History: A 42-year-old man presents with acute abdomen and right lower quadrant pain and tenderness.
1. What is the best diagnosis for this patient based on the imaging?
2. Which choice best characterizes the calcific density?
3. Which of the following statements about imaging of acute appendicitis is true?
B. An appendicolith is visible on plain radiography in 20% to 25% of cases.
C. Ultrasound is the modality of choice for children and young women.
4. Which of the following regarding CT imaging of the differential diagnosis of right lower quadrant pain is true?
C. Crohn’s disease is suggested by small bowel feces in the terminal ileum.
ANSWERS
CASE 2
Acute Appendicitis
1. A
2. A
3. C
4. D
Reference
Duran JC, Beidle TR, Perret R, et al: CT imaging of acute right lower quadrant disease. Am J Roentgenol. 1997;168:411–416.
Cross-Reference
Gastrointestinal Imaging: THE REQUISITES, 3rd ed, p 317.
Comment
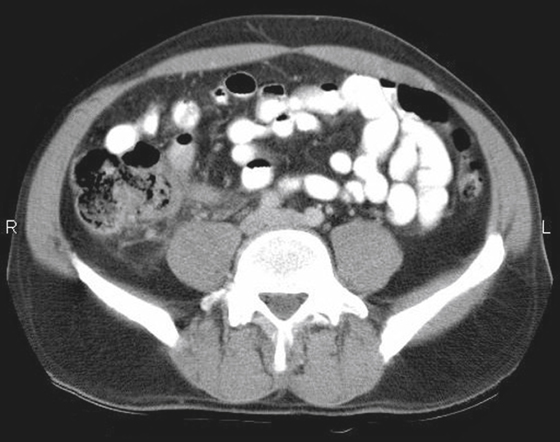
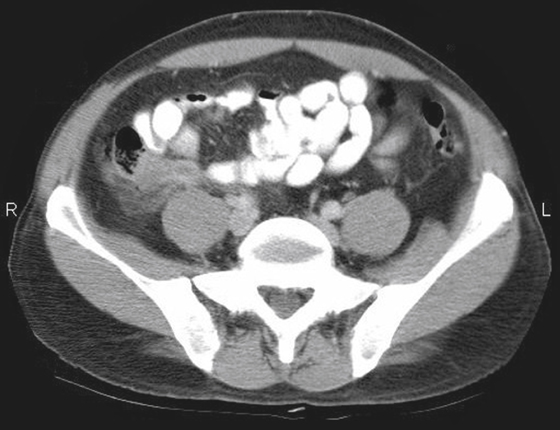
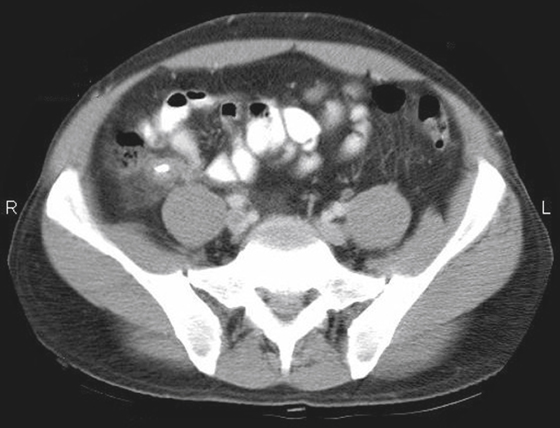
Acute appendicitis is a common abdominal emergency condition. Indeed, it is the most common acute abdominal emergency in industrialized countries. Its incidence is approximately 10 to 11 per 10,000, but it has been slowly declining. The surface anatomy of the appendix was first described by McBurney in the 19th century, giving rise to the well-known McBurney’s point in the right lower quadrant.
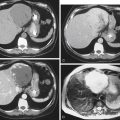
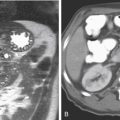
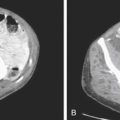
Although there has been much discussion about the merits of various modalities in the diagnosis, it is now clear that multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) is the imaging tool of choice. It is able to see the appendix easier than other methods, and it can also provide other crucial information, for example, regarding complications. Findings on MDCT include, in simple uncomplicated appendicitis, thickening of the appendix beyond 6 mm, appendiceal enhancement (vascular congestion), periappendiceal stranding, and occasionally small amounts of fluid around the appendix or in the cul-de-sac (see figures).
Plain film evaluation of appendicitis is usually not helpful. If a calcified appendicolith is seen in a patient with appropriate clinical symptoms, it is diagnostic (see figures). However, this is unusual. Occasionally one might see a focal ileus effect in the right lower quadrant, but by far the most common plain film finding is normal. Medical students and residents should discipline themselves to find the appendix on every abdominal CT case they encounter. Sometimes finding an unusually located appendix can be a chore. The more you do, the better you get at it.