CASE 191
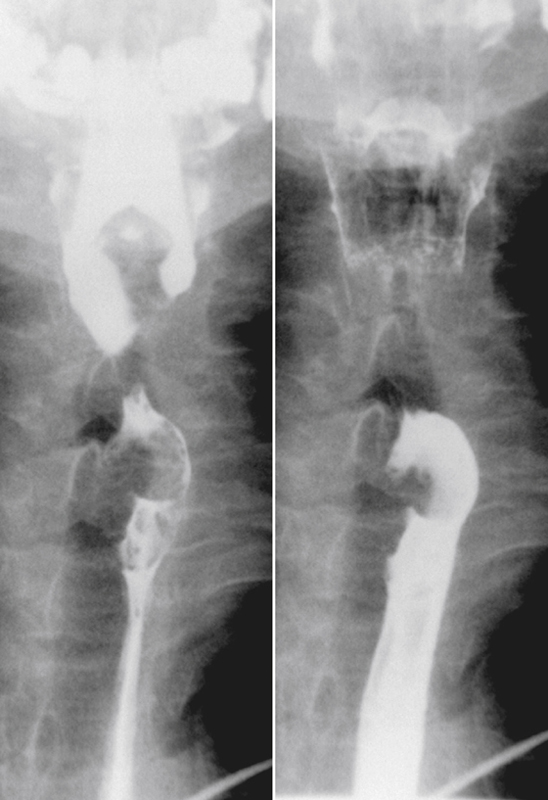
History: A 79-year-old man presents with dysphagia.
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis of the imaging finding shown in the figure? (Choose all that apply.)
2. What is the most common benign neoplasm of the esophagus?
3. What is the most common clinical presentation of a patient with a fibrovascular polyp of the esophagus?
4. Which of the following statements regarding fibrovascular polyps of the esophagus is false?
A. These lesions degenerate to malignant sarcomas.
B. These lesions are usually found in the proximal esophagus.
C. The lesion may appear of density less than water on CT imaging.
D. The lesion may appear of high signal intensity on T1-weighted MRI.
ANSWERS
CASE 191
Fibrovascular Esophageal Polyp
1. A, C, and E
2. A
3. A
4. A
References
Levine MS, Buck JL, Pantongrag-Brown L, et al: Fibrovascular polyps of the esophagus: clinical, radiographic, and pathologic findings in 16 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;166(4):781-787.
Cross-Reference
Gastrointestinal Imaging: THE REQUISITES, 3rd ed, p 10.
Comment
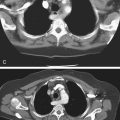
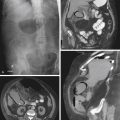
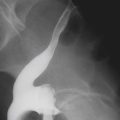
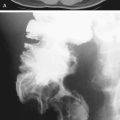
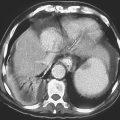
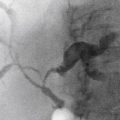
Polyps of the esophagus are unusual; the most common is the benign leiomyoma, or stromal cell tumor. They are usually solitary, but multiple leiomyomatosis of the esophagus has been encountered rarely. Fibrovascular polyps, which are composed of fibrovascular tissue, are also rare. Because of the presence of fatty tissue in some of these tumors, fibrovascular polyps may appear to have low density on CT scan. They have a propensity to develop in the upper portion of the esophagus, as seen in this case (see figure).
Fibrovascular polyps occur particularly in the cervical region of older patients, which is the opposite of most esophageal tumors, occurring typically seen in the middle to distal esophagus. These polyps occur more commonly in men. Because of their soft nature, these tumors can grow quite large before producing symptoms. The cervical location exposes the polyps to repeated peristalsis and dragging by ingested materials that may cause the tumors to become pedunculated or mobile. The most dramatic clinical finding is when the patient states that he or she has regurgitated a mass into the oropharynx and then swallowed it. These tumors may cause bleeding. If large enough, airway obstruction has been reported in these very mobile tumors.
Granular cell tumors are also rare and are believed to originate in Schwann cells. However, only about 10% occur in the gastrointestinal tract, usually the esophagus. Squamous cell papillomas in the esophagus have been reported, more frequently in men. Most are asymptomatic. It is unclear whether papillomas are true neoplasms.