CASE 149
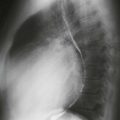
1. Which abnormalities are seen on the radiograph? (Choose all that apply.)
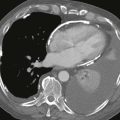
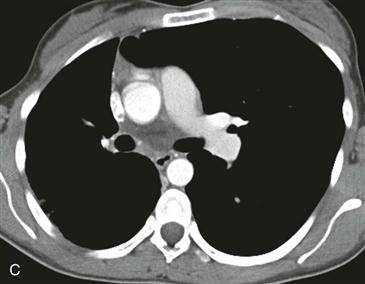
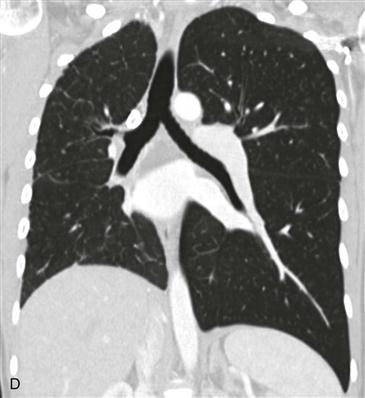
2. Which structure is absent on the CT scan?
A. Aortic arch
B. Trachea
C. Esophagus
3. What is the most likely diagnosis?
D. Proximal interruption of the right pulmonary artery
4. How does the right pulmonary artery system receive its blood supply?
A. Reconstitution of the right pulmonary artery
ANSWERS
References
Hernandez RJ. Magnetic resonance imaging of mediastinal vessels. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2002;10(2):237–251.
Zylak CJ, Eyler WR, Spizarny DL, et al. Developmental lung anomalies in the adult: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2002;22(Spec No):S25–S43.
Comment
Anatomy
Proximal interruption of pulmonary artery, or “absent pulmonary artery,” is a rare anomaly that occurs contralateral to the aortic arch. Although the proximal segment of the pulmonary artery is absent, there is a rudimentary artery in the hilum. The affected lung is usually hypoplastic, and it receives blood flow via systemic-to-pulmonary collateral channels arising from the bronchial, intercostal, brachiocephalic, subclavian, and smaller systemic arteries. Interruption of the left pulmonary artery is commonly associated with other congenital heart defects (most commonly tetralogy of Fallot).
Imaging
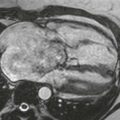
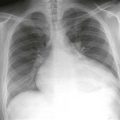
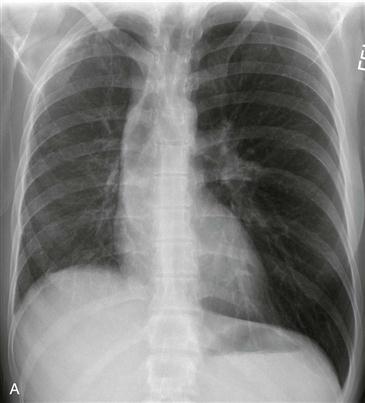
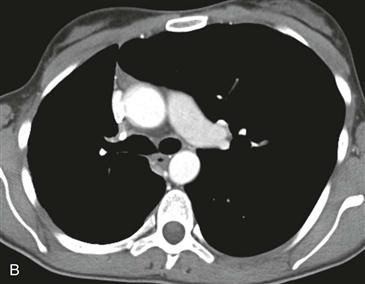
The diagnosis depends on nonvisualization of the artery on echocardiography, CT scan, or MRI (Figs. B–D). Chest radiographic findings (Fig. A) include a small hemithorax with signs of volume loss (e.g., ipsilateral mediastinal shift, hemidiaphragm elevation, and contralateral lung rotation to the opposite side from compensatory hyperinflation). The ipsilateral hilum is small, and there may be unilateral rib notching from enlarged intercostal arteries. The contralateral hilum appears enlarged because the pulmonary artery receives the entire right ventricular stroke volume. Important differential diagnostic considerations for the radiographic appearance include Swyer-James syndrome (constrictive bronchiolitis from a childhood infection) and pulmonary hypoplasia, such as occurs in scimitar syndrome.