CASE 147
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
B. Sarcoidosis
D. Myocarditis
2. What is an appropriate dose of gadolinium chelate contrast agent for late gadolinium enhancement imaging?
A. 0.01 mmol/kg
B. 0.05 mmol/kg
C. 0.15 mmol/kg
D. 0.5 mmol/kg
3. What is the most likely diagnosis if the patient’s chest radiograph was clear and his chest pain started after a viral illness?
A. Amyloidosis
B. Myocarditis
C. Infarction
D. Sarcoidosis
4. What is an appropriate delay between administration of gadolinium chelate contrast agent and the acquisition of the inversion recovery sequences?
A. 10 seconds
B. 2 minutes
C. 10 minutes
D. 30 minutes
ANSWERS
References
Feldman AM, McNamara D. Myocarditis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(19):1388–1398.
Ordovas KG, Higgins CB. Delayed contrast enhancement on MR images of myocardium: past, present, future. Radiology. 2011;261(2):358–374.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 91–92, 292–294.
Comment
Clinical Features
Myocarditis is the inflammation of myocardial tissue that most commonly follows a viral infection. It is a cause of sudden cardiac death in young patients. Endomyocardial biopsy is considered the gold standard for diagnosis, but it is invasive and may be negative because of sampling error. Myocarditis is usually self-limiting, and supportive therapy may be indicated.
MRI
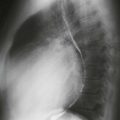
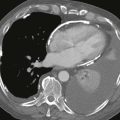
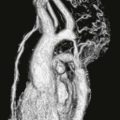
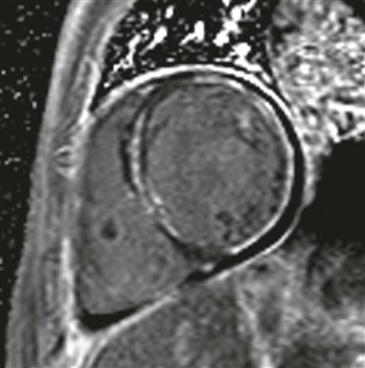
MRI is often used to diagnose myocarditis. Several MRI sequences can be performed, but the most useful is the inversion recovery late gadolinium enhancement sequence. Late gadolinium enhancement in a nonischemic pattern (typically midmyocardial) supports the diagnosis of myocarditis (Figure). MRI identifies the disease in 30% of patients with chest pain, elevated troponin, and clinically normal coronary arteries. Three findings are assessed to make the diagnosis of myocarditis:
Test sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing myocarditis increase with more positive findings (i.e., T2 hyperintensity, early gadolinium enhancement, and late gadolinium enhancement).
Prognosis
Late gadolinium enhancement occurring 4 weeks after the acute episode has shown prognostic value in predicting poor functional and clinical outcomes. A reduced ejection fraction and right ventricular involvement are echocardiographic markers of an increased risk for sudden cardiac death and future need for cardiac transplantation. Patients with myocarditis are usually treated supportively with heart failure and arrhythmia management. Immunosuppressive therapy is initiated when it results from an autoimmune disease.