CASE 19
A married couple in your practice is planning their first pregnancy. They are both asthmatics, on regular inhalant therapy. They have both been hospitalized twice and one of them was intubated once for exacerbations. They are concerned to know the likelihood of a genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and so on, that might affect development of asthma in their child. You discuss these issues and the classic presentation and diagnosis of asthma.
QUESTIONS FOR GROUP DISCUSSION
RECOMMENDED APPROACH
THERAPY
Arachidonic Acid: Precursor of Leukotrienes
Arachidonic acid is released from the No. 2 position of membrane-bound glycerophospholipids (e.g., phosphatidylinositol) by the action of phospholipase A2 (PL-A2). Arachidonic acid may also be released from the No. 2 position of 1-2 diacylglycerol (DAG) by DAG lipase. DAG is generated after the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate by phospholipase C (PL-C). Activation of PL-A2 and PL-C occurs after the ligand interaction with a plasma membrane receptor on cells. A variety of different receptor/ligand interactions can trigger these signaling cascades, and these, in turn, may vary with the cell type (e.g., neutrophils). (Prostaglandins are produced after the action of cyclooxygenase 1 on arachidonic acid.) Cells do not synthesize the arachidonic (fatty) acid and so it, or its precursor linoleic acid, must be derived from the diet.
ETIOLOGY: ASTHMA
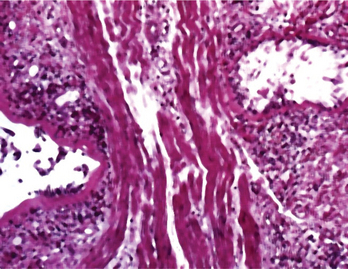
Asthma is a multifactorial disease with a marked inflammatory component and bronchial smooth muscle spasm, both of which can lead to airway obstruction. Inflammatory cells and mucus accumulate in the airway (Fig. 19-1). In susceptible individuals this inflammation causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, dyspnea, and cough, particularly at night and in the early morning. Airway obstruction is generally reversible with appropriate pharmacologic therapy. However, in some cases there is evidence for only partial reversibility, suggesting that structural remodeling of the airway may develop in the long term.
Role of Th2 Cytokines in Asthma
More recently it has been shown that IL-13 mediates a nonoverlapping (with IL-4) role in mucus overproduction and eosinophilia seen in the bronchial airways of asthmatics. (IL-13 also plays a role in intestinal worm expulsion.)