CASE 181
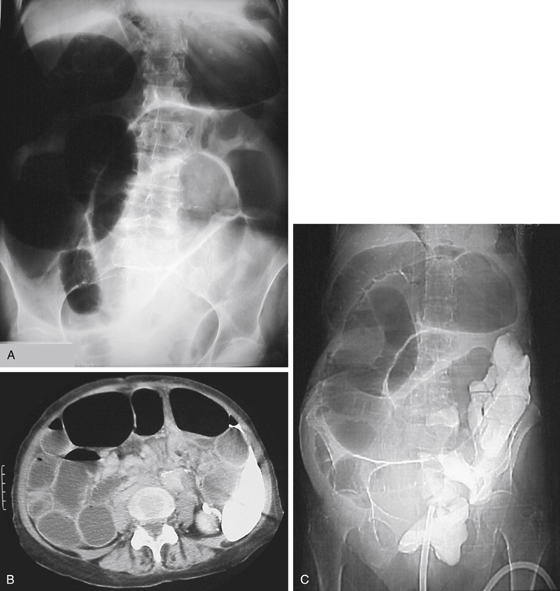
History: An 85-year-old woman presents with abdominal distension.
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis of the imaging finding shown in Figure A? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Small bowel paralytic ileus
2. What is the most common cause of large bowel obstruction?
3. What is the most common type of colonic volvulus?
4. What therapeutic option can a radiologist offer this patient?
A. Nasogastric placement of long small bowel decompression tube
B. Fluoroscopically guided insertion of rectal decompression tube
C. Hydrostatic contrast enema reduction
ANSWERS
CASE 181
Volvulus of the Transverse Colon
1. B and D
2. A
3. C
4. D
References
Newton NA, Reines HD. Transverse colon volvulus: case reports and review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1977;128(1):69-72.
Cross-Reference
Gastrointestinal Imaging: THE REQUISITES, 3rd ed, p 310.
Comment
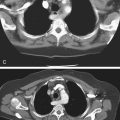
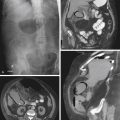
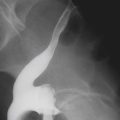
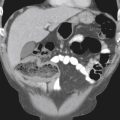
The plain conventional anteroposterior image of this 85-year-old woman, presenting with a distended abdomen and severe pain, shows dilated loops of colon and some small bowel (see figures). The natural history of volvulus and other high-grade colonic obstructions and dilation of the colon can lead to ischemia and perforation. The patient immediately went to surgery where she was found to have a volvulus of the transverse colon.
The most common cause of colonic obstruction is cancer, followed by diverticulitis and volvulus. Most commonly, volvulus is in the sigmoid (80%), but it is also seen in the cecum (15%) and the transverse colon (5%). Predisposing factors are an extra long mesocolon and marked redundancy in the transverse colon. Some authors believe that patients with colonic interposition anterior to the liver (Chilaiditi syndrome), reaching the diaphragm, are at increased risk for volvulus. However, other authors consider the interposition a variant, with no clinical significance. Splenic flexure volvulus, which may be considered a form of transverse volvulus, is the least common type of colonic volvulus. Surgery is the most acceptable form of definitive treatment. The bowel may be complicated by vascular compromise. In such an event, mortality and morbidity rates are high. Simple reduction of all types of colonic volvulus is associated with a high recurrence rate.