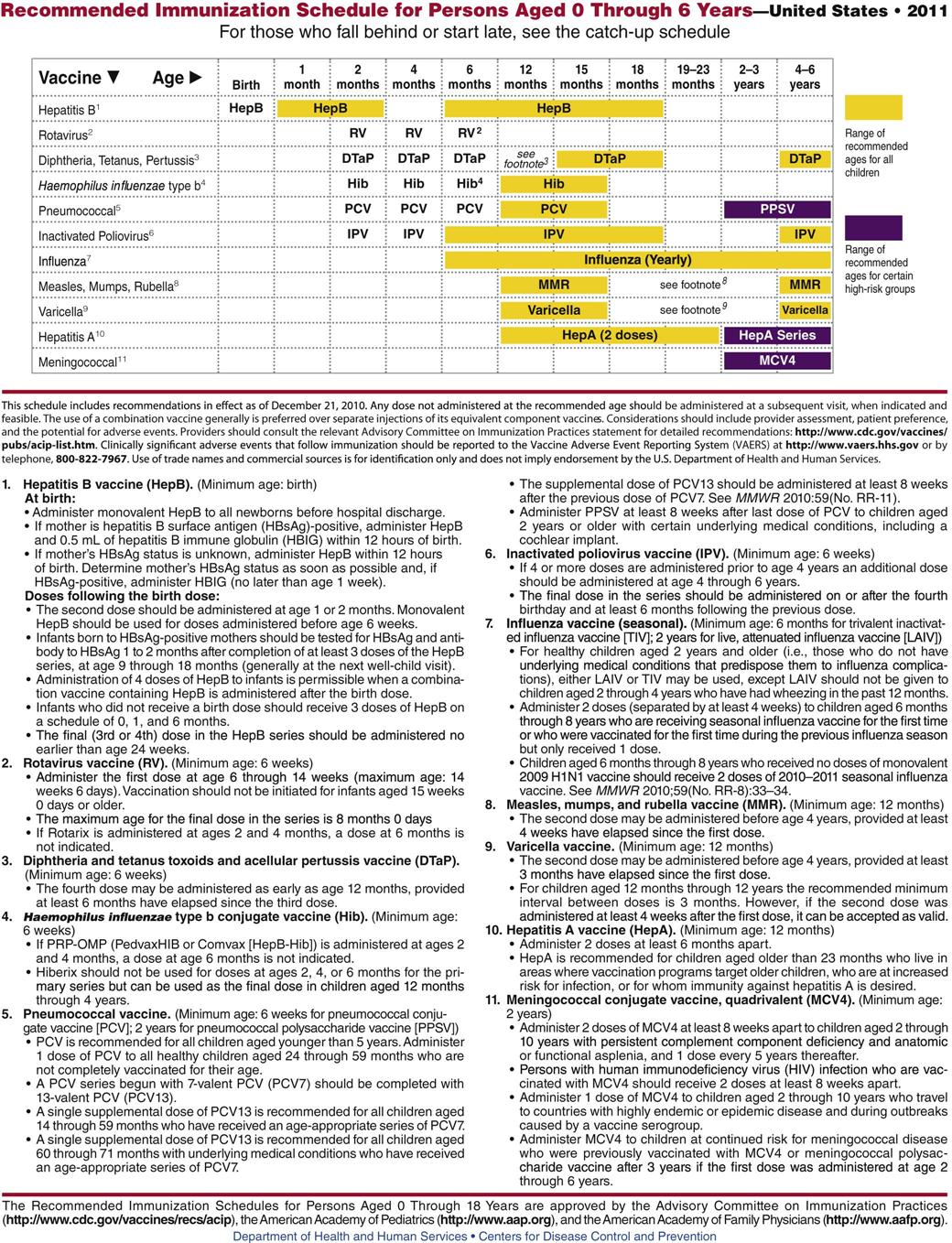
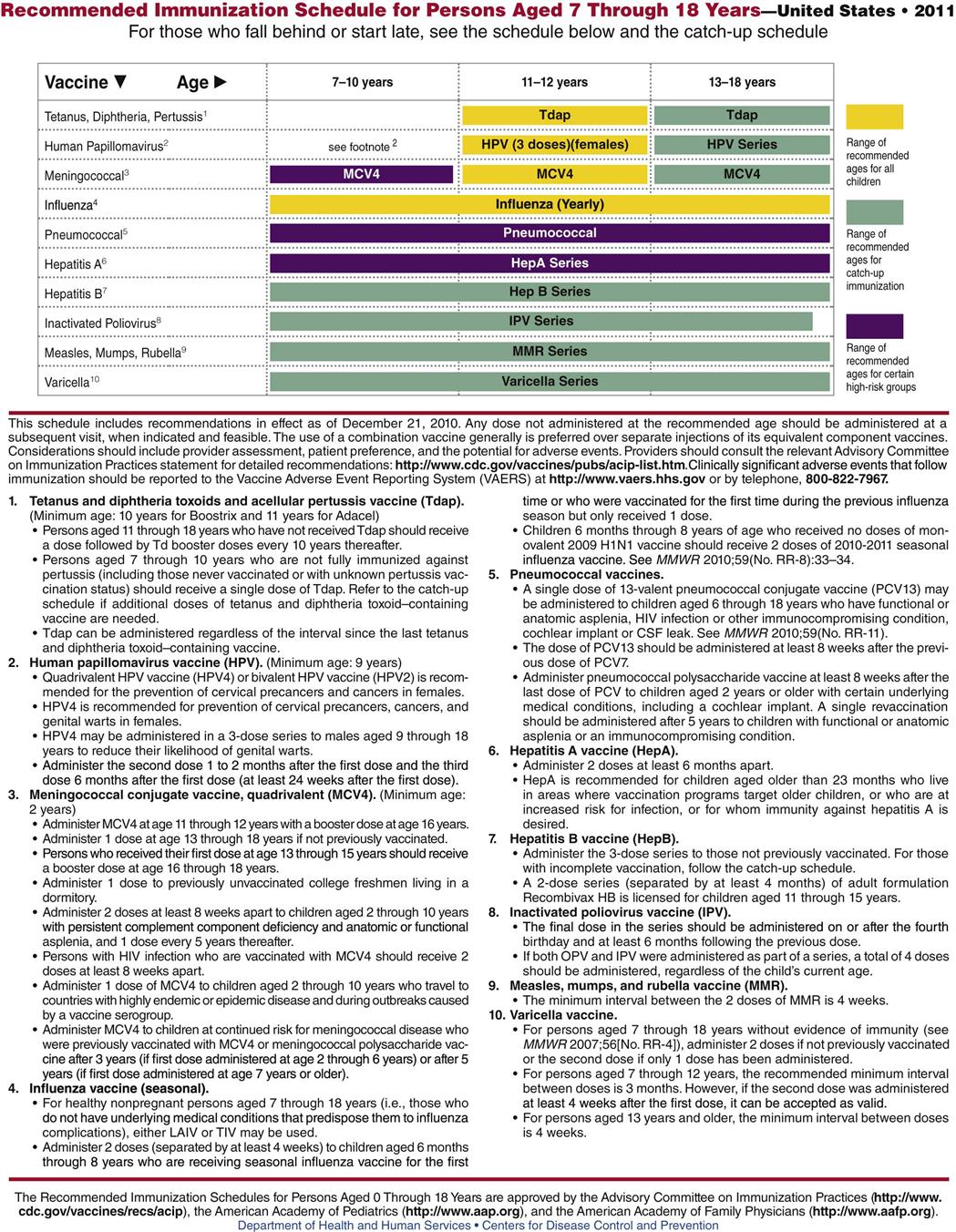
Infants and children can be immunized against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, Haemophilus influenzae type B, polio, measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella. These primary immunizations dramatically reduce the incidence of disease in a community and lower mortality and morbidity rates from diseases that were once fatal to many young children. Although most children in the United States have been immunized by the time they enter school, the United States lags behind many other countries in the percentage of children immunized at an early age. Children who are homeschooled often are not immunized. Thus these diseases continue to be widespread and to do damage, particularly when young children bring infections home to older individuals whose immunity may be impaired. We now know that some early immunizations lose their ability to provide long-term immunity. Thus some adults who were vaccinated when they were children may develop pertussis or other diseases to which they believed they were immune. Widespread failure of diphtheria-pertussis-tetanus immunizations led to high rates of pertussis in California recently and guidelines now suggest that all health care providers have pertussis booster immunizations to increase their own immunity.
Every year different immunizations are offered for seasonal flu. As epidemics develop for particular diseases, such as H1N1 influenza, a limited number of immunizations are available. Health care workers should take advantage of these immunizations to protect themselves and to limit exposing their families to these organisms.
Two widespread fallacies have led to the lowered rate of immunizations for children. The first is that immunizations should be withheld if the child is sick. In most cases, a child should be immunized even if they have a mild upper respiratory tract infection or other infection. The second is the fear created by the idea that vaccine immunization in children is linked to the development of autism. There have been no reputable scientific studies to suggest this connection. Licensed practical and vocational nurses should immunize their own children and educate those around them that the risks to children not being immunized is greater than getting an immunization.
Uses
Vaccines and toxoids are the biologic agents used in the routine schedule of active immunizations for adults and children. Specific biologic agents are reserved for use in people who live in areas where specific diseases (e.g., yellow fever, cholera, typhoid) are endemic (common in the community), and there is a high risk of infection. Other vaccines (e.g., pneumococcal vaccine, influenza vaccine) are recommended for people at high risk for specific diseases such as pneumonia or flu.
An additional group of biologic agents (e.g., purified protein derivative [PPD], histoplasmin, coccidioidin) is used in screening procedures to identify people who have been exposed to a specific disease or who may have an active disease such as tuberculosis.
In special circumstances, certain biologic agents (e.g., gamma globulins) may be useful to modify a disease process in the previously unimmunized person.
Adverse Reactions
In general, mild adverse effects of vaccines and other immune agents are common and include localized pain and swelling that are typically mild and of short duration. Claims that immunizations are linked to other health problems have not been supported by scientific studies and data. Although it is true there are rare instances of more serious problems, the risk of complications from the disease far outweighs the risk of adverse effects for all biologic products. Adverse effects occasionally seen include altered levels of consciousness, headaches, lethargy (sleepiness), rash, urticaria (hives), vesiculation (blistering), diarrhea, increased respiratory rate, shortness of breath, arthralgia (joint pain), fever, lymphadenopathy, and malaise (weakness).
Most states have laws requiring infants and children to be properly immunized before starting school. To reduce the liability faced by pharmaceutical companies, a special fund, the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program, has been established by the federal government to reimburse medical costs incurred if a patient has a serious adverse effect from required immunizations. A certain percentage of the fee paid by the patient for each immunization goes toward this fund, which is administered by the Public Health Service, a division of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Drug Interactions
When several vaccines are given at the same time—for example, when cholera, plague, and typhoid vaccines are given together—the potential for adverse effects is increased. Someone who has passive immunity to a disease (has received antibodies from a maternal or a vaccine source or through blood products) may not have an adequate active antibody response to the administration of a live, attenuated vaccine.
 Nursing Implications and Patient Teaching
Nursing Implications and Patient Teaching
n Assessment
Find out as much as possible about the patient’s health history, including the patient’s previous immunization status and reaction to biologic agents; history of allergy, especially to eggs or feathers; results of any known allergy testing; the presence of underlying disease or concurrent infections; the use of immunosuppressant drugs, immune serums, blood, or blood products; or the possibility of pregnancy.
The patient may have a history of exposure to a specific organism or might plan to travel to areas where disease may be common. Find out if the person is at risk for infection, as well as whether there are children who require primary immunizations. The U.S. State Department regularly issues travelers’ warnings, and the nurse can call the embassy of a foreign government to see if certain immunizations are required for entry into that country.
n Diagnosis
Determine the patient’s risk for infection. Has the patient or parent verbalized reservations about being able to return for scheduled immunizations? If so, the risk for noncompliance with the immunization schedule must be shared with the primary health care provider so that adjustments can be made. Enhancing the likelihood that immunizations will be completed involves the entire health care team.
n Planning
The best policy is that immunizations should not be given to patients with active infection, severe febrile illness, or a history of serious side effects from previous vaccinations. Live, attenuated vaccine is usually contraindicated in pregnancy. To be safe, clinicians often do not provide immunizations to children who are being seen for minor illnesses. However, because many children are taken to the health care provider only when they are ill, clinicians may have to give the immunizations then. Otherwise, they may lose a very valuable opportunity to provide increased protection to the child.
Many biologic agents are prepared with animal serum or in chick embryos. Thus people with known allergies may have sensitivity reactions to these preparations. Live, attenuated virus vaccine should not be given if there is a recent history of acquired passive antibodies (immune globulins).
Patients should be screened for current illness. There is an increased risk in using immunologic agents in any person with a compromised immune status (for example, neonates, older adult patients, patients on immunosuppressive therapy, patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome, or patients with chronic disease).
All vaccines should be used with caution in women who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
n Implementation
It is important to follow specific protocols and schedules for administration. There are usually specialized storage instructions, modes of administration, sites, and site preparation techniques for each vaccine. It is also important to consult the package insert for each manufacturer’s product information, because these products often differ in some way.
Figure 22-2 shows the dosage schedule recommended for primary immunization of infants, children, and adolescents.
Uncomfortable reactions to active vaccines are frequent and generally range from localized irritation and soreness to a systemic response with fever, malaise, and anorexia (lack of appetite). Specific biologic agents may predispose the patient to a variety of allergic reactions. These range from a localized rash, pruritus (itching), or urticaria to an anaphylactic (shock) reaction.
A record of the patient’s immunizations should be kept, and the patient should be provided with a copy of the record to take home for their personal file.
Occasionally, determining antibody blood titers before vaccine administration is helpful to assess antibody development. This is particularly true for rubella.
Table 22-1 provides a summary of agents used for immunity.
n Evaluation
Patients receiving immune serums should be evaluated for suppression of the disease. Other patients should be monitored for adverse effects. Adverse effects may occur immediately or be delayed for some time after the preparation has been administered. At all visits, patients should be asked whether their immunizations are current. There has been a decrease in the number of children who are getting the recommended immunizations over the past few years. In addition, few adults obtain the booster immunizations they need unless they are in the military, travel to foreign countries, or work in the food industry.