CASE 164
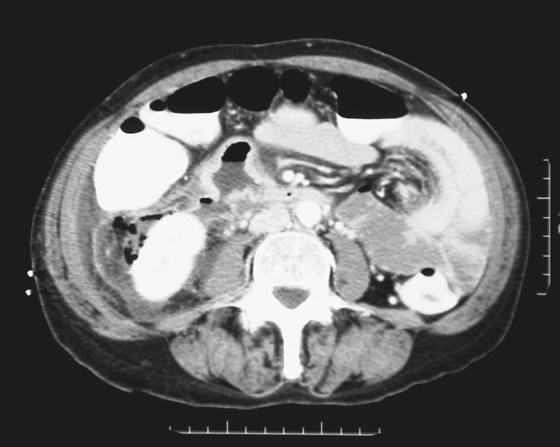
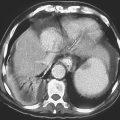
History: A 51-year-old woman presents with right-sided abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting of brackish dark emesis. She is a long-term user of aspirin and Goody’s Powder pain reliever.
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis of the imaging finding shown in the figure? (Choose all that apply.)
D. Emphysematous pyelonephritis
E. Post–endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and postsphincterotomy
2. Which statement regarding possible causes of duodenal perforation is true?
A. Duodenal diverticula are most commonly bulbar.
B. Blunt force trauma usually does not cause duodenal perforation.
C. Duodenal perforation after ERCP and sphincterotomy is mostly managed surgically.
D. Peptic ulceration is diagnosed at CT by the presence of circumferential wall thickening.
3. Which of the following conditions is associated with “benign” pneumoretroperitoneum?
4. From where does most of the gas in the bowel come?
C. By-product of food digestion
D. Product of tissue metabolism
ANSWERS
CASE 164
Pneumoretroperitoneum
1. B, C, D, and E
2. B
3. D
4. A
References
Jayaraman MV, Mayo-Smith WW, Movson JS, et al: CT of the duodenum: an overlooked segment gets its due. Radiographics. 2001;21(Spec No):S147–S160.
Zissin R, Osadchy A, Gayer G, et al: CT of duodenal pathology. Br J Radiol. 2002;75(889):78–84.
Cross-Reference
Gastrointestinal Imaging: THE REQUISITES, 3rd ed, p 98.
Comment
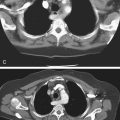
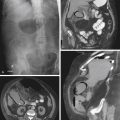
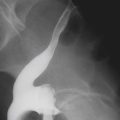
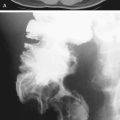
Occasionally, one sees a patient with free intraperitoneal air and no symptoms. Usually the free intraperitoneal air is the result of a burst serosal bleb in patients with the cystic type of pneumatosis coli. However, air in the retroperitoneum is never benign and is always associated with significant underlying causes (see figure). Perhaps the most common cause is a perforated hollow viscus that is located behind the posterior peritoneal layer of the peritoneal cavity (the retroperitoneum), in which lie parts of the duodenum, ascending colon, pancreas, kidney, and adrenal glands.
Besides perforation of peptic ulcer disease, other considerations include perforation secondary to endoscopy or ERCP or trauma. A large pneumomediastinum could also cause some air to percolate through the diaphragmatic hiatus into the retroperitoneum. In cases of significant pneumoretroperitoneum, the air tends to be streaky and linear in nature, following the iliopsoas muscle, perhaps outlining the kidney. There is no Rigler’s sign, or air collecting under the diaphragm, or air outlining the falciform ligament, as seen with a pneumoperitoneum. Blunt trauma to the abdomen affecting the retroperitonized portions of the colon and resulting in leakage of air can produce these findings as well. Streaky linear air collections are seen on the plain image of the abdomen shown with this case. However, CT is much more sensitive in the detection of retroperitoneal air, especially small amounts, and is now the standard study.