CASE 162
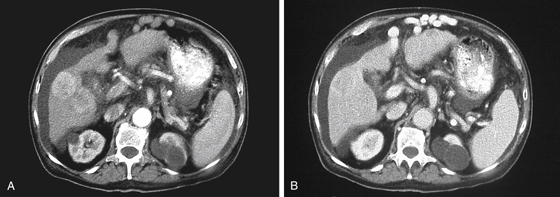
History: An 83-year-old man presents with lower limb pitting edema.
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis of the imaging finding shown in Figure A? (Choose all that apply.)
B. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
2. What is the predisposing condition most commonly associated with this diagnosis in whites in the United States?
3. What is the predisposing condition most commonly associated with this diagnosis in Asians?
D. Environmental contamination
4. What elevated serum factor is commonly seen with this disease?
B. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
D. Beta-human chorionic gonadotropin
ANSWERS
CASE 162
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. B, C, and D
2. C
3. A
4. A
References
Clark HP, Forrest Carson WF, Kavanagh PV, et al: Staging and current treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiographics. 2005;25(Suppl 1):S3–S24.
Cross-Reference
Gastrointestinal Imaging: THE REQUISITES, 3rd ed, p 195.
Comment
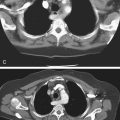
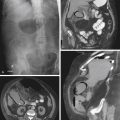
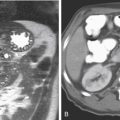
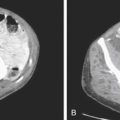
HCC is a primary malignancy of the hepatocyte. In the West, the disease is uncommon compared with Asia. However, it is usually associated with alcoholism and cirrhosis in the West. Hepatic infections, especially hepatitis B, and parasitic infections of the liver are thought to be the major etiologic factors in Asia. The disease has a dismal prognosis with survival usually not exceeding 6 to 18 months after diagnosis. At the time of diagnosis, at least 50% of patients have tumor spread to the portal veins. There seems to be an increasing incidence of HCC in the West, possibly relating to an increasing incidence of hepatitis B and C. The disease is more commonly seen in men, especially in Asia.
The advent of high-quality multidetector CT and MRI has not changed the mortality rate. The CT image in this case shows typical HCC mass lesions of the right lobe of the liver (see figures). Generally, distortion of the liver architecture by cirrhosis further complicates the process of detecting subtle or early lesions (see figures). An elevated AFP level is helpful for its positive predictive value, but if serum AFP is normal, it does not exclude the disease. In practice, the higher the AFP levels, the greater the likelihood of HCC. CT-guided liver biopsy, if not contraindicated by the possibility of abnormal bleeding and clotting issues, is the most efficient method of diagnosis.