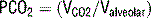CHAPTER 2 Respiratory and Pulmonary Physiology
1 What is the functional residual capacity? What factors affect it?
 Diaphragmatic muscle tone (individuals with paralyzed diaphragms have less FRC when compared to normal individuals)
Diaphragmatic muscle tone (individuals with paralyzed diaphragms have less FRC when compared to normal individuals)2 What is closing capacity? What factors affect the closing capacity? What is the relationship between closing capacity and functional residual capacity?
5 Discuss the factors that affect the resistance to gas flow. What is laminar and turbulent gas flow?
where R is resistance, L is the length of the tube, μ is the viscosity, and r is the radius of the tube. At higher flow rate (in obstructed airways and heavy breathing), the flow is turbulent. At these flows the major determinants of resistance to flow are the density of the gas (ρ) and the radius of the tube, r.
6 Suppose a patient has an indwelling 7-mm endotracheal tube and cannot be weaned because of the increased work of breathing. What would be of greater benefit, cutting off 4 cm of endotracheal tube or replacing the tube with one of greater internal diameter?
10 Review the different zones (of West) in the lung with regard to perfusion and ventilation
 Zone 1: Alveolar pressure (PAlv) exceeds pulmonary artery pressure (Ppa) and pulmonary venous pressure (Ppv), leading to ventilation without perfusion (alveolar dead space) (PAlv > Ppa > Ppv).
Zone 1: Alveolar pressure (PAlv) exceeds pulmonary artery pressure (Ppa) and pulmonary venous pressure (Ppv), leading to ventilation without perfusion (alveolar dead space) (PAlv > Ppa > Ppv). Zone 2: Pulmonary arterial pressure exceeds alveolar pressure, but alveolar pressure still exceeds venous pressure (Ppa > PAlv > Ppv). Blood flow in zone 2 is determined by arterial-alveolar pressure difference.
Zone 2: Pulmonary arterial pressure exceeds alveolar pressure, but alveolar pressure still exceeds venous pressure (Ppa > PAlv > Ppv). Blood flow in zone 2 is determined by arterial-alveolar pressure difference. Zone 3: Pulmonary venous pressure exceeds alveolar pressure, and flow is determined by the arterial-venous pressure difference (Ppa > Ppv >PAlv).
Zone 3: Pulmonary venous pressure exceeds alveolar pressure, and flow is determined by the arterial-venous pressure difference (Ppa > Ppv >PAlv).11 What are the alveolar gas equation and the normal alveolar pressure at sea level on room air?
The alveolar gas equation is used to calculate the alveolar oxygen partial pressure:
where PAO2 is the alveolar oxygen partial pressure, FiO2 is the fraction of inspired oxygen, Pb is the barometric pressure, PH2O is the partial pressure of water (47 mm Hg), PaCO2 is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide, and RQ is the respiratory quotient, dependent on metabolic activity and diet and is considered to be about 0.825. At sea level the alveolar partial pressure (PAO2) is:
Knowing the PaO2 allows us to calculate the alveolar-arterial O2 gradient (A-a gradient). Furthermore, by understanding the alveolar gas equation we can see how hypoventilation (resulting in hypercapnia) lowers PaO2, and therefore PaO2.
12 What is the A-a gradient and what is a normal value for this gradient?
14 What are the causes of hypoxemia?
 Low inspired oxygen concentration (FiO2): To prevent delivery of hypoxic gas mixtures during an anesthetic, oxygen alarms are present on the anesthesia machine.
Low inspired oxygen concentration (FiO2): To prevent delivery of hypoxic gas mixtures during an anesthetic, oxygen alarms are present on the anesthesia machine. Hypoventilation: Patients under general anesthesia may be incapable of maintaining an adequate minute ventilation because of muscle relaxants or the ventilatory depressant effects of anesthetic agents. Hypoventilation is a common problem after surgery.
Hypoventilation: Patients under general anesthesia may be incapable of maintaining an adequate minute ventilation because of muscle relaxants or the ventilatory depressant effects of anesthetic agents. Hypoventilation is a common problem after surgery. Shunt: Sepsis, liver failure, arteriovenous malformations, pulmonary emboli, and right-to-left cardiac shunts may create sufficient shunting to result in hypoxemia. Since shunted blood is not exposed to alveoli, hypoxemia caused by a shunt cannot be overcome by increasing FiO2.
Shunt: Sepsis, liver failure, arteriovenous malformations, pulmonary emboli, and right-to-left cardiac shunts may create sufficient shunting to result in hypoxemia. Since shunted blood is not exposed to alveoli, hypoxemia caused by a shunt cannot be overcome by increasing FiO2. Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch: Ventilation and perfusion of the alveoli in the lung ideally have close to a one-to-one relationship, promoting efficient oxygen exchange between alveoli and blood. When alveolar ventilation and perfusion to the lungs are unequal (V/Q mismatching), hypoxemia results. Causes of V/Q mismatching include atelectasis, lateral decubitus positioning, bronchial intubation, bronchospasm, pneumonia, mucous plugging, pulmonary contusion, and adult respiratory distress syndrome. Hypoxemia caused by V/Q mismatching can usually be overcome by increasing FiO2.
Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch: Ventilation and perfusion of the alveoli in the lung ideally have close to a one-to-one relationship, promoting efficient oxygen exchange between alveoli and blood. When alveolar ventilation and perfusion to the lungs are unequal (V/Q mismatching), hypoxemia results. Causes of V/Q mismatching include atelectasis, lateral decubitus positioning, bronchial intubation, bronchospasm, pneumonia, mucous plugging, pulmonary contusion, and adult respiratory distress syndrome. Hypoxemia caused by V/Q mismatching can usually be overcome by increasing FiO2.19 Define absolute shunt. How is the shunt fraction calculated?
where Qs is the physiologic shunt blood flow per minute, Qt is the cardiac output per minute, CiO2 is the ideal arterial oxygen concentration when V/Q = 1, CaO2 is arterial oxygen content, and CvO2 is mixed venous oxygen content. It is estimated that 2% to 5% of cardiac output is normally shunted through postpulmonary shunts, thus accounting for the normal alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient (A-a gradient). Postpulmonary shunts include the thebesian, bronchial, mediastinal, and pleural veins.
21 Calculate arterial and venous oxygen content (CaO2 and CvO2)
where 1.34 is the O2 content per gram hemoglobin, SaO2 is the hemoglobin saturation, [Hgb] is the hemoglobin concentration, and PaO2 is the arterial oxygen concentration.
and
23 How is PCO2 related to alveolar ventilation?
where VCO2 is total CO2 production and Valveolar is the alveolar ventilation (minute ventilation less the dead space ventilation). In general, minute ventilation and PCO2 are inversely related.
27 What are the causes of hypercarbia?
 Hypoventilation: Decreasing the minute ventilation ultimately decreases alveolar ventilation, increasing PCO2. Some common causes of hypoventilation include muscle paralysis, inadequate mechanical ventilation, inhalational anesthetics, and opiates.
Hypoventilation: Decreasing the minute ventilation ultimately decreases alveolar ventilation, increasing PCO2. Some common causes of hypoventilation include muscle paralysis, inadequate mechanical ventilation, inhalational anesthetics, and opiates. Increased CO2 production: Although CO2 production is assumed to be constant, there are certain situations in which metabolism and CO2 production are increased. Malignant hyperthermia, fever, thyrotoxicosis, and other hypercatabolic states are some examples.
Increased CO2 production: Although CO2 production is assumed to be constant, there are certain situations in which metabolism and CO2 production are increased. Malignant hyperthermia, fever, thyrotoxicosis, and other hypercatabolic states are some examples. Iatrogenic: The anesthesiologist can administer certain drugs to increase CO2. The most common is sodium bicarbonate, which is metabolized by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase to form CO2. CO2 is absorbed into the bloodstream during laparoscopic procedures. Rarely CO2-enriched gases can be administered. Carbon dioxide insufflation for laparoscopy is a cause. Exhaustion of the CO2 absorbent in the anesthesia breathing circuit can result in rebreathing of exhaled gases and may also result in hypercarbia.
Iatrogenic: The anesthesiologist can administer certain drugs to increase CO2. The most common is sodium bicarbonate, which is metabolized by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase to form CO2. CO2 is absorbed into the bloodstream during laparoscopic procedures. Rarely CO2-enriched gases can be administered. Carbon dioxide insufflation for laparoscopy is a cause. Exhaustion of the CO2 absorbent in the anesthesia breathing circuit can result in rebreathing of exhaled gases and may also result in hypercarbia.1. Barash P.G., Cullen B.F., Stoelting R.K. Clinical anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006;790-812.
2. Wilson W.C., Benumof J.L. Respiratory physiology and respiratory function during anesthesia. In: Miller R.D., editor. Miller’s anesthesia. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone; 2005:679-722.








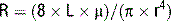
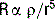

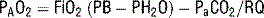
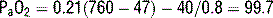
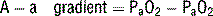
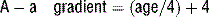







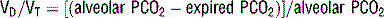
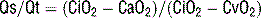
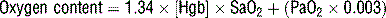
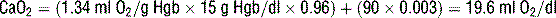
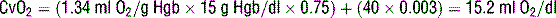
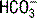 ) (70%), and combined with hemoglobin (23%).
) (70%), and combined with hemoglobin (23%).