CHAPTER 19 PSYCHIATRY
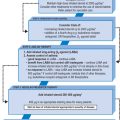
DEPRESSION
Management
Prescribing
ANXIETY
Diagnosis
Management
Prescribing
OBSESSIVE–COMPULSIVE DISORDER
INSOMNIA
Insomnia can be divided into acute and chronic. The chronic variety is more common in the elderly.
Diagnosis
PSYCHOSOMATIC ILLNESS
Management
The above process is often spread over many consultations and may be repeated as patients ‘relapse’.
FATIGUE
Management
SUICIDE
Premorbid diagnosis
Management
EATING DISORDERS
ANOREXIA NERVOSA
DEMENTIA
Seventy-five per cent of patients with Alzheimer’s disease die within 2–4 years of diagnosis.
Diagnosis
History.
Dementia is characterised by slowly progressive deterioration in cognitive function:
DISTURBED BEHAVIOUR
Management
Medical or psychiatric admission?
A patient with an acute psychiatric emergency should look generally well physically. There should be no suggestion of an acute medical problem and the predominant features of the illness should be a disturbance of thought or behaviour.
If the patient is unwilling to go into hospital, consider compulsory admission (p. 307).
VIOLENCE
After an episode of threatened or actual violence
SECTIONING
Requirements of the Act
How to organise a compulsory admission
BENZODIAZEPINE ADDICTION
Management
Patients who want to stop taking benzodiazepines
OPIATE ADDICTION
Diagnosis
Management
Prescribing controlled drugs.
(For the main rules, see p. 319.)
Additional rules for addicts include:
ALCOHOL ABUSE
Diagnosis
Alcohol abuse presents in a number of ways:
History.
The first task is to establish a diagnosis of alcohol abuse.
Management
Crisis intervention.
Occasionally the patient presents with an acute medical or psychiatric problem due to alcohol abuse:
Detoxification
SMOKING
Smoking is now recognised as an addiction treatable at the expense of the NHS.
NRT (nicotine replacement therapy) and bupropion are two forms of treatment available on the NHS.
Formulations
NRT patch
Using the patches.
Prescribe 3 weeks supply on an NHS prescription and get the patient to set a quit date. The patient stops smoking on the quit date and uses one patch every day. If they are still abstinent after 3 weeks then a further prescription for 3 weeks can be issued. Each brand of patch has its own schedule for dose reduction and total duration of use.