CHAPTER 18 NEUROLOGY
DIZZINESS
LABYRINTHITIS
Management
HEADACHE
MIGRAINE
Migraine affects 10 % of the population. It can cause significant disability.
Management
FACIAL PAIN
The common causes of facial pain in general practice are:
A rare, but important, cause of facial pain is temporal arteritis.
Often the cause of a patient’s facial pain cannot be neatly categorised. Patients with depression can present with a facial pain that is probably psychosomatic (see p. 297).
BELL’S PALSY
Diagnosis
Management
CEREBROVASCULAR ACCIDENT (CVA)
Management
Prescribing.
For non-haemorrhagic stroke start the patient on aspirin 75 mg od, consider e.g. an ACE inhibitor such as ramipril 2.5 mg increasing to 10 mg a day, and a statin (see p. 150). In addition to aspirin for antiplatelet activity, prescribe dipyridamole m/r 200 mg bd for the 2 years following each ischaemic event. If the patient is allergic to aspirin, prescribe clopidogrel 75 mg od instead.
Management of the patient with disability
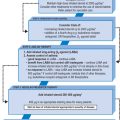
TRANSIENT ISCHAEMIC ATTACK (TIA)
TREMOR
PARKINSON’S DISEASE
One per cent of people over 60 years of age have Parkinson’s disease.
Management
FALLS
Falls are common in the elderly and have a multitude of possible causes:
EPILEPSY
Diagnosis
History
Management
Counselling after a diagnosis of epilepsy has been made
Anticonvulsant drug interactions.
Check whether the patient is taking any drugs that may interfere with anticonvulsants, especially the contraceptive pill. The effectiveness of both combined oral contraceptives and progestogen-only pills is reduced by carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital and primidone. Use 50 μg oestrogen pills or an alternative method (see p. 6).
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
The average GP’s list of 2000 patients will contain one or two patients with multiple sclerosis.
The mean age of onset is 35 years, with a range, commonly, of between 20 and 40 years of age.
Diagnosis
Management
All suspected cases should be referred for a neurological opinion.