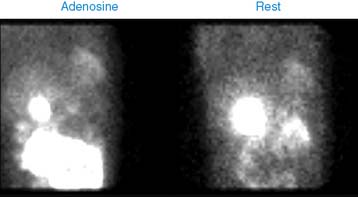
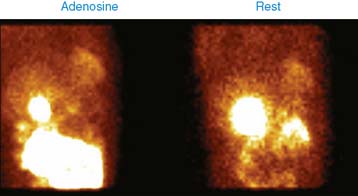
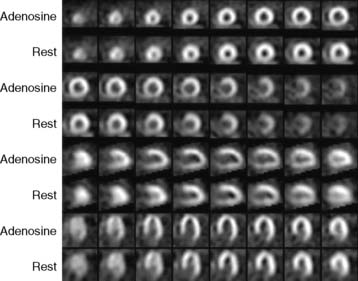
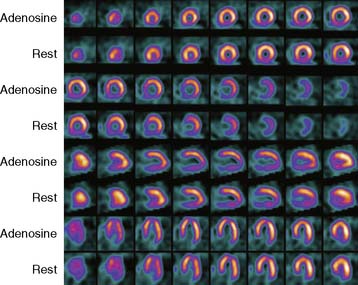
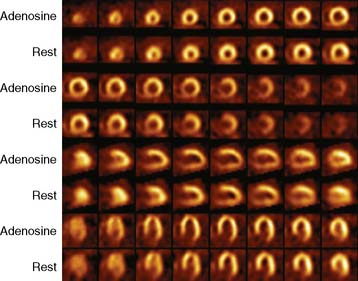
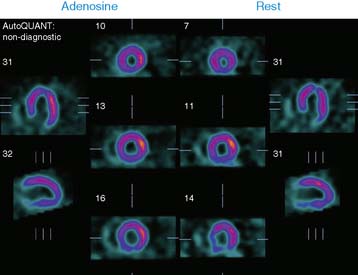
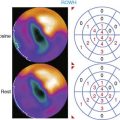
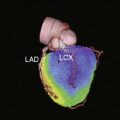
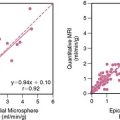
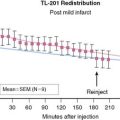
Case 17
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is an independent risk factor for obstructive coronary artery disease, and patients with CKD have higher cardiovascular mortality (See Chapter 16). Another important management factor to consider in this patient is tighter BP control. The patient will need to undergo coronary angiography after he starts hemodialysis. If he receives another renal transplant, he will need catheterization prior to the surgery.
1. Cook J.R., Dillie K.S., Hakeem A., et al. Effectiveness of anemia and chronic kidney disease as predictors for presence and severity of coronary artery disease in patients undergoing stress myocardial perfusion study. Am J Cardiol. 2008;102:266-271.
2. Chonchol M., Whittle J., Desbien A., et al. Chronic kidney disease is associated with angiographic coronary artery disease. Am J Nephrol. 2008;28:354-360.
3. Rabbat C.G., Treleaven D.J., Russell J.D., et al. Prognostic value of myocardial perfusion studies in patients with end-stage renal disease assessed for kidney or kidney-pancreas transplantation: A meta-analysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:431-439.