CHAPTER 16 Preoperative Medication
1 List the major goals of premedication
Premedication needs to be tailored to the needs of individual patient. Important goals include:
7 List the most common side effects when opioids are used as a premedication
| Pruritus | Histamine release |
| Nausea and vomiting | Delayed gastric emptying |
| Respiratory depression | Stiff chest syndrome |
| Orthostatic hypotension | Sphincter of Oddi spasm |
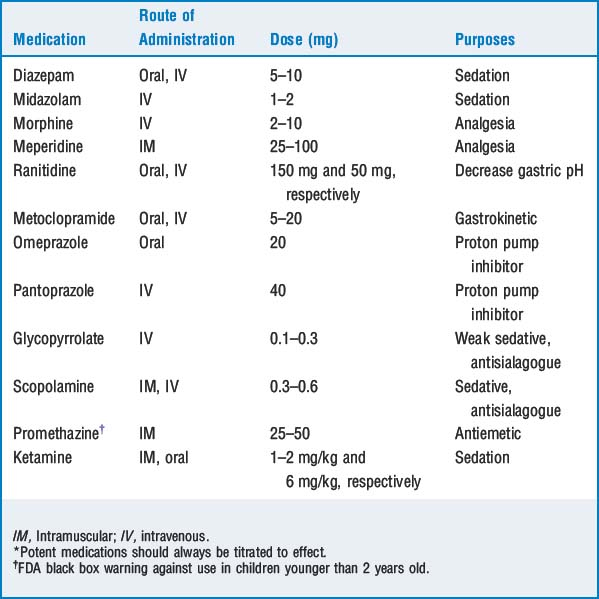
8 Describe the reasons to include an anticholinergic agent in premedication
The main indications for these drugs include the following:
 Drying of airway secretions. They are particularly useful for intraoral or airway surgery, before applying topical anesthesia to the airway, and general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation.
Drying of airway secretions. They are particularly useful for intraoral or airway surgery, before applying topical anesthesia to the airway, and general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation. Prevention of reflex bradycardia when vagal overactivity is anticipated, particularly during pediatric anesthetic induction and airway manipulation. Atropine or glycopyrrolate can best be given intravenously just before anticipated vagal stimulation.
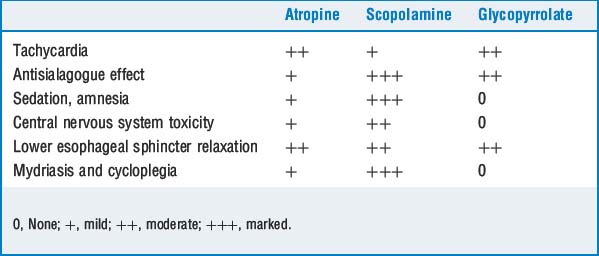
Prevention of reflex bradycardia when vagal overactivity is anticipated, particularly during pediatric anesthetic induction and airway manipulation. Atropine or glycopyrrolate can best be given intravenously just before anticipated vagal stimulation. Sedative and amnestic effect: Being tertiary amines, scopolamine and atropine can cross the blood-brain barrier and produce sedation and amnesia. In this regard scopolamine is about 8 to 10 times as potent as atropine. Glycopyrrolate is a quaternary amine, does not cross the blood-brain barrier, and therefore is devoid of appreciable sedative effect.
Sedative and amnestic effect: Being tertiary amines, scopolamine and atropine can cross the blood-brain barrier and produce sedation and amnesia. In this regard scopolamine is about 8 to 10 times as potent as atropine. Glycopyrrolate is a quaternary amine, does not cross the blood-brain barrier, and therefore is devoid of appreciable sedative effect.11 A patient in the preoperative holding area is delirious after receiving only 0.4 mg of scopolamine as a premedication. What is the cause of the delirium? How is it managed?
12 How does the concern for aspiration pneumonitis influence the choice of premedication?
Aspiration is discussed more fully in Chapter 39. The actual incidence of clinically significant aspiration pneumonitis is extremely rare in healthy patients having elective surgery. In the past many anesthesiologists routinely administered pharmacologic agents such as H2 antagonists, antacids, and gastrokinetics in an attempt to reduce the volume and increase the pH of the gastric contents of their patients in the preoperative period. In view of the extremely low incidence of clinically significant aspiration pneumonitis in healthy patients having elective surgery, routine and indiscriminate use of antacids, gastric acid secretion blockers, antiemetics, anticholinergics, and gastrokinetic medications is not warranted.
KEY POINTS: Preoperative Medication 
16 Describe the preoperative management of a morbidly obese patient with a difficult airway. Assume that the patient is otherwise healthy
1. Dotson R., Wiener-Kronish J.P., Ajayi T. Preoperative evaluation and medication. In: Stoelting R.K., Miller R.D., editors. Basics of anesthesia. ed 5. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 2007:157-177.
2. Kararmaz A., Kaya S., Turhanoglu S., et al. Oral ketamine premedication can prevent emergence agitation in children after desflurane anaesthesia. Paediatr Anaesth. 2004;14:477-482.